- Home
- >
- Application
- >
- Camera Module Adhesive
Camera Module Adhesive
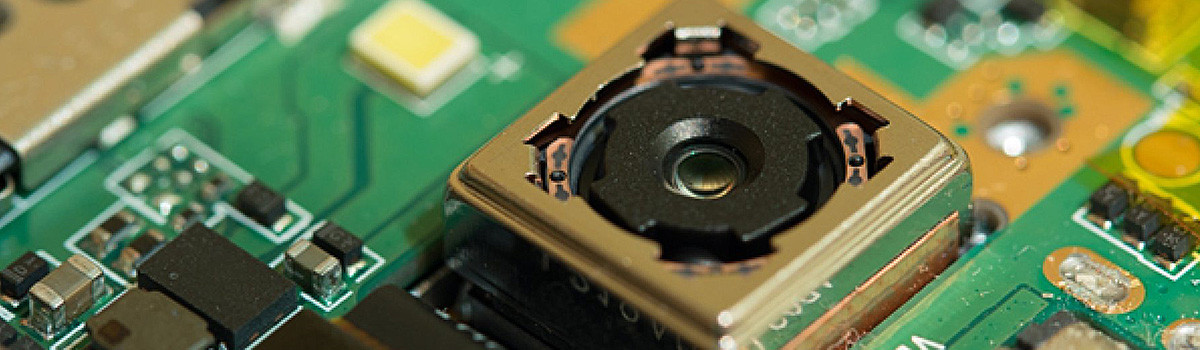
Camera modules have become integral components in devices ranging from smartphones to security cameras. The adhesive used in these modules is not just a bonding agent; it is pivotal in ensuring stability, precision, and durability. In this guide, we’ll explore the various facets of Camera Module Adhesive, shedding light on its applications, considerations, and innovations.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is the primary purpose of adhesive in camera modules?
In-camera modules and adhesives are crucial in securing and bonding various components. The primary purposes of adhesives in camera modules include:
- Component Bonding:Adhesives are used to bond different camera module components together. This includes attaching the lens, image sensor, and other optical elements to ensure they are correctly aligned and secured.
- Vibration Damping:Adhesives help dampen vibrations that may affect the camera’s performance. Vibrations can lead to image blurring or distortion, so adhesives are applied strategically to minimize these effects.
- Sealing and Waterproofing:Adhesives can create seals that protect the camera module from dust, moisture, and other environmental factors. This is particularly important to enhance the durability and reliability of the camera, especially in outdoor or challenging conditions.
- Alignment and Calibration:Adhesives aid in the precise alignment of optical components during the manufacturing process. Ensuring accurate alignment is essential for achieving optimal image quality in the final camera product.
- Structural Support:Adhesives can support delicate components, helping distribute stress evenly and preventing damage during handling or accidental impacts.
- Temperature Stability:Some adhesives are designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, contributing to the overall stability of the camera module under varying environmental conditions.
- Flexibility and Miniaturization:As cameras become smaller and more compact, adhesives offer a way to securely bond components without adding unnecessary weight or bulk. They allow for greater flexibility in the design and assembly of miniature camera modules.
Adhesives in camera modules serve multiple purposes, including securing components, dampening vibrations, providing environmental protection, ensuring precise alignment, offering structural support, and contributing to the overall reliability and performance of the camera system.
How does Camera Module Adhesive contribute to the structural integrity of imaging devices?
The Camera Module Adhesive plays a crucial role in the structural integrity and overall performance of imaging devices, such as smartphones, digital cameras, and other electronic devices with built-in cameras. Here are some ways in which the adhesive contributes to the structural integrity:
Secure Attachment:
- The camera module adhesive is used to securely attach the camera module to the device’s housing or chassis. This ensures that the camera is firmly in place and does not move or become misaligned during regular use or if the device is subjected to vibrations or shocks.
Vibration Damping:
- Electronic devices are often exposed to vibrations from everyday handling, transportation, or other external factors. The adhesive helps dampen vibrations and absorbs shocks, protecting the camera module and its delicate components from potential damage.
Temperature Stability:
- Camera modules can be sensitive to temperature variations. The adhesive must provide stability and prevent the camera components from shifting or getting damaged due to expansion or contraction caused by temperature changes.
Water and Dust Resistance:
- Some camera module adhesives contribute to the overall sealing of the device, helping to make it more resistant to water and dust ingress. This is especially important for devices that must meet IP (Ingress Protection) water and dust resistance ratings.
Alignment Precision:
- The adhesive helps precisely align the camera module within the device. This is crucial for achieving optimal focus and image quality. Any misalignment could result in blurry images or other performance issues.
Electromagnetic Shielding:
- In some cases, the adhesive may include materials that provide electromagnetic shielding. This helps protect the camera module from electromagnetic interference, ensuring the device’s proper functioning and preventing potential image quality degradation.
Durability and Longevity:
- The adhesive contributes to the device’s overall durability by securely holding the camera module in place. This is important for the device’s longevity, as it helps prevent issues arising from movement, shocks, or environmental factors.
The camera module adhesive is critical beyond simply holding the camera in place. It contributes to imaging devices’ structural integrity, durability, and performance, ensuring that the camera functions optimally and withstands the various challenges it may encounter during its lifespan.
Are there different types of adhesives used for various camera module designs?
Yes, there are different types of adhesives used for various camera module designs, and the choice of adhesive depends on several factors, including the specific requirements of the camera module, the materials involved, and the device’s intended application. Here are some common types of adhesives used in camera module assembly:
UV-Curable Adhesives:
- UV-curable adhesives are often used in camera module assembly due to their quick curing time when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. These adhesives are suitable for applications where rapid bonding is essential.
Epoxy Adhesives:
- Epoxy adhesives are known for their high strength and durability. They are commonly used in camera modules to provide a secure and long-lasting bond. Epoxy adhesives are versatile and can bond well to various materials.
Thermal Conductive Adhesives:
- In some camera modules, especially those with high-performance sensors or components, thermal conductive adhesives may be used. These adhesives help dissipate heat efficiently, preventing overheating of the camera module and maintaining optimal performance.
Double-Sided Adhesive Tapes:
- Double-sided adhesive tapes are convenient for attaching camera modules, particularly in thin, compact devices. They are easy to apply and can provide a strong bond. Some recordings may also have insulating or damping properties.
Pressure-Sensitive Adhesives (PSAs):
- PSAs are adhesive materials that bond when pressure is applied. They are commonly used in camera modules requiring a solid bond and offer easy application. PSAs can be particularly useful in applications where a flexible bond is needed.
Conductive Adhesives:
- Conductive adhesives may be used in camera modules that require electrical conductivity between components. These adhesives help maintain electrical connections while providing a bonding function.
Hot Melt Adhesives:
- Hot melt adhesives are solid at room temperature but become liquid when heated. They are applied in a molten state and solidify upon cooling. These adhesives are often used for quick bonding in high-volume production environments.
Silicone Adhesives:
- Silicone adhesives are known for their flexibility and resistance to environmental factors, including moisture and temperature extremes. They may be used in camera modules where flexibility and ecological resistance are crucial.
The choice of adhesive depends on the camera module’s specific requirements and the electronic device’s overall design. Factors such as bonding strength, curing time, thermal conductivity, flexibility, and environmental resistance are carefully considered in selecting the most suitable adhesive for a particular camera module application. Manufacturers often choose adhesives that meet the performance and durability standards required for the device’s intended use.
What role does adhesive play in enhancing the performance of camera modules?
Adhesives play a crucial role in enhancing the performance of camera modules in several ways. Here are some key aspects:
- Bonding Components:Adhesives are used to bond various camera module components together. This includes attaching lenses, image sensors, filters, and other optical elements to the housing or substrate. A strong and reliable bond ensures the components stay in place, maintaining the optical alignment critical for image quality.
- Vibration Damping:Cameras can be exposed to vibrations, especially in mobile devices or handheld cameras. Adhesives with vibration-damping properties help absorb and reduce vibrations, preventing them from affecting the stability and focus of the camera. This is essential for capturing sharp and clear images.
- Shock Absorption:Cameras may be subjected to shocks or impacts in addition to vibration. Adhesives with shock-absorbing properties help protect delicate components within the camera module, such as the image sensor, from damage caused by sudden impacts.
- Sealing and Waterproofing:Adhesives create seals that protect camera modules from environmental factors like dust, moisture, and water. This is particularly important for outdoor or rugged applications where cameras may be exposed to harsh conditions. Sealing also helps prevent the fogging of lenses in varying temperature conditions.
- Thermal Management:Cameras generate heat during operation, and efficient thermal management is crucial for preventing overheating, which can degrade image quality and affect the longevity of components. Adhesives with good thermal conductivity dissipate heat from the camera module, ensuring optimal performance.
- Size and Weight Considerations:Adhesives offer advantages in size and weight compared to traditional mechanical fasteners. In compact devices like smartphones, where space and weight are premium, adhesives allow for a more compact and lightweight design.
- Manufacturing Efficiency:Adhesives can contribute to the efficiency of the manufacturing process. They allow for automated assembly processes, reducing the time and cost of production. Adhesive bonding can also enable the integration of components in a way that might be challenging with traditional mechanical methods.
Adhesives play a multifaceted role in camera module design and manufacturing. They contribute to the structural integrity, durability, and overall performance of camera systems in various environmental conditions while facilitating efficient and cost-effective manufacturing processes.
How does the choice of adhesive impact the overall image quality produced by camera modules?
The choice of adhesive in camera modules can significantly impact the overall image quality. Here are several factors to consider:
- Optical Clarity:Camer module adhesives must have excellent optical clarity to avoid interference with light transmission through lenses and other optical components. Even a slight distortion or cloudiness introduced by the adhesive can degrade image quality by reducing sharpness and contrast.
- Index of Refraction:The refractive index of the adhesive should match that of the optical elements to minimize optical aberrations. Mismatched refractive indices can cause color fringing, distortion, and reduced overall image quality.
- Adhesive Thickness:The thickness of the adhesive layer between optical elements can affect the focal length and visual performance. Precise control over the adhesive thickness is crucial to maintain the intended graphic design and focus accuracy.
- Vignetting:Vignetting, which is the darkening of image corners, can occur if the adhesive obstructs the light path. Properly selected and applied adhesives ensure the image sensor receives uniform illumination without diluting loss at the edges.
- Durability and Stability:The long-term stability of the adhesive is essential to prevent any shifts or movements of optical components over time. If the adhesive degrades or changes properties, it can misalign lenses and negatively impact image quality.
- Temperature Resistance:Adhesives should withstand the temperature variations the camera module might experience during operation. Temperature changes can affect the viscosity and other properties of the adhesive, potentially leading to optical distortions.
- Anti-Reflection Coatings:Some adhesives have anti-reflection coatings or properties that reduce unwanted reflections within the visual system. Minimizing internal reflections enhances image contrast and clarity.
- Moisture Resistance:Moisture can impact the optical performance of a camera module. Adhesives with good moisture resistance help prevent fogging of lenses and degradation of visual elements, ensuring consistent image quality in various environmental conditions.
- Color Stability:Adhesives should be color-stable to avoid introducing color shifts in the optical path. Any changes in the adhesive’s color can affect the captured images’ overall color accuracy.
- Cleaning Compatibility:The adhesive should be resistant to damage from cleaning agents commonly used on camera lenses. Any degradation of the adhesive due to cleaning can impact image quality.
The choice of adhesive in camera modules is critical for maintaining optical performance. Engineers and manufacturers must carefully consider factors such as optical clarity, refractive index, thickness control, stability, temperature resistance, and other properties to ensure that the adhesive contributes positively to the overall image quality produced by the camera module.
Can Camera Module Adhesive withstand extreme environmental conditions, such as temperature variations?
The ability of a camera module adhesive to withstand extreme environmental conditions, including temperature variations, depends on the specific adhesive used and its intended application. Different adhesives have varying temperature resistance, and manufacturers often provide specifications regarding the temperature range their products can effectively perform.
For camera modules or electronic devices that may be exposed to extreme temperatures, it’s crucial to use adhesives specifically designed for such conditions. Some adhesives are formulated to have a wide operating range, making them suitable for applications where temperature variations are expected.
Commonly used adhesives for electronic components, including camera modules, are epoxy adhesives, silicone adhesives, and polyurethane adhesives. Each type has its properties, and some formulations within each class may have better temperature resistance than others.
When selecting an adhesive for camera modules or other electronic components, it’s essential to consider the following factors:
- Temperature Range:Ensure the adhesive’s range suits the anticipated environmental conditions. Adhesive specifications typically provide information on the minimum and maximum operating temperatures.
- Application Requirements:Consider the specific needs of the camera module and the intended use. Some applications may require adhesives with temperature resistance and other properties such as flexibility, electrical insulation, or moisture resistance.
- Testing and Validation:Before deployment in extreme conditions, it’s advisable to conduct testing and validation to ensure that the adhesive performs as expected. Manufacturers may provide guidelines for testing and usage in challenging environments.
Always refer to the product datasheet or technical specifications provided by the adhesive manufacturer for accurate information on its performance in different environmental conditions. If in doubt, consulting with the adhesive supplier or seeking guidance from an expert in materials and adhesives can help ensure the selection of an appropriate adhesive for the specific requirements of the camera module and its operating environment.
Are there eco-friendly options available for Camera Module Adhesive?
Yes, there are eco-friendly or environmentally friendly adhesive options available, and the choice of adhesive can contribute to overall efforts in sustainability. Here are some characteristics and types of adhesives that are often considered more eco-friendly:
- Water-Based Adhesives:These adhesives use water as a carrier instead of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) in many solvent-based adhesives. They tend to have lower environmental impact and emit fewer harmful substances.
- Bio-Based Adhesives:These adhesives are derived from renewable resources such as plants or other natural materials. They can be more sustainable than adhesives based on fossil fuels.
- Solvent-Free Adhesives:Adhesives that do not contain or have minimal amounts of harmful solvents are considered more eco-friendly. Solvent-free formulations reduce the release of volatile organic compounds into the environment.
- Recyclable Adhesives:Some adhesives are designed to be easily recyclable, which can contribute to reducing waste in the manufacturing process.
- Low-Impact Formulations:Adhesive manufacturers may develop formulations with a lower environmental impact regarding energy consumption, resource use, and emissions during production.
- Biodegradable Adhesives:Adhesives that break down naturally over time, either through biological or environmental processes, can be considered more environmentally friendly.
When seeking eco-friendly camera module adhesives, looking for products with certifications or labels indicating their environmental credentials is essential. These certifications may include:
- Green Seal:Indicates that a product meets environmental and performance standards.
- EcoLogo:A certification for products with reduced environmental impact.
- Cradle to Cradle:Assesses a product’s environmental impact throughout its lifecycle.
Additionally, consider engaging with adhesive suppliers or manufacturers to inquire about the environmental aspects of their products, as transparency in the supply chain can be valuable in making sustainable choices.
It’s important to note that the requirements for camera module adhesives may vary, so it’s advisable to balance eco-friendly considerations with the adhesive’s performance characteristics to meet the intended application and environmental goals.
How does the adhesive selection influence the manufacturing process of camera modules?
The selection of adhesives in the manufacturing process of camera modules can significantly impact the overall performance, reliability, and production efficiency. Camera modules are critical components in various devices, such as smartphones, digital cameras, and other imaging devices. Adhesive selection plays a crucial role in the assembly and performance of these modules. Here are some ways in which adhesive selection influences the manufacturing process of camera modules:
Bonding Strength:
- Adhesives bond different camera module components, such as lenses, sensors, filters, and housing. The bonding strength of the adhesive is crucial to ensure the structural integrity of the camera module. A solid and durable bond is essential for maintaining the alignment and functionality of the optical components.
Optical Clarity:
- Camer module adhesives should have excellent optical clarity to minimize light distortion or scattering. This is particularly important for maintaining the image quality and sharpness of the captured photos. Adhesives with low haze and high light transmission are preferred.
Temperature Resistance:
- Camera modules can be exposed to a wide range of temperatures during operation. Adhesives must have the appropriate temperature resistance to ensure stability and reliability under various environmental conditions. This is particularly important for cameras used in automotive, industrial, or outdoor applications.
Vibration and Shock Resistance:
- Cameras in mobile devices or those used in vehicles may be subjected to vibrations and shocks. Adhesives should provide sound vibration and shock resistance to prevent dislocation or misalignment of critical components. This is crucial for maintaining the accuracy of focus and image stabilization features.
Manufacturing Process Compatibility:
- The adhesive should be compatible with the manufacturing processes involved in camera module assembly. This includes considerations for dispensing methods, curing time, and curing conditions. Adhesives that can be applied efficiently in a high-volume production environment are preferred.
Adhesive Dispensing Precision:
- Some camera modules require the exact placement of adhesive to ensure the accurate alignment of components. The viscosity and dispensing properties of the adhesive must be suitable for the specific application requirements to achieve the desired precision in bonding.
Environmental Considerations:
- Adhesives should comply with environmental regulations and standards. This includes considerations for volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and other potentially harmful substances. Choosing environmentally friendly adhesives aligns with sustainable manufacturing practices.
Cost Considerations:
- The cost of adhesives can impact the overall production cost of camera modules. Manufacturers often seek adhesives that balance performance requirements with cost considerations to maintain competitiveness in the market.
Adhesive selection in the manufacturing process of camera modules is a critical decision affecting the final product’s performance, durability, and production efficiency. Manufacturers must consider various factors to ensure that the selected adhesives meet the specific requirements of camera module applications.
What are the common challenges associated with Camera Module Adhesive, and how can they be addressed?
Camera module adhesive is crucial in securing the camera module to the device, ensuring stability, and maintaining image quality. However, several challenges are associated with camera module adhesive, and addressing them is essential for optimal performance. Here are some common challenges and potential solutions:
Image Quality Degradation:
- Challenge:Adhesive material can affect the clarity and quality of images captured by the camera module.
- Solution:Choose optically clear adhesives that do not interfere with the light path. Conduct thorough testing to ensure the adhesive does not cause distortions or reduce image quality.
Durability and Reliability:
- Challenge:Adhesive must withstand environmental factors like temperature variations, humidity, and mechanical stress.
- Solution:Select adhesives with high durability and resistance to environmental factors. Conduct reliability testing under various conditions to ensure long-term performance.
Alignment Issues:
- Challenge:Incorrect alignment during the attachment of the camera module can lead to misalignment issues.
- Solution:Implement precise manufacturing processes and automated alignment systems to ensure accurate camera module placement. Regularly calibrate equipment to maintain accuracy.
Temperature Sensitivity:
- Challenge:Temperature variations can affect adhesive properties, leading to performance issues.
- Solution:Choose adhesives with a wide temperature tolerance range. Conduct thermal testing to ensure the adhesive maintains its properties across the expected operating temperatures.
Adhesive Curing Time:
- Challenge:Some adhesives may have a long curing time, affecting the manufacturing process efficiency.
- Solution:Opt for adhesives with a quick curing time to improve production efficiency. Ensure that the curing process does not compromise the quality of the bond.
Adhesive Residue:
- Challenge:Residue from the adhesive can accumulate on the camera module or surrounding components.
- Solution:Select adhesives with low or no residue. Implement thorough cleaning processes during manufacturing to remove any residue that may be present.
Cost Considerations:
- Challenge:Balancing performance with cost-effectiveness is crucial in the manufacturing process.
- Solution:Evaluate different adhesive options based on performance, durability, and cost. Conduct a cost-benefit analysis to find the most suitable adhesive that meets the required specifications.
Compatibility with Different Materials:
- Challenge:Camera modules may be attached to various materials, and the adhesive should adhere well.
- Solution:Test the adhesive with different materials commonly used in device manufacturing to ensure compatibility. Choose adhesives with broad substrate compatibility.
Regular testing and quality control throughout manufacturing are essential to address these challenges effectively. Collaborating with adhesive suppliers and staying informed about advancements in adhesive technology can also contribute to overcoming these challenges.
Are there recent technological advancements in Camera Module Adhesive?
Specific details about the most recent technological advancements in camera module adhesive may not be available. However, It can provide you with general trends and potential areas of improvement that could have been developed or enhanced in recent times:
Improved Optical Properties:
- Adhesives that offer better transparency and minimal light absorption to ensure they do not impact the optical performance of the camera module.
Enhanced Durability and Reliability:
- Development of adhesives with increased resistance to environmental factors such as temperature extremes, humidity, and mechanical stress for improved long-term reliability.
Faster Curing Times:
- Adhesives are designed to cure more rapidly, reducing manufacturing cycle times and improving overall production efficiency.
Thermal Management:
- Adhesives that provide better thermal conductivity or insulation depend on the requirements of the camera module and the device it is integrated into.
Low Outgassing:
- Adhesives with reduced outgassing properties are crucial for applications in sealed environments to prevent fogging or contamination of optical surfaces.
Flexibility and Compatibility:
- Adhesives that are compatible with a broader range of materials commonly used in device manufacturing and that offer flexibility to accommodate design variations.
Reduced Residue and Cleaner Processing:
- Adhesives are designed to minimize residue after application, streamlining the manufacturing process and reducing the need for extensive cleaning steps.
Custom Formulations for Specific Applications:
- Tailored adhesive formulations are designed for specific camera module applications, considering factors such as module size, weight, and integration requirements.
Adhesives for Advanced Imaging Technologies:
- Development of adhesives suitable for emerging camera technologies, such as depth-sensing cameras, multiple lens configurations, or advanced image stabilization systems.
To obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information on recent advancements, it’s recommended to check with adhesive manufacturers, industry publications, and research articles. Additionally, staying informed about developments in materials science and adhesive technologies can provide insights into the latest trends in this field.
How does adhesive impact the lifespan and reliability of camera modules?
The choice of adhesive can significantly impact the lifespan and reliability of camera modules in electronic devices. Here are several ways in which adhesive plays a crucial role:
Structural Integrity:
- The adhesive is responsible for bonding the camera module to the device structure. A solid and durable bond is essential for maintaining the structural integrity of the camera module throughout the device’s lifespan. Proper bonding ensures the camera remains securely in place, preventing misalignment, tilt, or detachment.

Environmental Protection:
- Adhesives contribute to the sealing of the camera module, protecting it from environmental factors such as moisture, dust, and other contaminants. A well-sealed camera module helps enhance its resistance to adverse conditions, contributing to a longer lifespan and improved reliability.
Vibration and Shock Resistance:
- Devices, especially mobile ones, are subject to vibrations and shocks during daily use. Adhesive with good shock-absorbing properties can help protect the camera module from mechanical stresses, reducing the risk of internal damage and improving overall reliability.
Temperature Stability:
- Adhesive materials must maintain their properties across a range of temperatures. Temperature variations can affect the adhesive’s performance and the camera module’s stability. High-quality adhesives with good temperature stability contribute to the reliability of the camera module in different operating conditions.
Optical Performance:
- Adhesives can impact the visual clarity of the camera module. Optically clear adhesives are essential to ensure that the adhesive layer does not interfere with the light path, maintaining the image quality over time. Any degradation in optical properties can negatively affect the camera’s performance and lifespan.
Resistance to Aging and Degradation:
- Over time, exposure to environmental factors, such as UV radiation and chemicals, can lead to aging and degradation of adhesive materials. Choosing adhesives with resistance to such factors helps maintain the adhesive’s performance and, consequently, the reliability of the camera module over an extended period.
Flexibility and Material Compatibility:
- Adhesives must be flexible to accommodate any movements or expansions within the device. Additionally, compatibility with various materials used in the camera module and device construction is crucial to prevent issues like delamination or material degradation, which can impact reliability.
Adhesive Residue and Cleanliness:
- The residue left by adhesives during manufacturing can have long-term effects on the camera module. Adhesives with low residue are preferable to avoid interference with optical surfaces and to maintain cleanliness over time.
The adhesive used in camera modules is a critical component that influences structural stability, environmental protection, resistance to mechanical stresses, and optical performance. Choosing a suitable adhesive can contribute significantly to the overall lifespan and reliability of camera modules in electronic devices. Manufacturers often conduct rigorous testing to ensure that the selected adhesive meets the required performance standards and contributes to the longevity of the camera module.
Are there industry standards governing the composition and application of Camera Module Adhesive?
Specific industry standards universally governing the composition and application of camera module adhesives are needed. However, it’s important to note that industry standards can evolve, and new standards may be introduced over time.
The field of adhesives and sealants is broad, and specific applications, such as camera module adhesives, may have requirements outlined by the manufacturers or industries that produce and use them. These requirements could be related to adhesion strength, temperature resistance, durability, and other performance criteria.
To obtain the most accurate and up-to-date information, you should check with relevant industry organizations, standards bodies, or specific manufacturers that produce camera module adhesives. Industry-specific associations or standards organizations related to electronics, optics, or adhesives might have developed guidelines or standards since my last update.
Remember that industries often adhere to general adhesive standards (such as those provided by ASTM International or ISO), and manufacturers may give detailed specifications for their specific products.
What considerations should be made when choosing Camera Module Adhesive for mobile devices?
Choosing the suitable camera module adhesive for mobile devices involves considering various factors to ensure proper functionality and durability. Here are some key considerations:
Compatibility with Materials:
- Ensure that the adhesive is compatible with the materials used in the camera module, such as glass, metal, and plastic. Compatibility is crucial to prevent damage to components and ensure a secure bond.
Temperature Resistance:
- Mobile devices can be exposed to a wide range of temperatures. Select an adhesive with good temperature resistance to maintain its integrity in various environments. This is particularly important to prevent the camera module from detaching due to temperature fluctuations.
UV Resistance:
- UV-resistant adhesives are essential to prevent degradation and yellowing over time, especially for components exposed to sunlight. This helps maintain the clarity of camera modules and prevents a decrease in image quality.
Flexibility and Damping Properties:
- Mobile devices may experience mechanical stress, shocks, and vibrations. Choose an adhesive with appropriate flexibility and damping properties to absorb shocks and vibrations, reducing the risk of damage to the camera module.
Adhesive Strength:
- Ensure the adhesive provides a strong bond to keep the camera module in place. However, it should also allow for easy removal or repositioning during manufacturing or repair processes without causing damage to the components.
Ease of Application:
- Consider the ease of application during the manufacturing process. Adhesives that are easy to handle, dispense, and cure can contribute to increased efficiency in the assembly line.
Thickness and Gap Filling:
- Choose an adhesive with the appropriate thickness and gap-filling properties to accommodate variations in the surface of the components. This helps create a uniform bond and compensates for irregularities in the assembly.
Chemical Compatibility:
- Ensure the adhesive is chemically compatible with other materials used in the device. This is crucial to prevent any adverse reactions that could lead to the deterioration of the adhesive or surrounding components.
Curing Time:
- Consider the curing time of the adhesive. Quick-curing adhesives speed up the manufacturing process, while slower-curing adhesives may be suitable for applications that require repositioning or alignment adjustments.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Verify that the chosen adhesive complies with relevant industry standards and regulations, such as RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), to ensure the safety and environmental sustainability of the mobile device.
By carefully considering these factors, you can choose a camera module adhesive that meets the specific requirements of your mobile device, ensuring reliability and longevity.
How does adhesive contribute to the miniaturization of camera modules?
Adhesives are crucial in miniaturizing camera modules in mobile devices and other electronic gadgets. Here are several ways in which adhesives contribute to this process:
Reduced Mechanical Fasteners:
- Adhesives eliminate the need for traditional mechanical fasteners, such as screws and brackets, which take up space and add weight. This reduction in the number of components contributes to the overall miniaturization of the camera module.
Improved Bonding Precision:
- Adhesives provide a more precise and uniform bonding than mechanical fasteners. This allows the assembling of smaller, more tightly packed components in the camera module without sacrificing structural integrity.
Flexibility in Design:
- Adhesives offer greater design flexibility, enabling the creation of compact and intricate camera module layouts. This flexibility allows engineers to optimize available space, resulting in smaller, slimmer modules.
Gap Filling and Sealing:
- Adhesives with gap-filling properties are effective in sealing gaps and bonding irregular surfaces. This is particularly important in small camera modules where components may not have perfectly flat surfaces, and precise bonding is required to maintain a compact design.
Vibration Damping:
- Miniaturized camera modules are more susceptible to vibrations and mechanical stresses. Adhesives with damping properties can absorb vibrations, reducing the risk of damage to sensitive camera components and improving overall stability.
Lightweight Materials:
- Adhesives allow for the use of lightweight materials in camera module construction. This is important for miniaturization, as lighter materials contribute to reduced overall device weight and size.
Integration of Multiple Functions:
- Adhesives can be engineered to serve multiple functions, such as bonding, thermal management, and even electromagnetic shielding. Integrating tasks within a single adhesive layer can streamline the overall design and reduce the need for additional components.
Enhanced Thermal Management:
- Miniaturized camera modules generate heat; effective thermal management is crucial for their performance. Adhesives with thermal conductivity properties can help dissipate heat efficiently, allowing for the design of smaller modules without compromising performance.
Ease of Assembly:
- Adhesives simplify the assembly process compared to more complex mechanical fastening methods. This ease of assembly can contribute to faster production and increased efficiency in manufacturing miniaturized camera modules.
Customization and Adaptability:
- Adhesives can be tailored to specific requirements, allowing for customization and adaptability in camera module designs. This flexibility is essential in addressing the unique challenges of miniaturization in different electronic devices.
Adhesives contribute significantly to the miniaturization of camera modules by offering improved bonding precision, design flexibility, and the ability to integrate multiple functions within a compact space. These advantages enable the creation of smaller, lighter, and more efficient camera modules in modern electronic devices.
Is there compatibility testing between Camera Module Adhesive and different camera sensor types?
Yes, compatibility testing between camera module adhesives and different camera sensor types is essential to the manufacturing process. Camera sensors can vary in size, material, and sensitivity, and the adhesive used in the assembly must be compatible with the specific characteristics of the sensor. Here are some considerations in compatibility testing:
- Optical Clarity:Camera module adhesives must not introduce visual distortions or affect the clarity of the images captured by the camera sensor. Compatibility testing ensures the adhesive does not interfere with light transmission through the lenses and other optical elements.
- Material Compatibility:Camera sensors may have different materials, coatings, or filters. Compatibility testing helps determine whether the adhesive interacts negatively with these materials, ensuring that it does not degrade the performance or longevity of the camera sensor.
- Adhesive Properties:Different camera sensors may have varying requirements regarding temperature stability, vibration resistance, and other factors. Compatibility testing assesses whether the adhesive meets the specific performance criteria of the camera sensor and the overall camera module.
- Impact on Focus Accuracy:The adhesive should not affect the focus accuracy of the camera module. Testing includes evaluating the effects of the adhesive on the alignment of optical components and the overall focus performance of the camera system.
- Thermal Compatibility:Camera sensors can generate heat during operation, and the adhesive must be compatible with the thermal characteristics of the sensor. Compatibility testing involves assessing the adhesive’s performance under different temperature conditions to ensure stability and reliability.
- Environmental Resistance:Camer module adhesives should resist ecological factors such as moisture, humidity, and temperature variations. Compatibility testing verifies that the adhesive provides adequate protection to the camera sensor in real-world conditions.
- Adhesion Strength:The adhesive must bond strongly with the camera sensor and other optical components. Compatibility testing assesses the adhesion strength under various conditions to ensure that the adhesive maintains the structural integrity of the camera module.
Manufacturers typically conduct extensive testing to validate the compatibility of adhesives with different camera sensor types and overall camera module requirements. This testing helps ensure that the adhesive chosen for the assembly process meets the performance and reliability standards necessary for high-quality imaging in electronic devices like smartphones and digital cameras.
What role does adhesive play in camera module optical alignment and focus accuracy?
In the context of camera module assembly, adhesives play a crucial role in optical alignment and focus accuracy. Camera modules in electronic devices such as smartphones and digital cameras consist of multiple components, including lenses, image sensors, and other optical elements. The precise alignment of these components is essential for achieving optimal image quality and focus performance.
Here are some key ways in which adhesives contribute to optical alignment and focus accuracy in camera modules:
- Bonding Components:Adhesives are used to bond different optical components together. This bonding ensures the components are fixed correctly, maintaining the desired optical alignment. The adhesive provides stability and prevents any movement that could lead to misalignment.
- Optical Axis Alignment:The optical axis alignment is critical for proper focus and image quality. Adhesives are applied to secure lenses and other elements in a specific arrangement, ensuring that the optical axis of each component is aligned precisely with the others. This alignment is crucial for achieving sharp and clear images.
- Vibration Damping:Adhesives can help dampen vibrations and reduce mechanical stress on the optical components. Vibrations can affect focus accuracy and image stability. By using adhesives with vibration-damping properties, manufacturers can enhance the performance of the camera module under varying conditions.
- Temperature Stability:Adhesives with thermal stability properties are essential for camera modules, as temperature changes can impact the performance of optical elements. A stable adhesive helps maintain the alignment of components across a range of temperatures, ensuring consistent focus accuracy in different environmental conditions.
- Sealing and Protection:Adhesives are often used to seal the camera module, protecting the sensitive optical components from dust, moisture, and other environmental factors. This sealing is essential for maintaining the long-term reliability and performance of the camera module.
- Thin Profile:Some camera modules require a compact and light design, especially in slim devices like smartphones. Adhesives that provide strong bonding with minimal thickness contribute to achieving a thin and lightweight camera module without compromising optical alignment and focus accuracy.
Adhesives play a multifaceted role in camera module assembly by providing structural support, optical alignment, vibration damping, temperature stability, and environmental protection. The careful selection and application of adhesives are crucial for ensuring the overall performance and reliability of the camera module in capturing high-quality images.
Can Camera Module Adhesive be reworked or removed without causing damage?
The reworkability or removal of the camera module adhesive without causing damage depends on the specific type of adhesive used and the design of the camera module. Certain adhesives are generally designed to be reworkable, while others may be more challenging to remove without causing damage to the components.
Here are some considerations regarding the reworkability of camera module adhesive:
Temporary Adhesives: Some camera modules may use temporary adhesives that allow easier removal and rework during manufacturing or repair. These adhesives are designed to provide sufficient bonding strength during regular operation but can be peeled off or dissolved when needed.
Thermal Release Adhesives: Certain adhesives are formulated to be thermally releasable, meaning they can be softened or liquefied with heat application. This characteristic facilitates the disassembly of components without causing damage. Heat can be applied carefully to loosen the adhesive, making it easier to separate the parts.
Low-Tack Adhesives: Adhesives with low tack or low bond strength may be easier to remove without causing damage. However, it’s essential to strike a balance between ease of removal and providing sufficient adhesion for the stability and performance of the camera module.
Adhesive Dissolvers: In some cases, specialized solvents or dissolvers can break down the adhesive and facilitate its removal. However, using solvents requires caution, as it may impact other components or materials in the camera module.
It’s important to note that not all camera module adhesives are designed for reworkability. Some adhesives are chosen for their robust and permanent bonding properties to ensure the stability and durability of the camera module during its operational life.
If reworkability is a critical requirement, manufacturers may choose adhesives specifically formulated for easy removal or develop assembly processes that allow for the disassembly of components without damage. However, the choice of adhesive is often a trade-off between bond strength, reliability, and reworkability based on the intended application and design specifications.
In any case, if there is a need to rework or remove the camera module adhesive, it’s recommended to follow manufacturer guidelines and best practices to minimize the risk of damage to sensitive components and ensure the continued functionality of the camera module.
How does adhesive selection influence the overall cost of manufacturing camera modules?
The selection of adhesives in manufacturing camera modules can significantly impact the overall cost in various ways. Here are some factors to consider:
Material Cost:
- Different adhesives come with varying costs of material. Some specialized adhesives designed for electronic components or optical applications may be more expensive than generic adhesives.
- The quantity of adhesive required for each camera module also affects material costs.
Process Efficiency:
- The ease of application and curing time of the adhesive can affect the overall efficiency of the manufacturing process. Faster curing adhesives may allow quicker production cycles, reducing labor costs and increasing throughput.
Labor Costs:
- The application of adhesive can be a manual or automated process. Labor costs will depend on the complexity of the application process. Automated processes may require a higher upfront investment but can save long-term costs.
Quality and Reliability:
- The quality of the adhesive is crucial for the long-term reliability of the camera module. Choosing an adhesive with excellent bonding properties and resistance to environmental factors (such as temperature and humidity) can reduce the likelihood of defects and returns, ultimately lowering overall costs associated with rework or warranty claims.
Assembly Time:
- The time it takes for the adhesive to cure and set can impact the assembly time. Faster curing adhesives may allow quicker assembly processes, contributing to higher productivity and lower labor costs.
Testing and Inspection:
- The choice of adhesive may impact the complexity and frequency of testing and inspection processes. Adhesives known for consistent performance may reduce the need for extensive quality control measures, saving time and resources.
Environmental Considerations:
- Some adhesives may require special environmental conditions for curing. If additional equipment or facilities are needed to provide the right curing conditions, it can add to the overall manufacturing cost.
Regulatory Compliance:
- Adhesives must comply with industry and environmental regulations. Ensuring compliance may involve additional testing and documentation, affecting overall costs.
Supplier Relationships:
- Establishing solid relationships with adhesive suppliers can lead to bulk-purchasing discounts or other cost-saving agreements.
Product Design and Innovation:
- The adhesive selected can impact the overall design of the camera module. Innovative adhesives that allow for more compact designs or improved performance may contribute to the overall competitiveness of the product.
The choice of adhesive in manufacturing camera modules can have a cascading effect on various aspects of the production process, from material costs to labor efficiency and product quality. Manufacturers need to carefully consider these factors to optimize costs while ensuring the reliability and performance of their camera modules.
Are there any emerging trends or research areas related to Camera Module Adhesive?
However, remember that the field is dynamic, and there might be new developments since then. Here are some emerging trends and research areas as of my last update:
Miniaturization and Flexibility:
- There is a continued emphasis on miniaturization of camera modules for mobile devices and other applications. Adhesives for compact designs and flexibility in camera module integration have been a focus.
Advanced Optical Adhesives:
- Research has been conducted on adhesives with optical properties that enhance image quality. These adhesives may minimize light distortion, reduce reflections, and improve visual performance.
Thermal Management:
- Given the heat generated by electronic components in camera modules, there is a focus on adhesives with improved thermal management properties. Adhesives that help dissipate heat efficiently contribute to the longevity and reliability of camera modules.
Environmental Sustainability:
- The industry has shown an increasing interest in environmentally friendly adhesives. Researchers are exploring bio-based and recyclable adhesive materials to reduce the environmental impact of camera module production.
Smart Adhesives:
- Some research is directed towards developing “smart” adhesives that can offer additional functionalities, such as self-healing properties or the ability to change optical properties dynamically.
Adhesives for Advanced Imaging Technologies:
- With the rise of advanced imaging technologies such as 3D sensing and computational photography, there’s a need for adhesives that can support the integration of complex camera modules with multiple sensors and lenses.
High-Performance Adhesives for Harsh Environments:
- Applications like automotive and industrial settings require camera modules that withstand harsh environmental conditions. Research is focused on developing adhesives with high resistance to temperature variations, moisture, and other challenging factors.
Conductive Adhesives for Integration of Electronics:
- As camera modules become more integrated with electronics, there is a growing interest in conductive adhesives. These adhesives can provide mechanical bonding and electrical conductivity, facilitating the integration of sensors and other electronic components.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- The demand for AR and VR applications drives research into adhesives that can support the integration of complex camera setups required for immersive experiences.
Machine Learning for Adhesive Selection:
- Some research involves using machine learning algorithms to optimize adhesive selection based on specific performance requirements, considering factors such as camera module specifications, environmental conditions, and end-use applications.
To stay updated on the latest trends and research in camera module adhesives, it’s advisable to check recent publications, industry conferences, and news sources for any advancements in the field since my last update in early 2022.
What are the prospects for innovations in Camera Module Adhesive technology?
The prospects for innovations in Camera Module Adhesive (CMA) technology are promising, driven by the continuous evolution of camera technologies and the demand for more compact, high-performance, and versatile imaging solutions. Some key areas where innovations are expected in CMA technology include:
Miniaturization and Integration:
- Innovations will likely focus on developing adhesives that enable even smaller, more integrated camera modules. This is crucial for applications such as smartphones, wearables, and IoT devices where space is at a premium.
Flexible and Bendable Adhesives:
- As flexible and foldable displays become more prevalent, adhesives need to maintain strong bonds even in flexible and bendable camera module configurations. This is especially relevant for applications in foldable smartphones and other flexible devices.
Advanced Optical Adhesives:
- Innovations in optical adhesives will aim to improve image quality by minimizing distortions, reducing reflections, and enhancing light transmission. This is critical for achieving high-quality imaging in various lighting conditions.
Multi-Lens and 3D Sensing Integration:
- As camera modules incorporate multiple lenses and sensors for features like depth sensing and computational photography, adhesive innovations will focus on ensuring precise alignment, optical clarity, and robust bonding for complex camera setups.
Thermal Management Solutions:
- With the increasing performance demands on camera modules, especially in high-resolution and video-intensive applications, adhesive innovations will address thermal management challenges. Adhesives with improved heat dissipation properties will be crucial for maintaining optimal performance and reliability.
Environmental Sustainability:
- The industry will likely see innovations in environmentally friendly adhesives, focusing on bio-based materials and recyclability. This aligns with the broader trend toward sustainable and eco-friendly manufacturing practices.
Innovative Adhesives and Self-Healing Materials:
- Innovations may lead to developing “smart” adhesives that offer additional functionalities, such as self-healing properties. These adhesives could repair minor damage over time, enhancing the durability and lifespan of camera modules.
Conductive Adhesives for Electronics Integration:
- Innovations in conductive adhesives are anticipated with the increasing electronics integration in camera modules. These adhesives can provide mechanical bonding and electrical connectivity, supporting the seamless integration of sensors and electronic components.
Enhanced Durability for Harsh Environments:
- Innovations will likely focus on developing adhesives with enhanced durability to withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them suitable for automotive, industrial, and outdoor applications.
Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR):
- As AR and VR technologies advance, adhesive innovations will cater to the specific requirements of camera modules used in these applications. This includes addressing challenges related to multiple sensors, fast refresh rates, and precise alignment.
Machine Learning-Assisted Adhesive Selection:
- Innovations may involve the integration of machine learning algorithms to optimize adhesive selection based on specific performance requirements. This could streamline the design and manufacturing processes by predicting the most suitable adhesives for different camera module specifications and use cases.
These prospects indicate a dynamic landscape for innovations in Camera Module Adhesive technology, driven by the ongoing evolution of imaging technologies and the diverse applications of camera modules in various industries. Researchers and industry professionals are likely to explore novel materials, manufacturing processes, and functionalities to meet the evolving demands of the market.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, our journey through Camera Module Adhesive has unraveled its significance in the intricate world of imaging devices. As technology advances, so does the demand for adhesive solutions that ensure strong bonds and optimal performance. We aim to equip you with a comprehensive understanding of Camera Module Adhesive by addressing the diverse questions in this guide. Whether you’re a professional in the field or an enthusiast exploring the nuances of camera technology, this guide serves as your gateway to the pivotal role played by adhesive in achieving crystal-clear imagery.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy
The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy This article systematically expounds the quantitative relationship between the crosslinking density and the flexibility and hardness of adhesives. Combining the theories of polymer physics with experimental analysis methods, it reveals the mechanism of the action of the

Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives
Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives UV adhesives have been widely used in many fields such as electronics, optics, and medicine due to their advantages of rapid curing, high bonding strength, and environmental protection. However, their rapid curing property also brings challenges in some application scenarios.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment

Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions
Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions The dispensing process is an important part of the application of LED UV glue adhesive, and the quality of this process directly affects the final performance of the product. The physical properties of the glue,