- Home
- >
- Material Bonding
- >
- UV Cure Adhesive For Plastic
UV Cure Adhesive For Plastic
Table of Contents
ToggleHow does UV-cure adhesive work on plastic surfaces?
UV-cure adhesives, also known as ultraviolet (UV) light-cure adhesives, cure or harden when exposed to ultraviolet light. These adhesives are commonly used for bonding various materials, including plastics. The primary mechanism of how UV-cure adhesives work on plastic surfaces involves the following steps:- Composition of the Adhesive:UV-cure adhesives typically consist of monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and other additives. Monomers are the building blocks of the adhesive, and oligomers are short chains of monomers. Photoinitiators are chemicals that initiate the curing process when exposed to UV light.
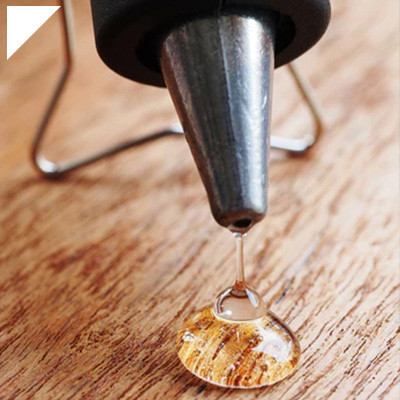
- Application to the Plastic Surface:The liquid UV-cure adhesive is applied to the plastic surfaces that need to be bonded. The adhesive forms a thin layer between the two surfaces.
- UV Exposure:Once the adhesive is applied, it is exposed to ultraviolet light. The UV light activates the photoinitiators in the adhesive.
- Initiation of Polymerization:The activated photoinitiators initiate a polymerization reaction in the adhesive. Polymerization involves the monomers and oligomers reacting to form long chains or networks, creating a solid and durable bond.
- Curing and Bond Formation:As the polymerization reaction progresses, the liquid adhesive transforms into a solid, creating a strong bond between the plastic surfaces. This process is relatively quick and can take a few seconds or minutes, depending on the specific adhesive and UV light intensity.
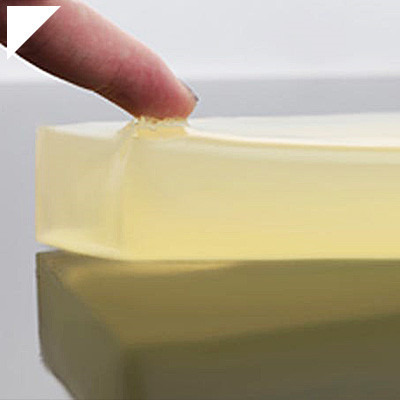
- Final Bond Strength:Once the UV exposure is complete, the adhesive is fully cured, and the bonded plastic surfaces achieve their absolute strength. The resulting bond is often clear and transparent and can have excellent adhesion properties.
What are the advantages of using UV-cure adhesives for plastic bonding?
UV-cure adhesives offer several advantages for plastic bonding applications. Here are some key benefits: Rapid Cure Time:- UV-cure adhesives cure quickly when exposed to ultraviolet light. This fast cure time can significantly reduce production cycle times, increasing the efficiency of manufacturing processes.
- UV-curing processes allow for precise control over the curing process. The adhesive only cures when exposed to UV light, providing flexibility in assembly and alignment before fixing.
- UV-cure adhesives generate minimal heat during the curing process. This is particularly important for bonding heat-sensitive plastics that might be damaged or distorted by elevated temperatures.
- UV-cure adhesives typically have low volatility, releasing fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during curing than other adhesive technologies. This is beneficial for both worker safety and environmental considerations.
- UV-cure adhesives can provide strong and durable bonds. The cured adhesive often forms a bond with high tensile strength, ensuring the assembly’s integrity.
- UV-cure adhesives are suitable for bonding plastics, including clear and colored substrates. They are also compatible with different shapes and sizes, making them versatile for multiple applications.
- The UV-curing process is generally clean and does not involve using solvents or water. This can simplify the cleaning and preparation of substrates before bonding.
- Since UV-cure adhesives cure on demand, there is minimal wastage. Excess adhesive not exposed to UV light remains liquid and can be reused.
- The instant cure provided by UV-cure adhesives allows for real-time quality control. Manufacturers can quickly inspect and verify the bond quality, reducing the likelihood of defective products reaching the market.
- UV-cure adhesives can contribute to a clean and aesthetically pleasing finish. The clarity and transparency of the adhesive can be important for applications where the appearance of the bonded surfaces is crucial.
Are UV-cure adhesives suitable for different types of plastics?
UV-cure adhesives can be suitable for bonding various plastics, but their compatibility depends on the specific formulations of both the adhesive and the plastics involved. UV-cure adhesives are versatile and can connect well with many plastic substrates. However, it’s essential to consider the following factors:- Adhesive Formulation:UV-cure adhesives come in different formulations, and some may be explicitly designed for bonding plastics. The adhesive should be chosen based on the types of plastics you are working with.
- Plastic Types:Not all plastics have the same surface characteristics or chemical composition. Some plastics may be inherently more challenging to bond than others. Common plastics like acrylics, polycarbonates, and certain types of polyethylene and polypropylene can be suitable for UV-cure adhesives, but it’s essential to check the compatibility.
- Surface Preparation:The surface of the plastics must be clean and free of contaminants such as oils, mold release agents, or dust. Some plastics may also require surface treatment (e.g., corona treatment) to enhance adhesion.
- Wavelength Sensitivity:UV-cure adhesives typically require a specific wavelength of UV light for curing. Ensure the adhesive and the plastic are compatible with the UV light source.
- Curing Depth:UV-cure adhesives cure when exposed to UV light. The depth of cure can be affected by factors such as the adhesive’s viscosity and the transparency of the plastic. Thicker adhesives may have limitations in terms of curing through certain plastics.
- Flexibility and Thermal Considerations:Consider the application’s flexibility and thermal resistance requirements. Some UV-cure adhesives may have better flexibility or resistance to temperature extremes, making them more suitable for specific plastic bonding applications.
What industries commonly use UV-cure adhesive for plastic applications?
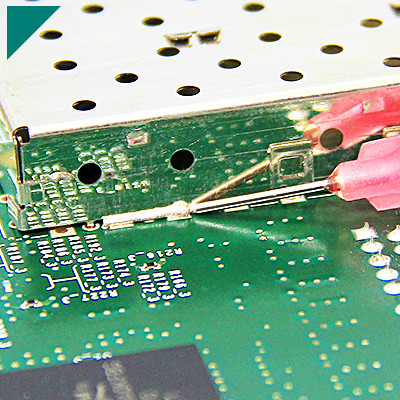
UV-cure adhesives are versatile and find applications in various industries, especially for bonding plastics. Some common industries that frequently use UV-cure adhesives for plastic applications include: Electronics and Electricals:- UV-cure adhesives assemble electronic components and devices made of plastic, such as mobile phones, tablets, and circuit boards.
- In the medical industry, UV-cure adhesives are employed for bonding and assembling plastic components of medical devices. The quick curing time is advantageous in maintaining production efficiency.
- Automotive manufacturers use UV-cure adhesives for bonding plastic parts in interior and exterior applications. This includes bonding dashboards, interior panels, and various external components.
- UV-cure adhesives are commonly used to assemble optical devices, such as lenses, cameras, and other optical components made from plastic materials.
- Some aerospace applications involve bonding plastic components, and UV-cure adhesives can be suitable for specific assembly processes where rapid curing is essential.
- UV-cure adhesives are utilized in the packaging industry for bonding plastic materials. This can include clicking plastic films, containers, and other packaging components.
- Various consumer goods, such as household appliances, toys, and electronics, use UV-cure adhesives to bond plastic parts.
- In addition to medical devices, UV-cure adhesives assemble plastic components for medical packaging to ensure a secure and sterile environment.
- UV-cure adhesives make point-of-purchase displays and signage, where bonding plastic components is expected.
- UV-cure adhesives are used in the printing industry for connecting plastic substrates in various applications, including signage and graphics.
Can UV-cure adhesives be used for bonding transparent plastics?
Yes, UV-cure adhesives can be used for bonding transparent plastics. UV-cure adhesives are particularly well-suited for connecting fine materials because they typically cure quickly and do not leave a visible residue. The adhesive is applied in liquid form and then exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light for a short period to initiate the curing process. When bonding transparent plastics, choosing a UV-cure adhesive compatible with the specific type of plastic you work with is essential. Different plastics have varying levels of transparency and may react differently to adhesives. Additionally, consider the wavelength of the UV light required for curing, which can also affect the bonding process. Here are some key considerations when using UV-cure adhesives for bonding transparent plastics:- Adhesive Compatibility:Ensure that the UV-cure adhesive you choose is compatible with the specific type of transparent plastic you connect. Some adhesives may work better with certain plastics, so checking the product specifications and recommendations is essential.
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving a solid bond. Make sure the surfaces to be bonded are clean, dry, and free from contaminants that could interfere with adhesion.
- UV Light Exposure:Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate UV light exposure time and intensity. This information is typically provided in the adhesive product’s technical data sheet. Insufficient or excessive exposure to UV light can affect the curing process and bond strength.
- Thickness of Adhesive:Pay attention to the recommended adhesive thickness. Some UV-cure adhesives may have limitations on the maximum thickness for adequate curing. If the adhesive layer is too thick, it may not cure completely.
- Curing in Shadowed Areas:UV-cure adhesives rely on exposure to UV light for curing. Ensure that the adhesive in shadowed or hard-to-reach areas receives adequate UV light exposure to cure correctly.
What factors affect the curing time of UV adhesive on plastics?
Several factors can influence the curing time of UV adhesive on plastics. UV adhesives, also known as ultraviolet light-curing adhesives, cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. Here are some key factors that can affect the curing time:
UV Light Intensity:
- The intensity of the UV light source is a crucial factor. Higher-intensity UV light sources can accelerate the curing process. Ensure that the UV light source is appropriately calibrated and provides the recommended intensity for your specific UV adhesive.

Wavelength of UV Light:
- Different UV adhesives are formulated to cure at particular UV wavelengths. Ensure that the UV light source emits light at the appropriate wavelength for the adhesive. Using the right wavelength may result in complete curing.
Adhesive Thickness:
- The thickness of the adhesive layer can impact curing time. Thicker coatings may require more time for the UV light to penetrate and cure the adhesive completely. Consider using adhesives that are specifically formulated for broader applications if needed.
Substrate Material:
- The type of plastic substrate can influence curing time. Some plastics may block or absorb UV light to varying degrees. Choosing a UV adhesive compatible with the specific plastic you are bonding is essential.
UV Absorbers or Inhibitors:
- Some plastics contain UV absorbers or inhibitors that can hinder the curing process. It’s critical to be aware of the composition of the plastic substrate and select a UV adhesive that works well with it.
Temperature:
- Temperature can affect the adhesive’s viscosity and the curing reaction’s rate. Higher temperatures can generally accelerate the curing process, but extreme temperatures may have adverse effects. Follow the recommended temperature range for the specific UV adhesive.
Oxygen Inhibition:
- Some UV adhesives may exhibit oxygen inhibition, where the presence of oxygen inhibits the curing process. This is more common in formulations with acrylate-based chemistries. Manufacturers may provide information on how to minimize oxygen inhibition effects.
Adhesive Formulation:
- Different UV adhesives have varying formulations, and each may have its recommended curing conditions. Follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific UV adhesive you are using.
By carefully considering these factors and following the guidelines provided by the adhesive manufacturer, you can optimize the curing process for UV adhesives on plastics.
Are there any safety considerations when working with UV-cure adhesives for plastics?
Yes, several safety considerations exist when working with UV-cure adhesives for plastics. UV-cure adhesives typically contain photoinitiators that react to ultraviolet (UV) light to initiate curing. Here are some safety considerations:
- Eye Protection:UV light can harm the eyes, causing damage such as photokeratitis (similar to sunburn of the cornea) or long-term damage. Always wear appropriate eye protection, such as UV-blocking safety goggles or glasses, when working with UV-cure adhesives.
- Skin Protection:UV radiation can also harm the skin, causing burns and other damage. It’s advisable to wear protective clothing, including gloves, to prevent direct skin exposure to the uncured adhesive.
- Ventilation:Some UV-cure adhesives may emit volatile compounds during the curing process. Ensure good ventilation in the work area to minimize exposure to these fumes. This is especially important if you are working with adhesives in confined spaces.
- Material Compatibility:Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the specific types of plastics you are working with. Some adhesives may have compatibility issues with certain plastics, leading to poor adhesion or other performance issues.
- Follow Manufacturer Guidelines:Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific UV-cure adhesive you use. This includes information on proper handling, storage, and application conditions.
- Curing Time and Intensity:Be aware of UV light’s recommended curing time and intensity for the adhesive you are using. Insufficient curing can result in incomplete bonding, while excessive exposure may lead to overcuring, affecting the material properties.
- Emergency Preparedness:Have appropriate emergency measures in place, including access to eye wash stations and first aid, in case of accidental exposure or contact with the adhesive.
- Equipment Maintenance:Regularly inspect and maintain UV light-curing equipment to ensure proper functioning and prevent accidental exposure due to equipment failure.
- Training:Ensure that individuals working with UV-cure adhesives are adequately trained in handling and safety precautions. This includes understanding the potential hazards of the specific adhesive and UV curing process.
Adhering to these safety considerations can minimize the risks of using UV-cure adhesives for plastics and create a safer working environment.
Can UV-cure adhesives bond dissimilar plastics successfully?
UV-cure adhesives can effectively bond dissimilar plastics, but their success depends on the specific types of plastics involved. UV-cure adhesives are typically acrylic-based and work by polymerizing and hardening when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. While they can bond many different materials, the success of the bond depends on the compatibility of the adhesive with the specific types of plastics being joined.
Here are some factors to consider:
- Surface Energy:Different plastics have varying surface energies, affecting adhesion properties. It’s generally easier to bond plastics with similar surface energies. If the dissimilar plastics have significantly different surface energies, it might be necessary to treat the surfaces to enhance adhesion.
- Chemical Compatibility:The chemical composition of the plastics plays a crucial role. Some plastics are chemically inert, making it challenging for adhesives to form strong bonds. UV-cure adhesives may work well with certain plastics, such as acrylics and polycarbonates, but may need to bond more effectively with others.
- Substrate Preparation:Proper substrate preparation is essential for successful bonding. Cleaning and surface treatment can improve adhesion by removing contaminants and increasing surface roughness.
- Adhesive Properties:The specific formulation of the UV-cure adhesive matters. Some adhesives are designed to work better with certain types of plastics. Choosing an adhesive that matches the requirements of the plastics you are bonding is essential.
- UV Exposure:Ensure the adhesive receives sufficient UV light for proper curing. Inadequate exposure can lead to complete curing and stronger bonds.
Before applying UV-cure adhesives to bond dissimilar plastics, it’s advisable to conduct compatibility tests and assess the application’s specific requirements. Consider consulting the adhesive manufacturer’s guidelines and testing the bond strength under relevant conditions to ensure optimal results. Primers or adhesion promoters designed for the specific plastics involved can enhance the bonding performance.
What are the temperature and environmental considerations for UV-cured plastic bonds?
UV-cured plastic bonds, often created using UV-curable adhesives, have specific temperature and environmental considerations that can impact their performance. Here are some key factors to consider:
Temperature Range:
- UV-curable adhesives typically have a recommended temperature range for application and curing. It’s essential to follow the manufacturer’s guidelines regarding acceptable temperature conditions.
- Extreme temperatures can affect the viscosity of the adhesive, potentially leading to issues with application and curing. High temperatures accelerate curing, while low temperatures slow or prevent proper curing.
Intensity and Wavelength of UV Light:
- The effectiveness of UV-curing depends on the intensity and wavelength of the UV light source. Ensure that the UV light source is appropriate for the specific adhesive.
- Temperature can influence the performance of the UV light source. Some adhesives may be sensitive to temperature changes, affecting the curing process.
Humidity and Moisture:
- Excessive humidity can interfere with the curing process of UV-curable adhesives. Moisture can hinder UV light penetration and negatively impact the quality of the bond.
- Working in a controlled environment with low humidity levels is crucial to ensure optimal curing conditions.
Substrate Compatibility:
- Different plastics have varying thermal expansion coefficients, and their compatibility with UV-curable adhesives can depend on factors such as composition, surface energy, and texture.
- Temperature changes may cause the substrates to expand or contract, potentially affecting the integrity of the bond.
UV Exposure Time:
- The curing time for UV-curable adhesives is influenced by factors such as the intensity of the UV light, the adhesive thickness, and the type of substrate.
- In extreme temperatures, adjustments to the exposure time may be necessary to achieve the desired bond strength.
Post-Curing:
- Some applications may benefit from post-curing to ensure complete polymerization of the adhesive. This may involve additional exposure to UV light or other curing methods.
- The post-curing process may need to be adjusted based on environmental conditions.
Thermal Resistance of the Bond:
- Assess the thermal resistance of the cured bond to ensure it can withstand the temperature variations it may encounter during its intended use.
Always refer to the specific guidelines provided by the adhesive manufacturer, as different formulations may have unique requirements and considerations. Testing under the intended environmental conditions is crucial to ensuring the reliability and durability of UV-cured plastic bonds.
How do UV cure adhesives compare to traditional adhesive options for plastics?
UV cure adhesives and traditional adhesives serve as bonding agents for plastics but differ in their curing mechanisms and application characteristics. Here are some key points of comparison between UV cure adhesives and traditional adhesives for plastics:
Curing Mechanism:
- UV Cure Adhesives:These adhesives cure quickly when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. They contain photoinitiators that initiate a polymerization reaction when exposed to UV light, leading to rapid bonding.
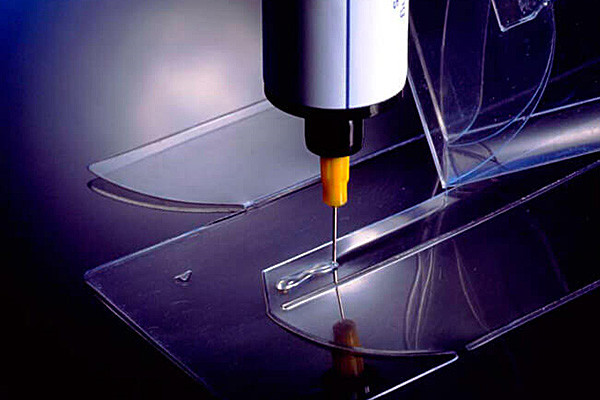
- Traditional Adhesives:Traditional adhesives cure through various mechanisms such as solvent evaporation, chemical reaction, or heat. The curing time can be longer compared to UV-cure adhesives.
Curing Time:
- UV Cure Adhesives:Cure almost instantly upon exposure to UV light. This rapid curing time can increase production efficiency.
- Traditional AdhesivesGenerally have longer curing times, and the bonding process may require clamping or additional time for the adhesive to set and cure.
Bond Strength:
- UV Cure Adhesives:These can provide strong and durable bonds. The fast curing process can also produce a more uniform bond than some traditional adhesives.
- Traditional Adhesives:Offer a wide range of bond strengths depending on the type of adhesive used. Some conventional adhesives may require longer curing times to achieve optimal strength.
Versatility:
- UV Cure Adhesives:These may be more suitable for applications where rapid curing is essential, such as high-speed production lines. They are often used for bonding transparent materials and in applications where minimal heat is desirable.
- Traditional Adhesives:Offer a variety of formulations suitable for different substrates and application conditions. Some conventional adhesives may be better suited for specific environments or bonding certain plastics.
Application and Equipment:
- UV Cure Adhesives:Require UV light sources for curing. UV curing equipment can be more specialized and may involve additional costs. The adhesive is often applied in a liquid form.
- Traditional Adhesives:Applied in various formats such as liquids, tapes, or films. Depending on the adhesive type, application methods may include dispensing, spraying, or brushing.
Environmental Considerations:
- UV Cure Adhesives:They tend to have lower VOC (volatile organic compound) emissions since they cure without needing heat or solvents.
- Traditional Adhesives:Some adhesives may contain solvents or emit VOCs during curing.
When choosing between UV cure adhesives and traditional adhesives for plastics, it’s crucial to consider the application’s specific requirements, production processes, and desired properties of the bonded materials. Each adhesive type has advantages and limitations, and the choice depends on factors such as bonding speed, bond strength, and environmental considerations.
Are there limitations to the thickness of plastic materials that UV adhesives can bond?
Various factors can influence the bonding capabilities of UV adhesives, and the thickness of the plastic materials is one of them. UV adhesives typically rely on ultraviolet (UV) light for curing, and there are some limitations to the thickness of materials that can be effectively bonded. Here are some considerations:
UV Light Penetration:
- UV light has a limited penetration depth. As the material’s thickness increases, UV light’s ability to penetrate through the material decreases. This can affect the curing of the adhesive in deeper layers.
Material Properties:
- Different plastics have varying degrees of transparency to UV light. Some plastics may absorb or block UV light, making it challenging for the adhesive to cure effectively in thicker sections.
Adhesive Composition:
- The formulation of the UV adhesive itself can impact its curing capabilities. Some UV adhesives are designed for broader applications and may include additives or components that enhance light penetration or curing depth.
Curing Equipment:
- The type and intensity of the UV light source used for curing also play a role. High-intensity UV lamps may provide better penetration for thicker materials, but it’s essential to appropriately match the adhesive and curing equipment.
Surface Preparation:
- The condition of the surfaces being bonded can affect the adhesive bond. Proper surface preparation, such as cleaning and ensuring good contact between the surfaces, is essential for successful bonding.
Adhesive Selection:
- Some UV adhesives are specifically formulated for bonding thicker materials. It’s crucial to choose an adhesive that is suitable for the specific application and material thickness.
Testing and Optimization:
- The optimal thickness for bonding with UV adhesives may need to be determined through testing and optimization. Manufacturers often provide guidelines and recommendations based on their product specifications.
It’s essential to consult the adhesive manufacturer for specific guidance on the maximum thickness their product can effectively bond. Additionally, conducting test bonding on sample materials with varying thicknesses can help determine the practical limitations of a specific application.
Can UV-cure adhesives be used for outdoor applications on plastics?
UV-cure adhesives can be used for outdoor applications on plastics, but their suitability depends on various factors. UV-cure adhesives offer several advantages, such as fast curing times, low heat generation, and bonding to a wide range of substrates. However, there are considerations to keep in mind for outdoor use:
- UV Stability:UV-cure adhesives may degrade over time when exposed to prolonged UV radiation from sunlight. Some formulations are designed to be more UV-resistant than others. Choosing adhesives specifically formulated for outdoor applications or ones that exhibit good UV stability is essential.
- Temperature Resistance:Outdoor environments can expose materials to various temperatures. Ensure that the UV-cure adhesive chosen has the required temperature resistance for the specific outdoor conditions where it will be used.
- Moisture Resistance:Outdoor applications often involve exposure to rain, humidity, or other forms of moisture. The adhesive should possess good moisture resistance to maintain its bond strength over time.
- Substrate Compatibility:Verify that the UV-cure adhesive is compatible with the specific types of plastics involved in your application. Some plastics may require unique surface treatments or primers to enhance adhesion.
- Flexibility:Outdoor applications may subject bonded materials to mechanical stress due to temperature variations, such as expansion and contraction. Consider the flexibility of the cured adhesive to ensure it can accommodate such movements without losing adhesion.
- Chemical Resistance:Depending on the outdoor environment, the adhesive may be exposed to chemicals, pollutants, or other substances that could affect its performance. Choose an adhesive with suitable chemical resistance for the intended application.
- Manufacturer Recommendations:Always follow the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific UV-cure adhesive you use. They often provide valuable information on application conditions, compatibility, and limitations.
Before using any UV-cure adhesive for outdoor applications on plastics, it’s advisable to conduct thorough testing to ensure that the adhesive meets the specific requirements of your project and provides the desired durability and performance in outdoor conditions.
Are there specific surface preparations required before using UV-cure adhesives on plastics?
Proper surface preparation ensures optimal bonding when using UV-cure adhesives on plastics. Here are some general guidelines for surface preparation before applying UV-cure adhesives:
Clean the Surface:
- Thoroughly clean the plastic surfaces to remove contaminants such as dust, grease, oil, or mold release agents. Use a mild detergent or a solvent appropriate for the specific type of plastic.
Abrasion or Sanding:
- Depending on the type of plastic, it may be beneficial to lightly rub or sand the surface. This helps to increase surface area and promotes better adhesion. However, some plastics may be sensitive to abrasion, so it’s essential to test a small area first.
Use of Primers:
- In some cases, adhesion promoters or primers designed for specific plastics can enhance bonding. These primers help in creating a more receptive surface for the adhesive. Make sure to choose a primer compatible with the plastic substrate and the UV-cure adhesive.
Selecting the Right UV-Cure Adhesive:
- Different UV-cure adhesives are formulated for specific substrates. Ensure you choose an adhesive designed for bonding the type of plastic you work with.
Avoid Contamination:
- Once the surfaces are prepared, handle them carefully to avoid recontamination. Even fingerprints can impact the bonding performance, so it’s advisable to use gloves and minimize direct contact with the prepared surfaces.
Optimizing UV Exposure:
- Ensure that the UV light can reach the adhesive on the bonded surfaces. The geometry and design of the components should allow for adequate exposure to the UV light source.
Follow the Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
- Always follow the recommendations and guidelines provided by the UV-cure adhesive manufacturer. Different adhesives may have specific requirements or variations in the preparation process.
Testing:
- Before applying the adhesive to a large or critical area, conduct small-scale tests to confirm that the chosen adhesive and surface preparation methods are adequate for your specific application.
Remember that the effectiveness of surface preparation can vary depending on the type of plastic, the specific UV-cure adhesive used, and the application requirements. It’s advisable to consult with the adhesive manufacturer for detailed recommendations based on your explicit materials and bonding needs.
What are the key features when selecting a UV-cure adhesive for plastic?
When selecting a UV-cure adhesive for plastic, several key features and factors must be considered to ensure optimal performance and compatibility. Here are some important considerations:
Substrate Compatibility:
- Ensure that the UV-cure adhesive is compatible with the specific type of plastic you are bonding. Different plastics have varying surface energies and chemical compositions, so choosing an adhesive designed for the target material is crucial.
Adhesive Type:
- UV-cure adhesives come in various formulations, such as acrylic, epoxy, and urethane. Select an adhesive type that suits the application requirements and the specific properties you need, such as flexibility, toughness, or chemical resistance.
Curing Speed:
- UV-cure adhesives offer fast curing times, but the exact speed can vary. Consider the production requirements and the time available for the adhesive to cure. Some applications may benefit from adhesives with slower curing times to allow for repositioning or adjustment.
UV Light Source Compatibility:
- Ensure the adhesive is compatible with the UV light source available in your process. Different adhesives may require specific wavelengths and intensities for efficient curing. Verify that your UV light source matches the requirements specified by the adhesive manufacturer.
Environmental Resistance:
- Consider the environmental conditions the bonded plastic will face, such as temperature extremes, humidity, and chemical exposure. Choose an adhesive that resists these environmental factors to ensure long-term bond durability.
Bond Strength:
- Evaluate the bond strength provided by the UV-cure adhesive. The strength necessary depends on the specific application, and some adhesives may offer enhanced adhesion to plastics through surface preparation or primers.
Flexibility and Elasticity:
- Depending on the application, you may need an adhesive that maintains flexibility and elasticity after curing. This is important for applications where the bonded parts experience movement or stress.
Optical Clarity:
- Optical clarity may be crucial in specific applications, especially optics or display manufacturing. Choose a UV-cure adhesive that offers transparency and does not introduce haze or discoloration.
Application Method:
- Consider the method of application. Some UV-cure adhesives come in liquid form, while others may be available as gels or pastes. Choose an application method that is convenient and compatible with your manufacturing process.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Ensure the selected adhesive complies with industry regulations or standards relevant to your application. This is especially important in industries like medical devices or electronics.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s technical data sheets and guidelines to make an informed decision based on the specific requirements of your application. Additionally, conducting tests and trials in your specific production environment can help ensure the chosen UV-cure adhesive meets your expectations.
Can UV-cure adhesives withstand exposure to chemicals on plastic surfaces?
UV-cure adhesives are known for their quick curing time and muscular bond strength. However, their chemical resistance can vary depending on the specific formulation of the adhesive and the type of chemicals involved. In general, UV-cure adhesives can exhibit good resistance to many chemicals. Still, their performance may be influenced by factors such as the substrate material (plastic, in this case), the type of chemicals involved, and the specific adhesive formulation.
Here are some considerations regarding the chemical resistance of UV-cure adhesives on plastic surfaces:
Type of Plastic:
- Different plastics have varying chemical resistance properties. Some plastics are more resistant to chemicals, while others may be more susceptible to chemical attack. It is essential to know the specific type of plastic you are working with and its compatibility with the UV-cure adhesive.
Adhesive Formulation:
- UV-cure adhesives come in various formulations; manufacturers often tailor them for specific applications. Some formulations may provide better resistance to certain chemicals than others. Check the product datasheet or consult with the adhesive manufacturer to understand the chemical resistance of a particular UV-cure adhesive.
Chemical Exposure:
- Consider the specific chemicals to which the adhesive will be exposed. Some UV-cure adhesives may resist certain chemicals but could be vulnerable to others. Evaluate the compatibility of the adhesive with the specific chemicals present in the environment.
Testing:
- In critical applications, it’s advisable to conduct compatibility testing. This involves applying the UV-cure adhesive to the plastic substrate and exposing the bonded assembly to the intended chemicals under controlled conditions. This can help determine the long-term performance of the adhesive in the specific chemical environment.
Manufacturer’s Recommendations:
- Always refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for proper usage and limitations. They may provide valuable information on the chemical resistance of their products.
It’s worth noting that while UV-cure adhesives can offer good chemical resistance, there may be limitations in extreme chemical environments. If high chemical resistance is critical, alternative adhesive technologies such as epoxy or chemical-resistant cyanoacrylate adhesives may be considered, depending on the specific application.
Do UV-cure adhesives for plastics come in different colors or transparency options?
Yes, UV-cure adhesives for plastics are available in various colors and transparency options. Manufacturers often produce UV-cure adhesives in different formulations to meet specific application requirements. Some standard options include:
- Clear/Transparent Adhesives:These adhesives are designed to be transparent or nearly transparent after curing. They are suitable for applications where a clear bond line is desired, and the adhesive should not interfere with the appearance of the bonded materials.

- Colored Adhesives:UV-cure adhesives come in various colors, including black, white, and other custom colors. Colored adhesives can be helpful when aesthetics or color matching are important or when the adhesive needs to blend in with the bonded materials.
- Fluorescent Adhesives:Some UV-cure adhesives are formulated to be fluorescent, which can be advantageous in applications where inspection under UV light is necessary. The fluorescence makes it easier to detect and verify the presence of the adhesive.
- Tinted Adhesives:Tinted adhesives may slightly color without being fully opaque. This can be useful in applications where a subtle tint is acceptable, and transparency is not critical.
When choosing a UV-cure adhesive for a specific application, it’s essential to consider factors such as bonded material, curing process, and aesthetic or functional requirements. Manufacturers typically provide information about the properties and characteristics of their UV-cure adhesives, helping users select the most suitable option for their needs.
What are the common challenges faced when using UV-cure adhesives on plastics?
UV-cure adhesives are widely used for bonding plastics due to their fast curing time, environmental friendliness, and muscular bond strength. However, there are some common challenges associated with using UV-cure adhesives on plastics:
Substrate Transparency:
- UV-cure adhesives rely on the absorption of UV light to initiate the curing process. Some plastics may not be transparent to UV light, preventing proper curing. This is particularly true for opaque or UV-blocking plastics.
Surface Sensitivity:
- The surface properties of the plastic substrate can influence the effectiveness of UV-cure adhesives. Contaminants, release agents, or surface treatments can hinder the adhesive’s ability to bond effectively.
Polymerization Inhibition:
- Certain plastic additives, such as stabilizers and UV blockers, can inhibit the polymerization process of UV-cure adhesives. This may result in incomplete curing and reduced bond strength.
Curing Depth:
- UV light has limited penetration depth, so properly curing in thicker or opaque plastic substrates can be challenging. Ensuring that the adhesive cures entirely throughout the bond line is essential.
Intensity and Exposure Time:
- There needs to be more UV light intensity or adequate exposure time to avoid incomplete curing. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the appropriate UV light intensity and exposure duration is crucial.
Temperature Sensitivity:
- UV-cure adhesives can be sensitive to temperature variations. Excessively high or low temperatures may affect the curing process and the bond strength. Adhesive manufacturers often provide temperature guidelines for optimal performance.
Post-Cure Stability:
- Some plastics may experience degradation or discoloration when exposed to prolonged UV radiation. This can be a concern in applications where the bonded parts are exposed to sunlight or other UV light sources over time.
Bond Strength on Certain Plastics:
- While UV-cure adhesives generally provide strong bonds on many plastics, their performance can vary depending on the type of plastic. It’s essential to select adhesives specifically designed for the target plastic substrate.
Moisture Sensitivity:
- UV-cure adhesives are generally sensitive to the presence of moisture. Ensuring a dry environment during bonding is crucial, as humidity can interfere with the curing reaction and compromise the bond strength.
Equipment and Safety Concerns:
- UV curing requires specialized equipment, and operators must follow safety guidelines to avoid exposure to UV radiation. Improper handling of equipment or inadequate safety measures can pose risks to personnel.
Addressing these challenges involves careful selection of UV-cure adhesives based on the specific plastics being bonded, proper surface preparation, and adherence to recommended curing conditions outlined by the adhesive manufacturer.
Can UV-cure adhesives be used for bonding flexible plastics?
UV-cure adhesives can be used for bonding flexible plastics, but the suitability depends on the specific types of plastics you are working with. UV-cure adhesives are often chosen for their fast curing times and ability to create strong bonds. They are commonly used in electronics, medical devices, and optics.
When working with flexible plastics, it’s essential to consider the flexibility and elongation properties of both the adhesive and the bonded materials. Some UV-cure adhesives are formulated to provide flexibility and elongation, making them suitable for bonding flexible substrates without compromising the strength of the bond.
Additionally, it’s crucial to ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the specific type of plastics you are bonding, as different plastics have varying chemical compositions and surface characteristics. Adhesive manufacturers typically provide guidelines regarding the compatibility of their products with other materials.
Before using a UV-cure adhesive for bonding flexible plastics, consider the following:
- Adhesive Type:Choose a UV-cure adhesive designed explicitly for flexible substrates. Manufacturers often have product lines that cater to different material requirements.
- Surface Preparation:Ensure that the surfaces to be bonded are clean and free of contaminants. Some plastics may require surface treatment (such as plasma or priming) to improve adhesion.
- Curing Time and Intensity:Follow the manufacturer’s fixing time and intensity recommendations. UV-cure adhesives generally cure quickly under UV light, but the specific conditions may vary.
- Testing:Conduct preliminary tests on a small scale to evaluate the bond strength and flexibility of the cured adhesive on your particular plastic materials.
Always refer to the technical data sheets and guidelines provided by the adhesive manufacturer for the best results. If in doubt, consult with the adhesive supplier or seek advice from technical experts specializing in adhesive applications for flexible plastics.
How does the cost of UV cure adhesives compare to traditional bonding methods for plastics?
The cost of UV-cure adhesives compared to traditional bonding methods for plastics can vary based on several factors. Here are some considerations:
Material Costs:
- UV cure adhesives might have a higher upfront material cost compared to traditional adhesives. UV cure adhesives often contain photoinitiators and other additives contributing to their curing process.
Equipment Costs:
- UV bonding may require UV curing equipment, which can be an additional cost. Traditional bonding methods may not require specialized curing equipment.
Labor Costs:
- The labor costs associated with UV curing can be lower because UV adhesives typically cure rapidly, reducing the time required for bonding compared to some traditional methods. However, training personnel in the proper use of UV equipment may add to labor costs initially.
Energy Costs:
- UV cure adhesives often require less energy for curing compared to heat-curing methods. This can result in lower energy costs over time.
Process Efficiency:
- UV curing is generally faster than traditional methods like heat-curing or solvent-based adhesives. Shorter curing times can lead to increased production efficiency and reduced overall costs.
Waste and Environmental Impact:
- UV cure adhesives are more environmentally friendly as they often produce less waste and emit fewer volatile organic compounds (VOCs) than traditional solvent-based adhesives.
Application Specifics:
- The specific application and requirements of the bonding process can significantly influence cost considerations. For particular applications, the benefits of UV curing, such as rapid curing and reduced processing time, may outweigh any higher upfront material costs.
Bonding Performance:
- Consider the performance requirements of the bonded parts. Traditional methods sometimes offer specific advantages regarding strength, flexibility, or other properties.
It’s essential to evaluate these factors based on the specific needs of your application. The choice between UV cure adhesives and traditional bonding methods depends on production volume, required bond strength, curing time, and budget constraints. In some cases, a combination of methods might be used for different aspects of the bonding process.
Are there any specific application techniques or equipment required for UV-cure adhesives on plastics?
UV-cure adhesives are commonly used for bonding plastics due to their fast curing time and muscular bond strength. Specific application techniques and equipment can enhance bonding when working with UV-cure adhesives on plastics. Here are some considerations:
Surface Preparation:
- Ensure that the surfaces to be bonded are clean and free from contaminants like grease, oil, or dust.
- Some plastics may require surface treatment, such as plasma or flame treatment, to enhance adhesion.
Adhesive Selection:
- Choose a UV-cure adhesive specifically designed for bonding plastics. Different formulations may be optimized for different types of plastics.
UV Light Source:
- Use a UV light source with the appropriate wavelength for the adhesive. Standard UV wavelengths for curing adhesives are 365 nm and 405 nm.
- Ensure the UV light source has sufficient intensity and coverage to cure the adhesive across the bonded area uniformly.
Intensity and Exposure Time:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for the optimal intensity and exposure time. Insufficient curing may result in a weaker bond, while excessive curing can lead to brittleness.
Adhesive Dispensing:
- Apply the adhesive evenly and correctly to avoid excess or insufficient coverage. Dispensing equipment like syringes, guns, or automated dispensing systems may be used.
Substrate Compatibility:
- Ensure the UV-cure adhesive is compatible with the specific types of bonded plastics. Some adhesives may be better suited for certain plastics, and compatibility testing is recommended.
Fixture or Clamping:
- Using a fixture or clamping the parts together during curing can help ensure proper contact and alignment, leading to a stronger bond.
Safety Precautions:
- Wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), such as UV-blocking safety glasses, when working with UV-cure adhesives to protect your eyes from UV exposure.
Post-Curing:
- Some applications may benefit from post-curing to ensure complete polymerization and maximize the adhesive’s performance.
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific UV-cure adhesive you are using, as different adhesives may have unique requirements. Additionally, testing the adhesive and bonding process on a small scale before full-scale production is advisable to optimize the process and ensure the desired bond strength.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, UV-cure adhesives have revolutionized the way we bond plastics. Their rapid curing, strong adhesion, and versatility make them a preferred choice in various industries. As you navigate the world of UV cure adhesives for plastics, armed with the knowledge gained from this guide, you’ll be better equipped to choose the suitable adhesive for your specific needs. Whether you’re looking for efficiency in manufacturing or a reliable solution for your DIY projects, UV cure adhesives offer a promising alternative for plastic bonding applications.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing becomes

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment

Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions
Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions The dispensing process is an important part of the application of LED UV glue adhesive, and the quality of this process directly affects the final performance of the product. The physical properties of the glue,

Aging Mechanism and Modification Strategies of LED UV Glue under Long-term Ultraviolet Irradiation
Aging Mechanism and Modification Strategies of LED UV Glue under Long-term Ultraviolet Irradiation LED UV glue, with its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness, has been widely used in fields such as optical device packaging, electronic assembly, and medical devices. However, in scenarios where it is exposed to ultraviolet environments