- Home
- >
- Application
- >
- PCB Circuit Board Adhesive
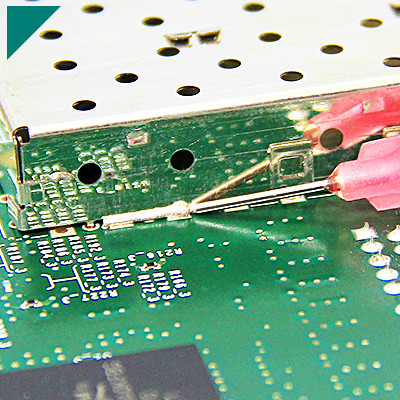
PCB Circuit Board Adhesive

In the intricate world of electronics, PCB Circuit Board Adhesive stands as a silent hero, ensuring the seamless operation and longevity of electronic devices. This comprehensive guide aims to illuminate the significance of PCB adhesive, exploring its mechanisms, types, and applications. As we delve into the complexities of adhesive technology, we will unravel its critical role in enhancing thermal performance, ensuring reliability, and contributing to the miniaturization of electronic components. From environmental considerations to high-frequency applications, safety precautions, and future trends, this guide thoroughly explores PCB adhesive, shedding light on its multifaceted contributions to the ever-evolving landscape of electronic engineering.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is PCB Circuit Board Adhesive?
PCB Circuit Board Adhesive is a specialized material designed to bond components and layers of a PCB together. This adhesive serves as the backbone, ensuring the structural integrity and reliability of the entire circuit board. It is applied during manufacturing, creating a strong bond between different layers and components, thus forming a durable and stable electronic assembly.
Key Characteristics of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive:
- Heat Resistance:PCBs often encounter temperature variations during operation. The adhesive is formulated to withstand these temperature changes, ensuring the components stay securely bonded even in challenging thermal conditions.
- Electrical Insulation:The adhesive binds the components and provides electrical insulation, preventing unwanted electrical connections between different elements on the circuit board.
- Chemical Resistance:Electronic devices may be exposed to various chemicals, such as cleaning agents or environmental pollutants. PCB Circuit Board Adhesive is engineered to resist chemical degradation, safeguarding the board’s integrity over time.
Significance in Electronic Devices:
- Enhanced Mechanical Strength:PCB Circuit Board Adhesive reinforces the mechanical strength of the entire assembly, preventing delamination and ensuring the board can withstand mechanical stresses.
- Improved Signal Integrity:The adhesive plays a crucial role in maintaining signal integrity by preventing interference or disruptions caused by movement or environmental factors. This characteristic is essential for ensuring the proper functioning of electronic devices.
- Extended Lifespan:The use of high-quality PCB Circuit Board Adhesive contributes to the longevity of electronic devices. The adhesive’s stability and resistance to external factors contribute to the device’s overall reliability.
How Does PCB Adhesive Work?
As electronic devices become increasingly sophisticated, the role of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) Adhesive becomes more pronounced. This exploration seeks to unravel the intricate mechanisms behind how PCB Adhesive works on circuit boards. From providing structural integrity to ensuring optimal electrical performance, the functionality of PCB Adhesive is essential for the seamless operation of electronic devices.
Working Mechanisms of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive:
Bonding Electronic Components:
PCB Adhesive creates a strong bond between electronic components and the circuit board. It securely adheres components such as resistors, capacitors, and integrated circuits, preventing movement or detachment during operation.
Insulating Electrical Connections:
One of the key functions of PCB Adhesive is to provide electrical insulation between different components on the circuit board. It forms a protective layer that prevents unintended electrical connections, ensuring that the circuit functions as intended without interference.
Heat Dissipation:
PCBs generate heat during operation, and the adhesive plays a crucial role in heat dissipation. By conducting heat away from sensitive electronic components, the adhesive helps maintain a stable operating temperature, preventing overheating and potential damage.
Vibration Damping:
Electronic devices, especially those in motion or subjected to external forces, may experience vibrations. PCB Adhesive dampens these vibrations, reducing the risk of mechanical stress on components. The effectiveness of this damping mechanism is significant in applications like automotive electronics.
Protection Against Environmental Factors:
PCB Adhesive is a barrier against environmental elements such as moisture, dust, and contaminants. This protective layer shields the delicate electronic components from external factors that could compromise their functionality.
Applications of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive:
Consumer Electronics:
In smartphones, laptops, and other consumer electronics, PCB Adhesive ensures the stability and reliability of intricate electronic circuits in compact designs.
Medical Devices:
Medical equipment relies on precise electronic components, and PCB Adhesive is crucial for maintaining the integrity of these components in various medical devices.
Aerospace and Defense Systems:
In aerospace and defense applications, where reliability and durability are paramount, PCB Adhesive contributes to the stability and functionality of electronic systems.
Considerations for Effective PCB Adhesive Application:
Precision Application:
PCB Adhesive must be applied with precision to ensure uniform coverage and adequate bonding between components.
Material Compatibility:
Compatibility with the materials used in the PCB is essential to prevent adverse reactions that could compromise the adhesive’s effectiveness.
Thermal Performance:
Adhesive formulations must exhibit thermal resistance to withstand the temperature variations experienced during electronic device operation.
Understanding the working mechanisms of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive is crucial for engineers and manufacturers in designing and producing electronic devices with optimal performance and reliability. The careful application of this adhesive ensures that electronic components function seamlessly within the complex architecture of modern circuit boards.
What Are the Different Types of PCB Adhesives?
Exploring the various types of PCB Circuit Board Adhesives provides valuable insights into the nuanced world of electronic manufacturing. Each formulation serves a unique purpose, addressing specific challenges and contributing to electronic devices’ overall reliability and functionality.
Different Types of PCB Adhesives:
Epoxy Resin Adhesives:
- Properties:Epoxy resin adhesives are renowned for their exceptional strength, durability, and chemical resistance. They are well-suited for applications requiring robust bonding and protection against environmental factors.
- Applications:PCB Circuit Board Adhesives are commonly used in consumer electronics, automotive electronics, and industrial applications due to their versatility and reliability.
Acrylic Adhesives:
- Properties:Acrylic adhesives offer good electrical insulation and thermal resistance. They are known for their quick curing times and flexibility, making them suitable for various electronic applications.
- Applications:PCB Circuit Board Adhesives are widely used in applications where rapid bonding and flexibility are crucial, such as LED displays and specific medical devices.
Polyurethane Adhesives:
- Properties:Polyurethane adhesives provide excellent flexibility and moisture resistance. They are known for their ability to withstand temperature variations and offer good electrical insulation.
- Applications:Commonly used in automotive electronics, flexibility and resistance to environmental factors are essential.
Silicone Adhesives:
- Properties:Silicone adhesives exhibit excellent thermal stability and resistance to extreme temperatures. They are also known for their flexibility and low toxicity.
- Applications:PCB Circuit Board Adhesives are found in applications requiring high-temperature resistance, such as aerospace electronics and specific industrial settings.
Cyanoacrylate Adhesives (Instant Adhesives):
- Properties:Cyanoacrylate adhesives are known for their quick curing times and strong bonding capabilities. They are often used for precise and rapid bonding.
- Applications:PCB Circuit Board Adhesives are commonly employed in applications where fast curing and strong bonding are crucial, such as assembling electronic components.
Considerations for Choosing PCB Adhesives:
Application Requirements:
The application’s specific requirements, including bonding strength, flexibility, and environmental resistance, play a crucial role in selecting the appropriate PCB adhesive.
Material Compatibility:
Compatibility with the materials used in the PCB is essential to ensure adequate bonding without causing adverse reactions.
Curing Time:
Depending on the manufacturing process, the adhesive’s curing time can impact production efficiency.
Why is Choosing the Right PCB Adhesive Important?
The importance of selecting the suitable PCB adhesive must be balanced. By considering factors such as temperature resistance, chemical compatibility, bond strength, electrical properties, flexibility, and moisture resistance, manufacturers can ensure electronic devices’ reliability, longevity, and superior performance. Choosing the suitable adhesive is an investment in the quality and durability of PCBs, ultimately benefiting end-users and the electronic industry.
Factors Influencing PCB Adhesive Selection:
Temperature Resistance:
PCBs are subjected to varying temperatures during operation. The adhesive must exhibit high-temperature resistance to prevent deterioration or failure under extreme conditions.
Chemical Compatibility:
The PCB adhesive should be compatible with the chemicals and solvents used in manufacturing. Chemical resistance ensures stability and prevents damage over time.
Bond Strength:
The adhesive’s bond strength is critical for maintaining the structural integrity of the PCB. A strong bond ensures that components remain securely attached even in demanding environments.
Electrical Properties:
PCB adhesives must not interfere with the electrical conductivity of the components. Optimal electrical properties ensure the efficient flow of current within the circuit.
Flexibility and Expansion:
The adhesive should provide the necessary flexibility to accommodate any expansion or contraction of materials due to temperature variations. This flexibility prevents stress on the PCB, minimizing the risk of cracking or delamination.
Moisture Resistance:
Moisture can adversely affect the performance of electronic components. The chosen adhesive should exhibit excellent moisture resistance to safeguard the PCB against environmental factors.
Benefits of Choosing the Right PCB Adhesive:
Enhanced Reliability:
Proper adhesive selection contributes to the overall reliability of the PCB, reducing the likelihood of premature failures or malfunctions.
Extended Lifespan:
A well-chosen adhesive enhances the durability of the PCB, ensuring a longer lifespan for electronic devices.
Improved Performance:
The suitable adhesive promotes optimal electrical performance, contributing to the efficient operation of the electronic circuit.
What Are the Applications of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive?
PCB circuit board adhesive applications extend far beyond consumer electronics, reaching into critical sectors such as automotive, medical, and industrial machinery. The adaptability and reliability of these adhesives contribute significantly to the advancement and functionality of electronic devices across diverse industries.
Consumer Electronics:
Mobile Devices:
PCB adhesives are widely employed in the assembly of mobile phones and tablets, providing structural support and ensuring the integrity of electronic components.
Computers and Laptops:
In the manufacturing of computers and laptops, PCB adhesives are used to affix components securely, contributing to these devices’ overall stability and reliability.
Televisions and Audio Systems:
The assembly of modern televisions and audio systems relies on PCB adhesives to create compact and robust circuit designs, enhancing the performance and durability of the devices.
Automotive Industry:
Automotive Control Systems:
PCB adhesives are employed in vehicles to assemble control systems, such as engine control units (ECUs) and anti-lock braking systems (ABS). The adhesives contribute to the longevity and resilience of these critical components.
Infotainment Systems:
PCB adhesives play a role in securing and connecting components within in-car infotainment systems, ensuring reliable performance in the demanding automotive environment.
Medical Devices:
Diagnostic Equipment:
Medical devices, including diagnostic equipment like MRI machines and ultrasound devices, often incorporate PCB adhesives to ensure electronic components’ precise and consistent functioning.
Monitoring Devices:
Patient monitoring devices utilize PCB adhesives for reliable circuit connections, contributing to the accuracy and stability of health-related measurements.
Industrial Machinery:
Automation Systems:
In industrial automation, PCB adhesives are used to assemble control panels and circuitry for machines, enhancing the efficiency and reliability of manufacturing processes.
Robotics:
Robotics applications benefit from PCB adhesives, ensuring the secure integration of electronic components in robotic systems for various industrial tasks.
How to Apply PCB Adhesive Properly?
Manufacturers can ensure electronic devices’ reliability, durability, and optimal performance by following these step-by-step guidelines for correctly applying PCB adhesive. Attention to detail in each stage of the process contributes to the overall quality of the PCB assembly.
Surface Preparation:
Cleaning:
Start by thoroughly cleaning the surfaces where the adhesive will be applied. Any contaminants, such as dust, grease, or residues, can compromise the adhesion quality.
Surface Roughening:
In some cases, especially with specific substrates, it might be beneficial to roughen the surface slightly to enhance adhesion. Engineers can achieve this by using abrasive techniques suitable for the materials involved.
Mixing the Adhesive:
Follow the Manufacturer’s Instructions:
Adhesives often come in two parts that must be mixed in specific ratios. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions precisely to ensure the adhesive cures properly.
Use Clean Tools:
Employ clean and dry tools for mixing to prevent any contamination that might affect the adhesive properties.
Application Techniques:
Dispensing:
Use an appropriate dispensing method, such as a syringe or automated dispenser, to apply the adhesive precisely and in controlled amounts.
Even Distribution:
Ensure an even distribution of the adhesive across the surfaces to be bonded. This practice promotes uniform adhesion and prevents issues like air pockets or uneven curing.
Avoid Excess Adhesive:
Be cautious not to apply excessive adhesive, as this can lead to overflow, which may cause electrical shorts or interfere with the functionality of components.
Curing Process:
Follow Recommended Curing Time:
Allow the adhesive to cure for the recommended time. Rushing the curing process can compromise the strength and durability of the bond.
Controlled Environment:
Ensure the curing environment meets the recommended conditions, including temperature and humidity, to facilitate the proper curing of the adhesive.
Quality Control:
Inspection:
After curing, inspect the bonded areas for irregularities, ensuring no voids, bubbles, or insufficient adhesion.
Functional Testing:
Conduct functional tests to verify that the adhesive has not interfered with the electrical performance of the PCB.
What Are the Challenges in Using PCB Adhesives?
PCB circuit boards play a crucial role in modern electronic devices as the foundation for the intricate network of components that make our gadgets function seamlessly. PCB circuit board adhesives are often employed to ensure the stability and durability of these electronic wonders. However, like any other technology, using PCB adhesives comes with challenges. This discussion will explore potential troubleshooting solutions to the common issues faced in applying PCB adhesives.
Challenges in Using PCB Adhesives:
Incomplete Curing:
- One frequent challenge is the incomplete curing of the adhesive, leading to weak bonds and compromised reliability.
- Inadequate curing may result from improper temperature or humidity conditions during the curing process.
Adhesive Compatibility:
- Selecting a suitable adhesive compatible with both the PCB materials and the components can be challenging.
- Mismatched adhesives may cause chemical reactions or poor adhesion, impacting the overall performance of the circuit board.
Thermal Stress:
- Electronic devices often experience temperature variations, and PCB adhesives must withstand thermal stress.
- Inadequate resistance to temperature fluctuations can cause the adhesive to degrade, affecting the stability of the components.
Mechanical Stability:
- Achieving a balance between flexibility and rigidity is crucial for the mechanical stability of the PCB.
- Adhesives that are too rigid may cause stress points, while overly flexible ones may lead to component misalignment.
Environmental Factors:
- Exposure to harsh environmental conditions, such as moisture or chemicals, can deteriorate the adhesive.
- Choosing adhesives with appropriate environmental resistance is essential for the long-term reliability of the PCB.
Troubleshooting Solutions:
Optimized Curing Conditions:
- Ensure the curing process occurs in controlled environments with the correct temperature and humidity levels.
- Use curing accelerators if necessary to expedite the curing process without compromising quality.
Thorough Material Compatibility Testing:
- Conduct comprehensive compatibility tests between adhesives and PCB materials before full-scale application.
- Consult with adhesive manufacturers for guidance on suitable options for specific PCB compositions.
Enhanced Thermal Management:
- Implement effective thermal management solutions, such as heat sinks or vias, to reduce stress on the adhesive during temperature fluctuations.
- Choose adhesives with high thermal conductivity for improved heat dissipation.
Balanced Mechanical Properties:
- Select adhesives with tailored mechanical properties that match the specific requirements of the PCB design.
- Experiment with different adhesive formulations to find the optimal balance between flexibility and rigidity.
Sealants and Coatings for Environmental Protection:
- Apply conformal coatings or sealants to protect the PCB and adhesive from environmental factors.
- Regularly inspect and replace coatings if necessary to maintain long-term reliability.
Can PCB Adhesive Enhance Thermal Performance?
Integrating PCB circuit board adhesive is crucial for enhancing thermal performance in electronic systems. By selecting adhesives with high thermal conductivity, optimizing heat dissipation, and considering the overall thermal design, engineers can create circuit boards that effectively manage heat, contributing to the reliability and efficiency of electronic devices. This exploration underscores the importance of adhesive technology in the continual pursuit of advancing thermal management in electronics.
Thermal Conductivity:
- PCB adhesives with high thermal conductivity are pivotal in efficiently transferring heat away from critical components.
- Enhanced thermal conductivity aids in preventing the accumulation of heat, maintaining the circuit board’s stability.
Improved Heat Dissipation:
- The strategic application of adhesives facilitates better contact between components and heat sinks.
- Improved heat dissipation minimizes hotspots, preventing potential damage to sensitive electronic elements.
Bonding and Stability:
- Adhesives contribute to the bonding and stability of components, creating a unified structure on the circuit board.
- This structural integrity promotes effective heat transfer, reducing the risk of overheating and ensuring consistent thermal performance.
Flexibility in Thermal Design:
- PCB adhesives offer flexibility in thermal design by allowing the creation of customized heat paths.
- Designers can strategically place adhesives to guide heat flow away from critical areas, optimizing thermal performance.
Thermal Resistance Reduction:
- Certain adhesives are formulated to minimize thermal resistance between components and the PCB.
- Lower thermal resistance ensures heat can be efficiently conducted through the adhesive, preventing heat buildup.
Adhesive Materials and Formulations:
- Choosing adhesives with specific materials and formulations designed for high thermal performance is crucial.
- Silicone-based adhesives, for example, are known for their excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to extreme temperatures.
Compatibility with Heat-Sensitive Components:
PCB adhesives must be compatible with heat-sensitive components to prevent thermal damage.
Adhesive selection should consider the operating temperatures of components to ensure consistent performance across diverse applications.
Is PCB Adhesive Environmentally Friendly?
In electronics manufacturing, Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are the backbone of countless devices. As technology advances, the need for robust and reliable adhesives to secure components on PCBs becomes increasingly critical. However, as the world focuses more on sustainable practices, there is a growing concern about the environmental impact of these adhesives. This article aims to explore the eco-friendliness of PCB Circuit Board Adhesives.
Key Environmental Considerations:
- Chemical Composition: One of the primary factors influencing the environmental friendliness of PCB adhesives is their chemical composition. Adhesives containing volatile organic compounds (VOCs) can contribute to air pollution and adversely affect human health. Manufacturers are now opting for adhesives with reduced VOC content or exploring alternatives with more eco-friendly ingredients.
- Biodegradability: The biodegradability of PCB adhesives is crucial in assessing their impact on ecosystems. Adhesives that break down naturally over time pose fewer environmental risks than those with non-biodegradable components. The industry is witnessing a shift towards adhesives that decompose without leaving harmful residues.
- Energy Consumption in Production:Sustainable manufacturing processes are integral to environmentally friendly products. PCB adhesives produced using energy-efficient methods contribute less to carbon emissions. Manufacturers adopt greener production practices as consumers demand eco-conscious products to reduce their environmental footprint.
Advancements in Eco-Friendly Adhesives:
- Water-Based Adhesives: Water-based PCB adhesives have gained popularity due to their lower VOC content and reduced environmental impact. They offer a viable alternative to traditional solvent-based adhesives, meeting performance and sustainability criteria.
- Bio-Based Adhesives:Some manufacturers are exploring adhesives derived from renewable resources, such as plant-based materials. These bio-based adhesives not only provide a sustainable option but also contribute to the reduction of dependence on fossil fuels.
Evaluating the eco-friendliness and sustainability aspects of PCB Circuit Board Adhesives is crucial to adopting greener practices in the electronics industry. The ongoing shift towards environmentally friendly alternatives signifies a commitment to mitigating the environmental impact of electronic components and fostering a more sustainable future.
What Innovations are Emerging in PCB Adhesive Technology?
Staying ahead in Printed Circuit Board (PCB) technology is paramount in the rapidly evolving electronics landscape. A crucial but often overlooked component is the adhesive that binds the various elements of a PCB together. As industries continue to demand smaller, more efficient, and environmentally conscious electronics, innovations in PCB adhesive technology are emerging to meet these challenges head-on.
Key Innovations:
- Nanotechnology Integration: A notable breakthrough in PCB adhesive technology is the integration of nanomaterials. Nanoparticles, such as graphene and carbon nanotubes, are incorporated into adhesives to enhance their mechanical and thermal properties. This integration strengthens the bond between components and contributes to the overall durability and performance of the PCB.
- Low-Temperature Curing: Traditional PCB adhesives often require high temperatures during curing, posing challenges for heat-sensitive components. Recent innovations focus on low-temperature curing adhesives, ensuring that delicate electronic parts remain undamaged during manufacturing. This advancement also results in energy savings and increased manufacturing efficiency.
- Flexible and Stretchable Adhesives: The demand for flexible and stretchable electronics is rising, especially in wearable devices and flexible displays. Innovations in PCB adhesive technology now include formulations that allow for greater flexibility and stretchability without compromising adhesive strength. These advancements open up new possibilities for designing and applying electronic devices.
Environmental Considerations:
- Eco-Friendly Formulations:As sustainability becomes a top priority across industries, PCB adhesive manufacturers are developing eco-friendly formulations. Water-based adhesives and those with reduced volatile organic compounds (VOCs) are gaining popularity, aligning with global efforts to reduce the environmental impact of electronic manufacturing processes.
- Recyclability:Innovations in PCB adhesive technology also focus on enhancing the recyclability of electronic components. Adhesives that can be easily separated from the PCB, allowing for efficient materials recycling, are becoming more prevalent. This approach reduces electronic waste and promotes a circular economy in the electronics industry.
How Does PCB Adhesive Contribute to Circuit Board Reliability?
The analysis of PCB adhesive’s impact on the reliability and lifespan of electronic devices underscores its multifaceted role in ensuring circuit boards’ structural, environmental, and electrical stability. Choosing a suitable adhesive is a critical decision that directly influences the performance and durability of electronic devices in diverse operating conditions.
Bonding and Mechanical Stability:
Secure Component Attachment: PCB adhesive is the binding force that secures various components onto the board. A strong and reliable bond is essential for preventing mechanical failures and ensuring that components remain securely in place, even in challenging operating conditions.
Resistance to Vibration and Mechanical Stress: Electronic devices often experience vibrations and mechanical stress during operation or transportation. PCB adhesives with high mechanical stability and resistance to vibrations help maintain the integrity of the connections, reducing the risk of solder joint fractures or component displacement.
Environmental Protection:
Moisture and Environmental Sealing: PCB adhesive acts as a protective barrier against environmental factors, particularly moisture. Moisture can corrode components and lead to electrical failures. Adhesives with moisture-resistant properties create a protective seal, safeguarding the PCB and its components from environmental threats.
Temperature Stability: Electronic devices frequently encounter temperature fluctuations. PCB adhesives with temperature-resistant characteristics contribute to the reliability of circuit boards by ensuring that the adhesive remains stable across a range of temperatures, preventing thermal expansion or contraction that could compromise the integrity of the board.
Electrical Performance:
Dielectric Properties: PCB adhesives play a crucial role in maintaining the dielectric properties of the board. A well-selected adhesive with proper dielectric strength prevents electrical leakage and interference, contributing to the overall reliability of the electronic circuit.
Reduction of Signal Loss: Adhesives with low dissipation factors help minimize signal loss and interference, contributing to the efficient transmission of signals across the circuit board. Maintaining common dissipation factors is crucial in high-frequency applications where signal integrity is paramount.
Can PCB Adhesive Withstand Harsh Environmental Conditions?
In electronics, the functionality and longevity of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are pivotal. Ensuring that these essential components withstand harsh environmental conditions is critical to electronic design. One crucial factor in this resilience is the adhesive used in constructing PCBs.
Examining the resistance of adhesives:
Adhesives play a crucial role in securing components on a PCB and maintaining the board’s structural integrity. The ability of PCB adhesive to withstand harsh environmental conditions is essential for the reliability and performance of electronic devices. Here’s a closer look at how adhesives fare against factors like moisture, temperature, and chemicals:
Moisture Resistance:
Moisture can seep into electronic components, leading to short circuits and corrosion. PCB adhesive with high moisture resistance forms a protective barrier, preventing water ingress and ensuring the longevity of the circuit board.
Temperature Resistance:
Extreme temperatures can adversely affect the performance of electronic devices. Adhesives that exhibit temperature resistance ensure that PCBs remain functional in diverse environments, from cold to scorching heat, without compromising their structural integrity.
Chemical Resistance:
PCBs may be exposed to various chemicals in their operating environment. Adhesives that are resistant to chemicals protect the components from corrosive substances, enhancing the durability of the circuit board.
Vibration and Mechanical Stress:
Electronic devices, often subjected to vibrations and mechanical stress during operation or transportation, benefit from robust bonding adhesives. These adhesives help mitigate the impact of these forces, preventing damage to the PCB and associated components.
Long-Term Reliability:
Adhesives that exhibit a high level of resistance to environmental factors contribute to the long-term reliability of PCBs, a crucial characteristic in applications where electronic devices are deployed in challenging conditions, such as automotive or aerospace environments.
Are There Special Considerations for High-Frequency Applications?
In the ever-evolving landscape of electronics, the design and manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) play a crucial role in determining the performance of electronic devices. The adhesive used in PCB circuit boards is a critical aspect that demands special attention. This article delves into the information surrounding PCB circuit board adhesives, explicitly focusing on the special considerations required for high-frequency applications.
PCB Circuit Board Adhesive Overview:
- PCB adhesives are a crucial component in the assembly and construction of electronic devices. They provide structural support electrical insulation and facilitate the bonding of various elements on the PCB.
- The selection of an appropriate adhesive is influenced by factors such as the operating environment, temperature range, and the intended application of the electronic device.
Special Considerations for High-Frequency Applications:
Dielectric Constant (Dk):High-frequency applications often involve signals with rapid transitions. The dielectric constant of the adhesive becomes a critical factor as it determines the speed at which signals can propagate through the material. For high-frequency PCBs, choosing an adhesive with a low dielectric constant is essential to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity.
- Loss Tangent (Dissipation Factor):In high-frequency circuits, minimizing signal loss is paramount. Adhesives with low-loss tangent values help in achieving this goal. A low dissipation factor ensures that the adhesive does not absorb a significant portion of the signal energy, preserving the overall performance of the electronic device.
- Thermal Stability: High-frequency applications can generate heat, and the adhesive must withstand elevated temperatures without compromising its structural or electrical properties. Adhesives with high thermal stability are essential to ensure the reliability and longevity of the PCB in demanding environments.
- Adhesion Strength:While electrical properties are crucial, the adhesive must also provide robust mechanical bonding. The adhesive should exhibit excellent adhesion to different substrate materials used in PCBs, ensuring the integrity of the overall assembly.
How Does PCB Adhesive Facilitate Miniaturization of Electronic Components?
In the fast-paced world of electronics, the demand for smaller and more compact devices continues to grow. This trend poses unique challenges for manufacturers, especially concerning the assembly and integration of electronic components on printed circuit boards (PCBs). One pivotal factor contributing to the success of miniaturization efforts is the strategic use of PCB circuit board adhesives. This article delves into the information surrounding how PCB adhesives facilitate the miniaturization of electronic components.
PCB Circuit Board Adhesive Overview:
- PCB adhesives are a critical element in the assembly process, contributing to the structural integrity, electrical insulation, and overall performance of electronic devices.
- The choice of adhesive is influenced by factors such as the application environment, thermal requirements, and the specific demands of the electronic components used.
How Does PCB Adhesive Facilitate Miniaturization?
- Component Bonding:PCB adhesives are essential in securely bonding electronic components to the board. By forming solid and reliable bonds, adhesives enable the placement of parts nearby, allowing for a more compact design.
- Reduced Footprint: Advanced adhesives with excellent adhesion properties permit the placement of components on both sides of the PCB. This capability reduces the device’s overall footprint, contributing significantly to the trend of miniaturization.
- Thermal Management: Miniaturized electronic devices often face challenges related to heat dissipation. PCB adhesives with efficient thermal conductivity help manage heat, allowing for compact device design without compromising performance.
- Flexibility and Conformal Coating: Some PCB adhesives offer flexibility, allowing for the assembly of flexible and bendable PCBs. Additionally, conformal coating capabilities ensure that the adhesive conforms to the contours of the components, enabling the creation of sleek and space-efficient designs.
Challenges and Considerations:
- Compatibility: Ensuring compatibility between the adhesive and the materials used in miniaturized components is crucial. Compatibility issues can lead to performance issues and compromise the device’s reliability.
- Precision Application: Miniaturization requires precise application of adhesives to avoid spillage or excess material. Manufacturers must invest in advanced application techniques to achieve the desired level of precision.
What Role Does PCB Adhesive Play in Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs?
PCB (Printed Circuit Board) adhesive plays a crucial role in the design and functionality of both flexible and rigid-flex PCBs. Understanding PCB adhesive’s specific requirements and benefits in flexible circuit designs is essential for achieving optimal performance and reliability in electronic devices.

Key Role of PCB Adhesive:
- Bonding Components: PCB adhesive is primarily used for bonding various components onto the circuit board, ensuring a secure and stable connection. The importance of this secure bond is particularly critical in flexible and rigid-flex PCBs, where the board may undergo bending or flexing.
- Enhanced Mechanical Strength: The adhesive provides mechanical strength to the PCB, preventing components from detaching or breaking due to stress, vibrations, or other environmental factors. In flexible circuits, where repeated bending is standard, the adhesive is a protective layer against mechanical wear and tear.
- Improved Thermal Conductivity: PCB adhesive aids in efficient dissipation of heat generated by electronic components. Effective thermal management prevents overheating in flexible circuits in limited space. The adhesive enhances the thermal conductivity of the PCB, contributing to the device’s overall reliability.
- Flexibility and Durability: Flexibility is crucial for flexible and rigid-flex PCBs. PCB adhesive is formulated to maintain flexibility while ensuring durability. It allows the PCB to bend without compromising the integrity of the circuit, making it suitable for applications that require a high degree of flexibility.
Specific Requirements in Flexible Circuit Designs:
- Flexibility: In flexible circuit designs, the PCB adhesive must accommodate repeated bending and flexing without causing damage to the components or the circuit itself. The adhesive should be flexible enough for the PCB to conform to the desired shape without sacrificing performance.
- Thin Profile:Flexible circuits often have stringent space constraints. PCB adhesive for flexible designs is engineered to have a slim profile while maintaining the necessary bonding and mechanical strength. This engineering ensures that the overall thickness of the flexible PCB is minimized.
- Adhesion to Different Substrates:Flexible circuits may involve diverse substrates. The PCB adhesive should be capable of adhering to various materials, providing a reliable bond across the entire flexible PCB assembly.
Benefits of PCB Adhesive in Flexible and Rigid-Flex PCBs:
- Reliability: PCB adhesive enhances the overall reliability of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs, ensuring stable connections and preventing issues such as intermittent connections or solder joint failures.
- Compact Design: The thin profile of PCB adhesive allows for a more compact design in flexible circuits, facilitating the development of smaller and lighter electronic devices.
- Longevity:By protecting against mechanical stress and environmental factors, PCB adhesive contributes to the longevity of flexible and rigid-flex PCBs, making them suitable for applications where durability is critical.
Can PCB Adhesive Be Reversed or Removed?
In the realm of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design and assembly, questions often arise about the reversibility of processes, particularly when it comes to PCB adhesive. A crucial consideration for engineers and manufacturers is whether PCB adhesive can be reversed or removed. This article delves into this inquiry, discussing the methods and concerns involved in safely removing or replacing PCB adhesive when necessary.
Methods for PCB Adhesive Removal:
Solvent-Based Removal:
- Chemical Solvents: Certain chemical solvents can effectively break down and dissolve the adhesive, allowing for its removal. Choosing solvents compatible with the materials and components used in the PCB is essential to avoid damage.
- Careful Application: Solvents should be applied precisely to target the adhesive without affecting other components. This method requires careful handling to prevent unintended consequences.
Heat-Based Removal:
- Thermal Stripping: Applying controlled heat to the PCB can soften the adhesive, making it easier to peel off. Temperature control is critical to avoid damaging sensitive components or the circuit itself.
- Hot Air Reflow: In some cases, hot air reflow techniques may heat the entire PCB, effectively loosening the adhesive for removal.
Mechanical Removal:
- Scraping or Peeling:Manual removal using tools like scrapers or tweezers can be employed for smaller areas or components. This method requires precision to avoid damaging the PCB or components.
- Abrasive Techniques: Abrasive methods such as sanding or grinding may be considered for more robust adhesives. However, these techniques require careful control to prevent damage to the underlying circuitry.
Considerations for Safe Removal:
- Material Compatibility: Before employing any removal method, ensuring the chosen approach is compatible with the materials used in the PCB and its components is crucial. Chemical solvents or heat, for instance, may adversely affect certain materials.
- Component Sensitivity: Consideration must be given to the sensitivity of electronic components on the PCB. Excessive heat or aggressive solvents can damage or compromise the functionality of these components, necessitating a careful balance during the removal process.
- Residue Cleanup: Even after successful adhesive removal, residual traces may be left behind. Proper cleanup procedures are essential to eliminate any remnants and ensure a clean, ready-to-use PCB surface.
How Does PCB Adhesive Affect Signal Integrity?
Understanding how PCB Circuit Board Adhesive affects signal integrity is paramount for designing reliable electronic systems. By carefully considering material properties, optimizing loss tangents, and implementing effective thermal management, engineers can mitigate the potential negative impacts of adhesive choices on signal quality. Rigorous testing and quality control further contribute to ensuring PCBs’ overall reliability and performance in diverse applications. Balancing structural requirements with electrical considerations is essential for creating robust electronic devices that meet the demands of modern technology.
Examining the Potential Impact:
Dielectric Properties:
- The dielectric constant of the adhesive material can influence signal propagation speed.
- High dielectric constants may lead to signal delays and impedance mismatches.
Signal Loss:
- Adhesive layers can introduce signal attenuation, particularly at higher frequencies.
- Understanding the loss tangent of the adhesive is essential to assess its impact on signal strength.
Crosstalk and Interference:
- Inadequate adhesive choices may contribute to increased crosstalk between adjacent traces.
- Signal interference can result in data corruption and reduced overall performance.
Thermal Considerations:
- PCB adhesives exposed to temperature fluctuations can expand or contract, affecting signal paths.
- Thermal stability is critical to maintaining signal integrity, especially in varying temperatures.
Ways to Mitigate Negative Effects:
Material Selection:
- Opt for adhesives with low dielectric constants to minimize signal delay.
- Consider epoxy-based adhesives known for their electrical insulation properties.
Loss Tangent Optimization:
- Choose adhesives with low-loss tangents to minimize signal attenuation.
- Conduct thorough testing to assess the material’s impact on high-frequency signals.
Crosstalk Prevention:
- Increase the separation between traces to reduce crosstalk.
- Utilize shielding techniques or employ differential signaling to mitigate interference.
Thermal Management:
- Select adhesives with superior thermal stability to withstand temperature variations.
- Implement heat sinks or other cooling mechanisms to regulate the temperature of the PCB.
Testing and Quality Control:
- Rigorous testing protocols should be in place to evaluate the electrical performance of PCBs.
- Regular quality control measures can ensure that adhesive choices align with desired signal integrity goals.
What Safety Precautions Should Be Taken When Handling PCB Adhesives?
Prioritizing safety when handling PCB adhesives is imperative for protecting the well-being of personnel and maintaining a secure working environment. Adhering to these safety measures ensures the successful application of adhesives while minimizing potential health risks.
Highlighting the Importance of Safety Measures:
Material Composition: PCB adhesives often contain volatile compounds and chemicals that may pose health risks. It is crucial to be aware of the composition of the adhesive being used to implement appropriate safety precautions.
Inhalation Risks: If inhaled, the fumes released during the adhesive application can be harmful. Adequate ventilation systems or using personal protective equipment (PPE) like respirators is essential to mitigate these risks.
Skin Contact: Direct contact with PCB adhesives can lead to skin irritation or allergic reactions. Appropriate protective clothing, such as gloves and long sleeves, prevents skin exposure.
Eye Protection: Splashes or accidental contact with adhesive materials can lead to eye injuries. Safety goggles or face shields should be worn to protect the eyes from potential hazards.
Work Environment: Maintaining a clean and organized work environment is crucial for minimizing the risk of accidents. Spills or leaks of adhesive materials should be promptly cleaned, and spill response kits should be readily available.
Safety Precautions When Handling PCB Adhesives:
Risk Assessment: Before starting the adhesive application process, conduct a thorough risk assessment to identify potential hazards and implement appropriate preventive measures.
Training: Ensure that personnel handling PCB adhesives are adequately trained on the safe handling procedures, emergency response protocols, and the proper use of PPE.
Ventilation: Work in well-ventilated areas or use local exhaust systems to control and reduce the concentration of fumes released during adhesive application.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
Wear appropriate gloves made of materials resistant to the specific adhesive being used.
Use respiratory protection, such as masks or respirators, to prevent inhalation of harmful fumes.
Wear safety goggles or face shields to protect the eyes from splashes or accidental contact.
Emergency Preparedness: Have an emergency response plan, including access to eyewash stations, emergency showers, and first aid kits. Ensure that all personnel are familiar with the procedures in case of accidental exposure.
Is PCB Adhesive Compatible with Different Substrates?
The compatibility of PCB adhesives with different substrates is a nuanced consideration that requires a comprehensive understanding of material properties, environmental factors, and application methods. By meticulously investigating these aspects, manufacturers can make informed choices, enhancing the reliability and performance of PCBs in diverse applications.
Investigating Compatibility:
- Adhesive Composition: PCB adhesives come in various formulations, each designed with specific material compatibility. It is essential to scrutinize the composition of the adhesive to ensure it aligns with the materials used in the PCB assembly.
- Substrate Types:PCBs are fabricated using a range of substrates, including FR-4, aluminum, ceramic, and flexible materials like polyimide. The compatibility of adhesives must be assessed across these diverse substrate types to guarantee optimal performance.
- Thermal Considerations: Different substrates exhibit distinct thermal properties. The adhesive must withstand temperature variations during the manufacturing process and the operational life of the PCB. Compatibility with thermal expansion coefficients is crucial to prevent delamination or stress-induced failures.
- Electrical Compatibility: Adhesives should not interfere with the electrical properties of the PCB. Compatibility with the conductive traces and components is paramount to maintaining signal integrity and preventing electrical malfunctions.
- Chemical Resistance: PCBs may be exposed to various environmental factors, including chemicals. The adhesive must demonstrate compatibility with the chemicals the PCB might encounter during its lifespan, ensuring resistance to degradation and maintaining structural integrity.
- Flexibility Requirements: Adhesives must demonstrate compatibility with the flexible substrate’s bending and flexing to meet flexibility requirements in flexible PCBs, as rigidity or brittleness in the adhesive could compromise the flexibility of the PCB, potentially leading to mechanical failure.
Factors Influencing Compatibility:
- Surface Energy: The surface energy of different substrates varies, influencing how well adhesives adhere. Surface treatment or modification may be necessary to enhance compatibility with low-energy substrates.
- Adhesive Curing Mechanism: The curing process of adhesives can impact compatibility. Some adhesives cure through heat, while others cure at room temperature. Ensuring that the curing mechanism aligns with the substrate’s tolerance is vital.
- Adhesive Application Method:The adhesive method, whether through dispensing, screen printing, or other techniques, can influence compatibility. The application process should be chosen based on the substrate’s characteristics.
- Manufacturer Recommendations: Adhesive manufacturers often provide guidelines and recommendations regarding compatibility with specific substrates. Following these recommendations ensures that the adhesive is used optimally.
What Future Trends Can We Expect in PCB Adhesive Development?
Speculating on the future directions and innovations in the field of PCB adhesive technology opens a gateway to envisioning the transformative trends that lie ahead. PCB Circuit Board Adhesive, a critical element in electronic manufacturing, plays a pivotal role in ensuring electronic devices’ structural integrity and reliability. As technology advances at an unprecedented pace, the evolution of PCB adhesive materials is poised to follow suit. This article delves into the potential future trends in PCB adhesive development, shedding light on the innovations that could shape the industry.
Future Trends in PCB Adhesive Development:
Advanced Material Formulations:
- Expectations for developing novel adhesive formulations with enhanced thermal conductivity and dielectric properties rise.
- Nanocomposite materials may become prevalent, incorporating nanoparticles to improve performance and reliability.
Miniaturization and High-Density Interconnects:
- As electronic devices continue shrinking, PCBs are expected to undergo further miniaturization.
- PCB adhesives must adapt to accommodate high-density interconnects, demanding formulations that can withstand tighter spaces without compromising performance.
Flexible and Stretchable Adhesives:
- With the rise of flexible electronics, there is a growing need for adhesives that can adhere to and support flexible substrates.
- Stretchable adhesives may become essential for applications in wearable technology and flexible displays.
Environmentally Friendly Adhesives:
- The industry will likely shift towards eco-friendly and sustainable adhesive materials.
- Water-based and solvent-free formulations may gain prominence, aligning with global efforts towards greener electronics manufacturing.
Integration of Smart Features:
- PCB adhesives may evolve to include intelligent features such as self-healing capabilities to enhance the longevity of electronic devices.
- Integration of sensors within the adhesive could provide real-time monitoring of the PCB’s structural integrity.
Improved Process Efficiency:
- Future PCB adhesives might be designed to streamline the manufacturing process, reducing assembly time and costs.
- Quick-curing adhesives or formulations compatible with advanced manufacturing techniques like 3D printing could become mainstream.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the journey through the realms of PCB Circuit Board Adhesive has uncovered its pivotal role in electronics. From the nuanced application techniques to the profound impact on signal integrity, the guide has navigated through the intricacies of adhesive technology. As we stand at the cusp of future trends, it is evident that innovation in PCB adhesive development will continue to shape the electronic engineering landscape. The adhesive’s compatibility with different substrates, its influence on flexible designs, and itsits ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions underscore its versatility. With this guide, we have not only unraveled the wonders of PCB adhesive but also paved the way for the exciting possibilities in this dynamic field.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy
The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy This article systematically expounds the quantitative relationship between the crosslinking density and the flexibility and hardness of adhesives. Combining the theories of polymer physics with experimental analysis methods, it reveals the mechanism of the action of the

Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives
Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives UV adhesives have been widely used in many fields such as electronics, optics, and medicine due to their advantages of rapid curing, high bonding strength, and environmental protection. However, their rapid curing property also brings challenges in some application scenarios.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment

Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions
Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions The dispensing process is an important part of the application of LED UV glue adhesive, and the quality of this process directly affects the final performance of the product. The physical properties of the glue,