- Home
- >
- Application
- >
- Home Appliance Adhesive
Home Appliance Adhesive

In-home appliance adhesive solutions ensure durability, performance, and safety. Whether you’re a DIY enthusiast or a professional technician, understanding the various types of adhesives designed for home appliances is essential. This category page aims to provide insights into home appliance adhesives’ diverse applications, features, and benefits, helping you make informed choices for your repair or improvement projects.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat are the typical applications of home appliance adhesives?
Home appliance adhesives play a crucial role in various applications, contributing to appliances’ durability, efficiency, and safety. Some typical applications include:
Bonding and Assembly:
- Panel Bonding:Adhesives bond panels and surfaces together, ensuring a strong and secure assembly.
- Component Bonding:Adhesives are applied to bond various appliance components, such as electronic elements, metal parts, and plastic components.
Sealing and Gasketing:
- Waterproofing:Adhesives provide a water-resistant seal, preventing water or moisture ingress into electronic components and sensitive areas.
- Gasketing:Adhesives are used to create gaskets that help in sealing joints and preventing leaks, particularly in dishwashers, washing machines, and refrigerators.
Vibration Damping and Noise Reduction:
- Vibration Control:Adhesives help reduce appliance vibrations, contributing to quieter and more stable operation.
- Noise Reduction:They are applied to dampen noise generated by moving parts or vibrations within the appliance.
Thermal Management:
- Heat Transfer:Adhesives with thermal conductivity properties enhance heat dissipation, ensuring optimal performance of components like motors and electronic circuits.
- Insulation:Adhesives can also provide insulation to protect sensitive components from excessive heat.
Electronics and Wiring:
- Cable Management:Adhesives are employed to secure and organize wiring, preventing tangling and ensuring a clean and efficient layout.
- Component Fixation:They are used to fix electronic components in place, enhancing electronic systems’ overall stability and reliability.
Surface Protection and Finishing:
- Surface Coating:Adhesives may be used as protective coatings, safeguarding surfaces from corrosion, scratches, and wear.
- Aesthetic Finishing:Some adhesives contribute to the aesthetic appearance of appliances, providing a smooth and polished finish.
Repair and Maintenance:
- Quick Repairs:Adhesives are often used for fast repairs, providing a reliable and durable solution for fixing broken or damaged parts.
- Component Replacement:Adhesives facilitate the replacement of components by securely attaching new parts to the existing structure.
Energy Efficiency:
- Insulation:Adhesives with insulating properties contribute to the energy efficiency of appliances by preventing heat loss and optimizing thermal performance.
Home appliance adhesives are versatile and are used in various ways to enhance household appliances’ performance, reliability, and aesthetics. They contribute to appliances’ overall functionality and durability in both large and small applications.
How do adhesives contribute to the structural integrity of appliances?
Adhesives play a crucial role in contributing to the structural integrity of appliances in several ways. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Bonding Components:Adhesives are used to bond various components of appliances together. This bonding can create a unified structure that enhances the overall strength and stability of the appliance. By securely attaching different parts, adhesives help distribute stress and load across the entire structure, reducing the likelihood of failure.
- Reduced Weight and Improved Distribution:Adhesives often weigh less than traditional mechanical fasteners like screws or bolts. Additionally, they can be applied more evenly, distributing stress and loads across a larger area. This can result in a more balanced load distribution, reducing the risk of localized stress concentrations that can weaken the structure.
- Vibration Damping:Appliances, especially those with moving parts like washing machines or refrigerators, may generate vibrations during operation. Adhesives can act as dampeners, absorbing and dispersing these vibrations. This helps prevent excessive movement, reducing wear and tear on the appliance components and improving overall structural stability.
- Sealing and Protection:Adhesives are often used for sealing, creating a barrier against environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and chemicals. This protective layer helps prevent corrosion and deterioration of internal components, preserving the structural integrity of the appliance over time.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility:Adhesives provide greater design flexibility than traditional fastening methods. They allow for bonding dissimilar materials, enabling the design of lightweight and innovative structures. This flexibility can lead to more efficient use of materials and improved structural performance.
- Temperature Resistance:Certain adhesives are designed to withstand various temperatures. In appliances where temperature variations are common, such as ovens or refrigerators, these adhesives contribute to maintaining the structural integrity of the appliance by preventing material degradation or failure under extreme temperature conditions.
- Improved Aesthetics:Adhesives can be applied in a way that enhances the overall appearance of an appliance. By eliminating the need for visible mechanical fasteners, adhesives contribute to a sleek and modern design while maintaining structural integrity.
It’s important to note that the selection of the appropriate adhesive depends on factors such as the materials being joined, environmental conditions, and the specific requirements of the appliance. Engineers and manufacturers carefully choose adhesives based on these considerations to ensure appliances’ optimal performance and structural integrity.
Are there specific adhesives for heat-resistant applications in home appliances?
Yes, there are adhesives designed explicitly for heat-resistant applications in home appliances. These adhesives are formulated to withstand high temperatures and provide reliable bonding in environments where conventional adhesives might fail. Here are some types of heat-resistant adhesives commonly used in home appliances:
High-Temperature Epoxy Resins:
- Epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonding properties, and there are formulations available that can withstand high temperatures. They are suitable for bonding various materials in appliances where heat resistance is crucial.
Silicone Adhesives and Sealants:
- Silicone-based adhesives and sealants are known for their flexibility and resistance to extreme temperatures. They can often handle temperatures ranging from -60°C to 300°C (-76°F to 572°F). Silicone adhesives are commonly used in appliances like ovens and stoves.
Ceramic Adhesives:
- Ceramic adhesives are designed to bond ceramic components in appliances, such as heating elements. These adhesives can withstand high temperatures and offer excellent thermal resistance.
Cyanoacrylate (CA) Adhesives:
- While standard cyanoacrylate adhesives are not known for their high-temperature resistance, there are specialty formulations designed to withstand elevated temperatures. These are often labeled as high-temperature or heat-resistant cyanoacrylates.
Phenolic Resins:
- Phenolic adhesives are known for their resistance to high temperatures. They are used in applications where bonding materials need to endure elevated temperatures, such as in some heating elements.
Polyimide Adhesives:
- Polyimide adhesives have excellent thermal stability and can withstand extreme temperatures. They are often used in applications where high-temperature resistance is critical.
When selecting a heat-resistant adhesive for a specific application, it’s essential to consider factors such as the temperature range the adhesive needs to withstand, the materials being bonded, and the particular conditions of the appliance. Always follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for adequately applying and curing the adhesive.
Which adhesives are suitable for bonding metal components in appliances?
Choosing the suitable adhesive for bonding metal components in appliances depends on various factors, such as the type of metal, the specific application, and the environmental conditions the appliance will be exposed to. Here are some common types of adhesives that are often suitable for bonding metal components:
Epoxy Adhesives:
- Epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonding capabilities and resistance to heat and chemicals. They are ideal for bonding various metals and can provide excellent structural strength.
Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue):
- Cyanoacrylate adhesives are fast-curing and can connect metals quickly. They are suitable for applications where a quick bond is required. However, they may not be as heat-resistant as epoxy adhesives.
Polyurethane Adhesives:
- Polyurethane adhesives offer flexibility and good resistance to impact and vibration. They are suitable for bonding metal components in appliances that may experience movement or stress.
Acrylic Adhesives:
- Acrylic adhesives provide good bonding strength and are resistant to environmental factors. They are suitable for bonding various metals and are often used in appliance manufacturing.
Anaerobic Adhesives:
- Anaerobic adhesives are ideal for clicking metal components with limited air access. They cure in the absence of air and are commonly used for threaded fasteners and cylindrical assemblies.
Metal-Bonding Adhesives:
- Some adhesives are specifically formulated for bonding metal surfaces. These adhesives often contain metal particles or compounds designed to enhance the bond strength on metal substrates.
Heat-Resistant Adhesives:
- For appliances that generate heat, it’s crucial to use adhesives that can withstand high temperatures. High-temperature epoxy adhesives or specific heat-resistant formulations may be suitable for such applications.
Before selecting an adhesive, consider the operating conditions of the appliance, the type of metal surfaces being bonded, and any specific requirements for temperature resistance, flexibility, or other performance factors. Additionally, always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the chosen adhesive to ensure proper application and long-term durability.
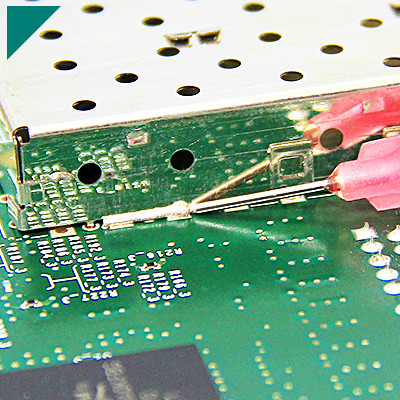
What role do adhesives play in enhancing electrical connections within appliances?
Adhesives play a crucial role in enhancing electrical connections within appliances by providing several benefits, including:
*Bonding and Securing Components:Adhesives are used to bond and secure various electrical components within appliances. This helps prevent the movement or separation of parts, ensuring a stable and reliable connection. This is especially important in environments where vibrations or mechanical stresses may occur.

*Sealing and Insulating:Adhesives can create a seal around electrical components, preventing the ingress of moisture, dust, or other contaminants. This is essential for maintaining the integrity of electrical connections and preventing corrosion or short circuits. Some adhesives also have insulating properties, adding an extra layer of protection.
*Thermal Management:Adhesives with good thermal conductivity can enhance heat dissipation in electrical components. Effective thermal management is crucial to prevent overheating, which can degrade the performance and lifespan of electronic devices. Thermally conductive adhesives help transfer heat away from sensitive components.
*Reducing Contact Resistance:Adhesives can be formulated to improve the contact between electrical conductors, reducing contact resistance. Lower resistance means more efficient electrical connections and can contribute to better overall performance of the appliance.
*Flexibility and Stress Relief:Some adhesives are designed to be flexible and can absorb mechanical stresses or vibrations. This is important in appliances where movement or mechanical shocks may occur, as it helps prevent damage to electrical connections.
*Space Savings:Adhesives can enable compact designs by eliminating the need for traditional mechanical connectors. This is particularly useful in modern, miniaturized electronic devices where space is at a premium.
*Ease of Manufacturing:Adhesives can simplify manufacturing by allowing for automated application. This can lead to increased efficiency and cost savings in producing electronic appliances.
*Environmental Protection:Adhesives can protect electrical connections from environmental factors such as humidity, chemicals, and pollutants. This helps maintain the performance and reliability of the appliance over time.
*Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC):Some adhesives are designed to provide electromagnetic shielding, which helps prevent interference between different electronic components within an appliance. This is important for maintaining EMC compliance and preventing signal degradation.
Adhesives play a multifaceted role in enhancing electrical connections within appliances, contributing to improved electronic device performance, reliability, and longevity.
Are there adhesives designed for sealing purposes in home appliances?
Yes, there are adhesives designed explicitly for sealing purposes in home appliances. These adhesives are formulated to provide a secure and airtight seal, preventing the leakage of liquids or gases. They are commonly used in various applications, such as sealing seams, joints, and gaps in refrigerators, ovens, washing machines, and dishwashers.
The choice of adhesive depends on the application’s specific requirements, such as temperature resistance, flexibility, and the type of materials being bonded. Some common types of adhesives used for sealing in home appliances include:
- Silicone Sealants:Silicone sealants are versatile and can withstand various temperatures. They are flexible and provide excellent adhesion to multiple materials commonly found in appliances. Silicone sealants are often used for sealing gaps and seams in appliances.
- Polyurethane Adhesives:Polyurethane adhesives are known for their flexibility and durability. They can bond well to different surfaces and provide a strong seal. Polyurethane adhesives are suitable for applications where movement or vibration may occur.
- Epoxy Resins:Epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonding properties. They are commonly used for bonding metal parts in appliances and can also be used for sealing purposes, especially in applications where a rigid bond is needed.
- Acrylic Adhesives:Acrylic adhesives are known for their quick curing time and strong bonding capabilities. They are suitable for bonding various materials and can be used for sealing purposes in appliances.
When choosing an adhesive for sealing home appliances, it’s essential to consider factors such as the machine’s operating conditions (temperature, moisture), the materials being bonded, and any specific requirements for flexibility or rigidity. Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for proper application and curing of the adhesive.
How can I choose a suitable adhesive for repairing plastic parts in appliances?
Choosing the suitable adhesive for repairing plastic parts in appliances involves considering several factors to ensure a solid and durable bond. Here are some key considerations to help you select a suitable adhesive:
Type of Plastic:
- Identify the type of plastic you are working with. Common types include ABS, PVC, polypropylene, polyethylene, and others. Some adhesives work better with certain plastics, so choose one compatible with the specific plastic material.
Adhesive Compatibility:
- Ensure that the adhesive you select is consistent with the plastic and any other materials involved in the repair. Adhesives designed for plastics typically indicate the types of plastics they are suitable for on the product label.
Bond Strength:
- Consider the strength requirements for the repaired part. Some adhesives provide a more flexible bond, while others offer a rigid bond. The application and stresses the part will experience will influence the required bond strength.
Temperature Resistance:
- Assess the temperature conditions to which the repaired appliance part will be exposed. Some adhesives may lose their effectiveness at high temperatures, so choose one that can withstand the temperature range of the appliance.
Chemical Resistance:
- Consider whether the repaired part will come into contact with chemicals, water, or other substances. Choose an adhesive that provides resistance to these elements to ensure the longevity of the repair.
Curing Time:
- Check the curing time of the adhesive. Some adhesives set quickly, while others may require more time. Consider the working time you need and the time it takes for the adhesive to reach full strength.
Flexibility:
- Determine whether the repaired part requires flexibility. Some plastics and applications benefit from adhesives that allow flexibility to accommodate movement or stress.
Application Method:
- Consider the ease of application. Some adhesives come in liquid form, while others are available in gel or paste form. Choose an adhesive that is easy to apply and suitable for the specific repair job.
UV Resistance:
- If the repaired part will be exposed to sunlight, consider an adhesive that offers UV resistance to prevent degradation over time.
Brand and Reviews:
- Choose a reputable brand and read reviews or seek recommendations from others who have used the adhesive for similar plastic repair projects.
Always follow the manufacturer’s instructions for proper surface preparation and application. Testing the adhesive on a small, inconspicuous area before complete application is a good practice to ensure compatibility and adhesion strength.
Do adhesives offer solutions for vibration damping in appliances?
Yes, adhesives can be used as a solution for vibration damping in appliances. Vibration damping is crucial in appliances to reduce noise, prevent wear and tear, and enhance overall performance. Adhesives can contribute to vibration damping in several ways:
Bonding and Damping Materials:
- Adhesives can be used to bond damping materials, such as viscoelastic polymers or rubber, to the surfaces of components in appliances. These materials absorb and dissipate vibration energy, reducing the overall vibration levels.
Flexible Joints and Mounting:
- Adhesives can be used to create stretchy joints or mounts between vibrating components. This flexibility helps absorb and dampen vibrations, preventing them from transferring between connected parts.
Structural Reinforcement:
- By bonding and reinforcing specific components with adhesives, the overall structure of the appliance can be improved, reducing the likelihood of vibrations and minimizing their impact.
Damping Pads and Tapes:
- Adhesive-backed damping pads or tapes can be directly applied to areas where vibration is a concern. These pads absorb and dampen vibrations, preventing them from transmitting to other appliance parts.
Viscoelastic Adhesives:
- Some adhesives are designed explicitly with viscoelastic properties, exhibiting viscous and elastic characteristics. These adhesives can absorb and dissipate vibrational energy effectively.
Isolation Mounts:
- Adhesives can be used in combination with isolation mounts to attach components in a way that minimizes the transmission of vibrations. The adhesive helps secure the mounts in place.
When selecting adhesives for vibration damping, it’s essential to consider factors such as the type of materials being bonded, the operating conditions of the appliance, and the frequency range of the vibrations. Testing and evaluating different adhesive solutions are often necessary to ensure optimal performance in specific applications. Additionally, working with adhesive manufacturers or consulting with experts in materials and vibration damping can be beneficial in choosing the most suitable adhesive for a particular appliance.
Are there eco-friendly adhesive options for environmentally conscious consumers?
Yes, there are eco-friendly adhesive options available for environmentally-conscious consumers. These adhesives are designed to minimize their environmental impact regarding raw materials, production processes, and end-of-life disposal. Here are some types of eco-friendly adhesives:
Water-Based Adhesives:
- These adhesives are based on water as the primary solvent, which reduces the emission of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) compared to solvent-based adhesives.
- Water-based adhesives are often used in packaging, paper products, and woodworking.
Plant-Based Adhesives:
- Adhesives from renewable resources, such as plant starch, soy, and corn, are more sustainable.
- These adhesives can be used in various applications, including paper, labels, and packaging.
Bio-Based Adhesives:
- Bio-based adhesives are derived from natural sources like vegetable oils, proteins, and cellulose.
- These adhesives often have a lower environmental impact compared to petroleum-based alternatives.
Recycled Adhesives:
- Adhesives made from recycled materials help reduce the demand for new resources.
- Some adhesives use recycled paper or cardboard as a base.
UV-Curable Adhesives:
- UV-curable adhesives use ultraviolet light for curing, eliminating the need for solvents or water.
- These adhesives are commonly used in electronics, optics, and medical applications.
Biodegradable Adhesives:
- Some adhesives are designed to break down naturally over time, reducing their environmental impact.
- Biodegradable adhesives are often used in temporary applications.
Low VOC Adhesives:
- Adhesives with low levels of volatile organic compounds are considered environmentally friendly.
- Low VOC adhesives are available in various formulations, including water-based and solvent-based options.
When choosing an eco-friendly adhesive, it’s essential to consider the specific application requirements and ensure it meets the necessary performance standards. Additionally, certifications such as the Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) or Green Seal can help identify products with environmentally friendly attributes.
Which adhesives are recommended for outdoor or weather-exposed appliances?
For outdoor or weather-exposed applications, it’s crucial to use adhesives that can withstand environmental conditions such as moisture, temperature fluctuations, UV exposure, and other weather-related challenges. Here are some types of adhesives that are recommended for outdoor use:
Polyurethane Adhesives:
- Polyurethane adhesives are known for their excellent weather resistance, making them suitable for outdoor applications.
- They are resistant to water, chemicals, and UV radiation.
Silicone Adhesives:
- Silicone adhesives are highly resistant to weathering, UV light, and extreme temperatures.
- They provide flexibility and durability, making them suitable for outdoor sealing and bonding.
Epoxy Adhesives:
- Epoxy adhesives offer solid bonds and are resistant to moisture and chemicals.
- Outdoor-grade epoxies are formulated to withstand exposure to the elements.
Acrylic Adhesives:
- Acrylic adhesives, especially those designed for outdoor use, offer good weather resistance.
- They are often used in applications such as signage and outdoor bonding.
Butyl Rubber Adhesives:
- Butyl rubber adhesives are known for their excellent water and weather resistance.
- They are commonly used in outdoor sealing applications.
UV-Curable Adhesives:
- UV-curable adhesives can be formulated to provide excellent resistance to UV exposure.
- They are suitable for bonding and sealing applications in outdoor environments.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Super Glue):
- While standard cyanoacrylate adhesives may not be ideal for outdoor use, some formulations are designed to be more resistant to moisture and temperature extremes.
When selecting an adhesive for outdoor applications, it’s essential to consider the specific requirements of the project, the types of materials being bonded, and the expected environmental conditions. Additionally, checking for product specifications and certifications related to outdoor performance can help ensure the adhesive meets the necessary durability and weather resistance standards.
How do adhesive technologies contribute to the energy efficiency of appliances?
Adhesive technologies play a crucial role in improving the energy efficiency of appliances in several ways. Here are some ways in which adhesives contribute to energy efficiency:
Reduced Weight and Material Usage:
- Adhesives often enable the use of lighter-weight materials in appliance construction. Lighter appliances require less energy for transportation and operation.
- By allowing the use of thinner materials without compromising structural integrity, adhesives contribute to resource conservation and energy efficiency.

Improved Thermal Management:
- Adhesives can enhance thermal conductivity and heat dissipation within appliances. This is especially important in refrigerators, air conditioners, and electronic components.
- Efficient thermal management ensures that appliances can operate at optimal temperatures, reducing the need for additional energy to compensate for heat-related inefficiencies.
Sealing and Insulation:
- Adhesives seal gaps and joints in appliances, prevent air leaks and improve insulation. This is crucial in appliances like refrigerators and freezers, where maintaining a consistent temperature is essential for energy efficiency.
- Proper sealing prevents the loss of conditioned air, reducing the workload on heating and cooling systems.
Vibration Damping:
- Adhesives can dampen vibrations and reduce noise in appliances like washing machines and dishwashers. Smoother operation reduces friction and the energy needed to overcome resistance.
Assembly Efficiency:
- Adhesives often simplify the assembly process by providing fast and reliable bonding. This can lead to streamlined manufacturing processes, reducing production time and energy consumption.
- Additionally, using adhesives allows for more flexibility in design, creating more compact and efficient appliance structures.
Corrosion Prevention:
- Adhesives can protect metal components from corrosion, extending the lifespan of appliances. Longer-lasting appliances reduce the need for frequent replacements, contributing to overall energy and resource efficiency.
Customization and Miniaturization:
- Adhesives enable the bonding of small, intricate components in appliances. This supports the trend toward miniaturization and creating more energy-efficient, compact devices.
Electronic Component Bonding:
- Adhesives are commonly used in the assembly of electronic components. By providing solid and reliable bonds, they contribute to electronic systems’ overall efficiency and reliability within appliances
Are there adhesives suitable for bonding dissimilar materials in appliances?
Yes, there are adhesives explicitly designed for bonding dissimilar materials in appliances. The choice of adhesive depends on the types of materials being connected, the appliance’s operating conditions, and the application’s specific requirements. Here are some common kinds of adhesives that are often used for joining dissimilar materials in appliances:
Epoxy Adhesives:
- Epoxy adhesives are known for their strong bonding capabilities and versatility. They can bond various materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue):
- Cyanoacrylate adhesives are quick-bonding and suitable for connecting dissimilar metals, plastic, rubber, and ceramics. They work well in applications where a fast cure time is essential.
Polyurethane Adhesives:
- Polyurethane adhesives offer a flexible and durable bond, making them suitable for applications with varying thermal expansion and contraction. They can bond materials like wood, metal, plastic, and glass.
Acrylic Adhesives:
- Acrylic adhesives provide good bonding strength and are suitable for joining dissimilar materials such as metal to plastic or metal to glass. They also have good resistance to temperature and environmental conditions.
Methyl Methacrylate (MMA) Adhesives:
- MMA adhesives are known for their high strength and durability. They are often used for bonding metals, plastics, and composites in demanding applications.
Silicone Adhesives:
- Silicone adhesives are flexible and resist heat, cold, and moisture. They are commonly used for bonding materials in appliances that experience a wide range of temperatures.
Structural Adhesives:
- Structural adhesives, such as those based on epoxy or polyurethane, are designed for high-strength bonding applications. They are suitable for bonding dissimilar materials in appliances where structural integrity is crucial.
Before selecting an adhesive, it’s essential to consider factors such as the operating environment, temperature range, and the specific properties of the bonded materials. Additionally, following the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the chosen adhesive is crucial for achieving optimal bonding results.
What safety considerations should be kept in mind when using home appliance adhesives?
Using home appliance adhesives involves specific safety considerations to ensure proper handling and minimize potential risks. Here are some essential safety tips to keep in mind:
Ventilation:
- Always work in a well-ventilated area to reduce exposure to fumes. Open windows or use exhaust fans to improve air circulation.
Protective Gear:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and safety glasses, to protect your skin and eyes from contact with adhesives.
Read and Follow the Instructions:
- Carefully read and follow the manufacturer’s instructions on the adhesive product. Consider recommended application methods, curing times, and specific safety precautions.
Avoid Skin Contact:
- Minimize skin contact with adhesives. If the adhesive comes into contact with your skin, wash the affected area immediately with soap and water.
Eye Protection:
- Wear protective goggles or a face shield if there is a risk of splashing or contact with adhesive in the eyes.
Storage:
- Store adhesives in a cool, dry place, and keep them away from heat sources or open flames. Ensure that the containers are tightly sealed when not in use.
Keep Out of Reach of Children:
- Store adhesives in a location that is inaccessible to children. The chemicals in adhesives can be harmful if ingested.
Fire Safety:
- Some adhesives are flammable, so avoid using them near open flames or ignition sources. Follow proper fire safety precautions.
Dispose of Waste Properly:
- Dispose of adhesive waste according to local regulations. Some adhesives may be considered hazardous waste and should be handled accordingly.
First Aid:
- Be familiar with the first aid measures recommended for the specific adhesive. In case of accidental ingestion, inhalation, or eye/skin contact, follow the instructions on the product label and seek medical attention if necessary.
Compatibility:
- Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the materials you are bonding. Some adhesives may have specific compatibility requirements.
Emergency Procedures:
- Know the emergency procedures for the particular adhesive, including steps to take in case of spills, leaks, or accidental exposure.
Always prioritize safety when using home appliance adhesives, and if you have any concerns or questions, contact the adhesive manufacturer for guidance.
Can adhesives be used for quick fixes in emergency appliance repairs?
Yes, adhesives can be used for quick fixes in emergency appliance repairs, but the suitability depends on the adhesive type and the repair needed. Here are some common types of adhesives and their potential uses in emergency appliance repairs:
- Epoxy Resin:Epoxy is a strong adhesive that can bond various materials, including metal and plastic. It’s suitable for repairs where strength and durability are essential. However, it usually takes some time to cure completely.
- Super Glue (Cyanoacrylate):Super glue is a fast-acting adhesive that forms a strong bond quickly. It’s suitable for minor, lightweight repairs like bonding plastic parts. Keep in mind that it may be better for high-stress applications.
- Heat-Resistant Adhesives:Some appliances generate heat during operation. Consider using heat-resistant adhesives designed to withstand elevated temperatures for repairs in high-temperature areas.
- Rubber Cement or Silicone Sealant:These flexible adhesives work well for sealing leaks or repairing flexible components. They are often used in repairing gaskets or hoses.
- Duct Tape:While not a traditional adhesive, duct tape can be a quick and temporary solution for emergency repairs. It’s versatile and can hold things together until a proper fix can be made.
Before using any adhesive, consider the following tips:
- Clean Surfaces:Make sure the surfaces you’re bonding are clean and free of debris or grease. This ensures better adhesion.
- Follow Instructions:Adhesives come with specific instructions regarding application and curing times. Follow these instructions for optimal results.
- Consider Safety:If the appliance involves electrical components, ensure it is unplugged before attempting repairs. Additionally, be aware of the potential health hazards associated with certain adhesives.
While adhesives can provide quick fixes in emergencies, it’s important to note that they may not always be a permanent solution. It’s recommended to consult the appliance’s manual, if available, or seek professional repair services for a more durable fix, especially for critical or high-stress components.
Are there specialized adhesives for high-stress areas in appliances?
Yes, there are specialized adhesives designed to withstand high-stress areas in appliances. These adhesives are formulated to provide exceptional bonding strength, resistance to temperature extremes, and durability. Here are some types of specialized adhesives commonly used for high-stress areas:
- Epoxy Adhesives:Epoxy resins are known for their high bonding strength and versatility. There are epoxy formulations designed explicitly for high-stress applications. They can bond with various materials, including metal, plastic, and ceramics. Some epoxy adhesives are also formulated to resist heat and chemicals.
- Cyanoacrylate (Super Glue):While super glue is generally known for its fast bonding in lightweight applications, there are specialized formulations with enhanced strength for use in high-stress situations. These adhesives can help bond rigid materials.
- Polyurethane Adhesives:Polyurethane adhesives offer strong bonding capabilities and are known for their flexibility. They can absorb shocks and vibrations, making them suitable for high-stress areas. Some polyurethane adhesives are also designed to be resistant to water and chemicals.
- Methacrylate Adhesives:Methacrylate adhesives, or structural adhesives, provide high strength and durability. They are designed for bonding metals, composites, and plastics in demanding applications. They often have good chemical and temperature resistance.
- High-Temperature Adhesives:Appliances that generate heat during operation may require adhesives that can withstand elevated temperatures. High-temperature adhesives, often silicone-based, are formulated to resist heat and maintain their strength in hot environments.
- Ceramic Adhesives:In appliances with ceramic components, ceramic adhesives can be used for high-stress bonding. These adhesives are formulated to provide strong bonds in applications where other adhesives may not be effective.
When selecting an adhesive for high-stress areas, it’s crucial to consider the application’s specific requirements, including the type of materials being bonded, the stress level, temperature conditions, and any other environmental factors. Reading the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for each adhesive is essential to ensure proper application and maximum effectiveness in high-stress situations.
How do temperature variations affect the choice of adhesives for appliances?
Temperature variations can significantly impact the performance of adhesives used in appliances. The choice of adhesive depends on the specific temperature range the device is exposed to during its operation. Here are some key considerations:
Operating Temperature Range:
- Low-Temperature Environments:In appliances that operate in low-temperature environments, such as refrigerators or freezers, it’s essential to use flexible adhesives and maintain their adhesive properties at low temperatures. Some adhesives become brittle and lose their bonding strength in cold conditions.
- High-Temperature Environments:Appliances like ovens or stovetops generate high temperatures. Adhesives for these applications must be heat-resistant to ensure they do not degrade, lose strength, or release harmful fumes when exposed to elevated temperatures.
Thermal Cycling:
- Appliances often experience thermal cycling, going through repeated heating and cooling cycles. Adhesives used in these applications should have good thermal stability to withstand such temperature variations without significantly changing their properties.
Material Compatibility:
- Adhesives need to be compatible with the materials they are bonding. Some adhesives may have different thermal expansion or contraction rates than the materials they connect, leading to delamination or loss of adhesion under temperature variations.
Thermal Conductivity:
- In some cases, such as in electronic appliances, the thermal conductivity of the adhesive may be a critical factor. Adhesives with good thermal conductivity can help efficiently transfer heat, preventing overheating of components.
Specialized Adhesives:
- Specialized adhesives, such as high-temperature epoxies or thermal interface materials, may be required for extreme temperature conditions. These adhesives are formulated to withstand specific temperature ranges and provide optimal performance in demanding environments.
Testing and Validation:
- Before selecting an adhesive for an appliance, it’s crucial to conduct thorough testing to ensure it meets the required performance standards under the expected temperature variations. Real-world testing can provide valuable insights into how an adhesive will perform over time.
The impact of temperature variations on appliance adhesives underscores the importance of selecting adhesives specifically designed to withstand the operational conditions of the appliance. Considering the temperature range, thermal cycling, material compatibility, and other unique factors associated with the appliance’s usage environment is essential.
What are the critical differences between liquid and gel adhesives in appliance applications?
Temperature variations can significantly influence the selection of adhesives for appliances. The performance of adhesives is often sensitive to temperature changes, and choosing the suitable adhesive for a specific temperature range is crucial. Here are some ways in which temperature variations affect the choice of adhesives for appliances:

Operating Temperature Range:
- Low Temperatures:For appliances operating in low-temperature environments (e.g., refrigerators, freezers), adhesives must remain flexible and maintain their bonding strength at cold temperatures. Some adhesives may become brittle and lose effectiveness in low-temperature conditions.
- High Temperatures:Appliances that generate heat, such as ovens or stovetops, require adhesives with high-temperature resistance. Adhesives used in these applications must withstand elevated temperatures without degrading, losing adhesion strength, or releasing harmful substances.
Thermal Cycling:
- Appliances often undergo thermal cycling, where they experience repeated cycles of heating and cooling. Adhesives chosen for these applications should exhibit good thermal stability to withstand expansion and contraction without compromising their adhesive properties.
Material Compatibility:
- Adhesives must be compatible with the materials they are bonding. Some adhesives may have different coefficients of thermal expansion than the materials they are adhering to, which can lead to issues such as delamination or reduced bond strength during temperature variations.
Thermal Conductivity:
- In appliances with critical heat dissipation, such as electronics, adhesives with good thermal conductivity may be preferred. These adhesives help in efficient heat transfer and prevent heat buildup in sensitive components.
Specialized Adhesives:
- Extreme temperature conditions may require specialized adhesives. High-temperature epoxies, thermally conductive adhesives, and other specialized formulations are designed to perform well in specific temperature ranges and challenging environments.
Testing and Validation:
- Thorough testing under realistic conditions ensures that the chosen adhesive meets the required performance standards. Manufacturers often conduct tests to evaluate adhesion strength, flexibility, and other properties under varying temperature conditions to validate the suitability of the adhesive for a particular application.
Environmental Considerations:
- Adhesives used in appliances may be exposed to different environmental conditions, such as humidity or moisture. The combined effects of temperature and environmental factors should be considered to ensure the adhesive’s long-term durability.
Understanding the temperature variations an appliance will experience is crucial in selecting adhesives that can withstand those conditions. Considering the operating temperature range, thermal cycling, material compatibility, and any specific appliance requirements will help choose adhesives that provide reliable and durable bonds over time.
Are there adhesives formulated explicitly for smart home devices and electronics?
Yes, there are adhesives explicitly formulated for smart home devices and electronics. These adhesives are designed to meet the unique requirements and challenges of electronic applications. Here are some key considerations and types of adhesives commonly used in the electronics and smart home device industry:
Thermal Interface Materials (TIMs):
- TIMs are adhesives that enhance the thermal conductivity between electronic components and heat sinks. They help dissipate heat efficiently, preventing the electronic devices from overheating. Thermal interface materials are crucial in maintaining the reliability and performance of electronic components.
Electrically Conductive Adhesives (ECAs):
- ECAs are adhesives that not only provide mechanical bonding but also conduct electricity. They are used to bond electrical components, create electrical connections, and provide electromagnetic shielding. ECAs are often employed in applications where soldering may need to be more practical.
Low Outgassing Adhesives:
- In particular, it’s essential to use adhesives that exhibit low outgassing for electronic applications, such as those in space or aerospace industries. Outgassing releases volatile components from the adhesive, harming sensitive electronic components or optics.
Flexible Adhesives:
- Many smart home devices and electronics have components that may undergo mechanical stress or vibrations. Flexible adhesives ensure that bonds can withstand movement without losing their adhesion properties. This is crucial in applications where the device may experience bending or flexing.
UV-Curable Adhesives:
- UV-curable adhesives provide rapid curing when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This quick curing process is advantageous in manufacturing electronic devices, allowing for faster production cycles. UV-curable adhesives are commonly used in applications requiring precise and rapid bonding.
Moisture-Resistant Adhesives:
- Electronics can be exposed to varying environmental conditions, including moisture. Adhesives with moisture resistance help protect electronic components from the harmful effects of humidity or water exposure.
Conformal Coatings:
- While not traditional adhesives, conformal coatings are applied to electronic assemblies to protect them from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and chemicals. These coatings enhance the reliability and lifespan of electronic devices.
Die Attach Adhesives:
- Attach adhesives bond semiconductor chips (die) to substrates or packages. These adhesives are critical in assembling integrated circuits and other semiconductor devices.
Manufacturers and engineers in the electronics and smart home industries often work closely with suppliers to select the most appropriate adhesive for their specific applications, considering factors such as temperature stability, electrical conductivity, flexibility, and environmental conditions.
How can adhesives contribute to noise reduction in certain appliances?
Adhesives significantly reduce noise in certain appliances by dampening vibrations and reducing the transmission of sound waves. Here are several ways adhesives contribute to noise reduction in appliances:
Vibration Damping:
- Adhesives with viscoelastic properties can absorb and dissipate vibrational energy. Applying these adhesives to components or surfaces prone to vibrations, such as panels or casings, helps reduce the overall level of mechanical noise produced by the appliance.
Bonding and Sealing:
- Properly bonding and sealing components using adhesives can prevent the generation of rattling or buzzing noises caused by loose or poorly fitted parts. Adhesives create a strong and secure bond between components, minimizing the potential for movement-induced noise.
Damping Pads and Sheets:
- Adhesive-backed damping pads or sheets, often made of materials like viscoelastic polymers or rubber, can be strategically applied to surfaces that resonate or vibrate. These pads absorb and dissipate energy, reducing the transmission of sound waves.
Acoustic Sealants:
- Acoustic sealants are designed to seal gaps and seams in appliances, preventing the escape of sound waves. The overall noise level can be reduced by using these sealants in areas where noise may escape, such as around panels or enclosures.
Flexible Adhesives and Materials:
- Adhesives that provide flexibility can absorb mechanical shocks and vibrations, contributing to a quieter operation. Flexible materials can help isolate components and prevent sound transmission between them.
Damping Adhesive Tapes:
- Adhesive tapes with damping properties are used to reduce noise and vibration. These tapes are applied to surfaces or components to absorb and dissipate energy, minimizing the impact of mechanical vibrations and noise.
Insulation:
- Adhesives with sound-absorbing or insulating materials can contribute to overall noise reduction. By bonding sound-absorbing materials to specific components or surfaces, adhesives can help create a barrier against sound transmission.
Anti-Resonance Coatings:
- Adhesives can be formulated with anti-resonance properties, which help mitigate the resonance of certain materials. Applying these adhesives to resonant surfaces can reduce the generation of specific frequencies that contribute to noise.
When designing appliances for noise reduction, engineers consider the specific noise sources, whether mechanical vibrations, rattling components, or the escape of airborne sound waves. Adhesives are then chosen to address these noise issues based on their damping, bonding, and sealing properties. It’s essential to conduct thorough testing and analysis to ensure that the selected adhesives effectively contribute to the desired level of noise reduction without compromising other aspects of appliance performance.
What are the best practices for home appliance adhesives’ storage and shelf life?
Proper storage and handling of adhesives are crucial to maintaining their performance and ensuring a longer shelf life. Here are some best practices for the storage of home appliance adhesives:
Temperature Control:
- Store adhesives in a controlled environment with a stable temperature. Extreme temperatures, both high and low, can negatively impact the chemical stability and performance of adhesives. The ideal storage temperature often depends on the specific adhesive, so refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
Avoid Direct Sunlight:
- Exposure to direct sunlight can lead to temperature fluctuations and may cause some adhesives to degrade. Store adhesives in a dark or opaque container and in a location where they are shielded from direct sunlight.
Humidity Control:
- Excessive humidity can affect the properties of certain adhesives. Store adhesives in a dry environment and, if applicable, consider using moisture-proof packaging or containers. Moisture-sensitive adhesives should be stored in airtight containers.
Seal Containers Tightly:
- Ensure that adhesive containers are tightly sealed after each use. This helps prevent the entry of moisture or air into the container, which could lead to premature curing or degradation of the adhesive.
Follow Manufacturer Recommendations:
- Adhesive manufacturers provide specific guidelines for storage conditions and shelf life. Follow these recommendations meticulously to ensure the adhesive retains its intended properties throughout its shelf life.
First-In, First-Out (FIFO):
- Adhere to the “First-In, First-Out” principle when using adhesives from multiple batches. Use older stock before newer stock to ensure adhesives are used within their recommended shelf life.
Store Upright:
- Store adhesive containers in an upright position to prevent leakage and maintain the integrity of the container’s seal. This is particularly important for liquid adhesives.
Labeling and Documentation:
- Clearly label adhesive containers with information such as the product name, batch number, and expiration date. Maintain proper documentation of the storage conditions and usage history of each adhesive.
Avoid Contamination:
- Prevent contamination by keeping storage areas clean and free of dust, dirt, and other foreign particles. Contamination can negatively affect the adhesive’s performance.
Regular Inspections:
- Periodically inspect stored adhesives for any signs of leakage, changes in color, or unusual odors. If any abnormalities are observed, consult the manufacturer or adhesive supplier for guidance.
Training for Personnel:
- Ensure that personnel handling adhesives are trained in proper storage and handling procedures. This helps minimize the risk of errors that could impact the quality of the adhesive.
By following these best practices, you can help extend the shelf life of home appliance adhesives and maintain their effectiveness when used in manufacturing or repair processes. Always consult the specific recommendations the adhesive manufacturer provides for the best results.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, navigating the world of home appliance adhesives requires knowledge about specific applications, material compatibility, and performance expectations. We hope this guide has shed light on the diverse aspects of adhesive technologies for home appliances, empowering you to make well-informed decisions for your repair and maintenance needs. Whether you’re bonding, sealing, or reinforcing, choosing the suitable adhesive can significantly enhance the longevity and efficiency of your home appliances. If you have more questions or need assistance, explore our detailed articles and product recommendations in each subcategory.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

Unraveling the Marvels of UV Glue: Understanding Its Mechanism and Applications
Unraveling the Marvels of UV Glue: Understanding Its Mechanism and Applications UV glue stands out in adhesives as a marvel of modern chemistry and engineering. This versatile substance has found its way into many industries, revolutionizing assembly processes and enabling the creation of intricate products that were once deemed impossible. But how does UV glue

Exploring Alternative Methods: How to Cure UV Resin Without UV Light
Exploring Alternative Methods: How to Cure UV Resin Without UV Light UV resin has become increasingly popular in crafting and DIY projects due to its versatility and quick curing properties. However, only some have access to UV light sources, which are typically used to cure UV resin. Fortunately, alternative methods are available for curing UV

The Luminescent Bond: Exploring UV Curing Optical Adhesives
The Luminescent Bond: Exploring UV Curing Optical Adhesives In modern manufacturing, where precision and efficiency are paramount, the demand for advanced bonding solutions has never been higher. Among these, UV-curing optical adhesives are a revolutionary technology, offering unparalleled speed, precision, and versatility in bonding applications. From electronics to medical devices, UV-curing optical adhesives have found

Unlocking the Power of UV Curing Glue for Plastic: A Comprehensive Guide
Unlocking the Power of UV Curing Glue for Plastic: A Comprehensive Guide In modern manufacturing and repair, where precision and efficiency are paramount, UV-curing glue for plastic has emerged as a game-changer. This innovative adhesive offers many benefits and has revolutionized various industries such as automotive, electronics, medical devices, etc. This comprehensive guide delves into

Unveiling the Brilliance of UV-Cured Epoxy Resin: Revolutionizing Industrial Applications
Unveiling the Brilliance of UV-Cured Epoxy Resin: Revolutionizing Industrial Applications Innovations in industrial materials often reshape the landscape of manufacturing, offering improved efficiency, durability, and versatility. Among these innovations stands UV-cured epoxy resin, a marvel gaining traction across various industries. This article explores the intricacies of UV-cured epoxy resin, its applications, benefits, and its

Illuminating the Best UV Lights for Curing Glue: A Comprehensive Guide
Illuminating the Best UV Lights for Curing Glue: A Comprehensive Guide In the realm of DIY projects, repair works, and professional craftsmanship, the significance of adhesives cannot be overstated. From bonding delicate materials in electronics to securing heavy-duty components in manufacturing, adhesives play a pivotal role. However, the efficiency and durability of adhesive bonds often