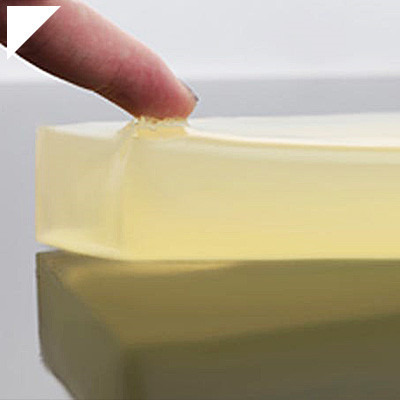
Low Viscosity Adhesive

In the intricate world of adhesive technology, viscosity stands as a defining factor, influencing an adhesive’s behavior and efficiency. Enter the realm of low-viscosity adhesives, where fluidity becomes a prized asset, enabling these bonding agents to penetrate surfaces with remarkable ease and precision. These adhesives, characterized by their low thickness and exceptional flow properties, redefine the landscape of efficient bonding. Their ability to permeate substrates and establish robust connections is poised to revolutionize various industries, from woodworking to electronics and healthcare. Let’s delve into the nuances of low-viscosity adhesives, exploring their defining traits, applications across diverse sectors, and the transformative impact they hold for the future of bonding techniques.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat defines low-viscosity adhesives and their primary characteristics?
Low-viscosity adhesives are pivotal in various industries due to their unique properties and versatile applications. These adhesives are defined by their fluid-like consistency and exhibit several primary characteristics that make them indispensable in numerous manufacturing and assembly processes.
Characteristics
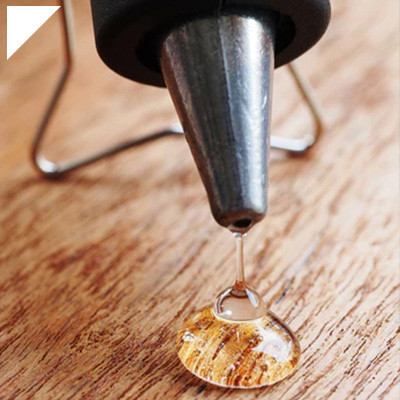
- Flowability:The primary defining feature of low-viscosity adhesives is their fluid or liquid-like consistency. They have a low flow resistance, allowing them to spread quickly and penetrate small spaces or tight gaps.
- Fast Cure Time:These adhesives often boast rapid curing properties, enabling quick surface bonding. Their ability to set or harden swiftly makes them ideal for applications that require expedited production processes.
- Excellent Penetration:Their low viscosity enables these adhesives to seep into substrates, ensuring a solid bond by maximizing surface contact. This characteristic is particularly advantageous in bonding porous materials or irregular surfaces.
- High Bond Strength:Despite low viscosity, these adhesives offer impressive bonding strength. Once cured, they create durable and reliable bonds that withstand various environmental conditions and stresses.
- Versatile Applications:Low-viscosity adhesives find extensive use across multiple industries, including automotive, electronics, aerospace, and healthcare. They are employed in bonding components, sealing joints, and encapsulating electronic devices, among other applications.
Applications and Benefits
- Electronics:These adhesives are vital in electronic manufacturing, facilitating precise bonding of delicate components without causing damage. They aid in the assembly of circuit boards, ensuring secure connections and electrical insulation.
- Automotive Industry:In the automotive sector, low-viscosity adhesives contribute to lightweight vehicle assembly, enhancing structural integrity while reducing overall weight. They are used in bonding metals, plastics, and composites, improving vehicle safety and performance.
- Medical Devices:Their biocompatibility and ability to bond different materials make them valuable in medical device manufacturing. From bonding medical tubing to assembling devices, these adhesives ensure reliability and compliance with stringent safety standards.
- Construction:Low-viscosity adhesives play a role in construction applications, such as sealing joints, anchoring bolts, or repairing cracks. Their ability to penetrate substrates ensures strong, long-lasting bonds in various building materials.
How does low viscosity impact adhesive performance and bonding efficiency?
Adhesives are crucial in various industries as invisible heroes in assembling components. Low-viscosity adhesive stands out for its unique properties among the different adhesive types. Here’s a closer look at how its low viscosity impacts adhesive performance and bonding efficiency:
What is Low-Viscosity Adhesive?
- Definition:Low-viscosity adhesives are fluids with a thinner consistency, allowing them to flow easily.
- Composition:They typically comprise polymers, solvents, or reactive monomers.
- Application:It is used in scenarios where precise bonding, penetration, and fast curing are vital.
Impact on Bonding Efficiency
Improved Penetration
- Low-viscosity adhesives penetrate surfaces easily, reaching intricate areas thicker adhesives can’t access.
- This process ensures a more comprehensive and uniform bond across the entire surface.
Enhanced Bond Strength
- Sealing into substrates leads to stronger adhesion by maximizing contact between surfaces.
- The application of the adhesive creates a more robust bond, even when applied to porous or irregular surfaces.
Faster Curing Time
- Due to their thin consistency, low-viscosity adhesives cure rapidly.
- This results in quicker assembly processes and increased productivity.
Reduced Waste and Cleanup:
Their fluid nature reduces excess adhesive, minimizing cleanup efforts.
Reduces material wastage, contributing to cost-effectiveness.
Factors Influencing Performance
- Surface Type:Low-viscosity adhesives excel on porous surfaces where deeper penetration is essential.
- Temperature and Environment:Some variants require specific temperature ranges or environmental conditions for optimal performance.
- Application Method:Applicator choice and technique impact the adhesive’s effectiveness.
- Challenges and Considerations:
- Runoff and Spillage:Due to their fluidity, controlling application is crucial to prevent runoff and spillage.
- Thinner Bonds:While delicate bonds may offer advantages for penetration, they often lack the necessary thickness required for specific load-bearing applications.
What are the key components or chemical compositions of these adhesives?
Low-viscosity adhesives are integral to various industries, providing strong bonding capabilities while maintaining fluidity. Understanding their chemical compositions sheds light on their versatile applications and effectiveness. Here are the key components and chemical compositions that define these adhesives:
Resins
- Epoxy Resins: Predominantly used due to their exceptional bonding properties and resistance to various environmental factors.
- Acrylic Resins:They are known for their fast-curing abilities and excellent adhesion to various substrates.
Additives
- Plasticizers:Enhance flexibility and reduce brittleness, improving the adhesive’s overall performance.
- Fillers:Provide strength, enhance viscosity, and modify specific properties like thermal conductivity or flame resistance.
Solvents or Carriers
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs): Commonly used carriers aid in the application and initial fluidity of the adhesive.
- Water:Present in water-based formulations, offering environmental advantages and easy clean-up.
Curing Agents
- Amines or Polyamides:Accelerate the curing process in epoxy-based adhesives, contributing to their strong bond formation.
- Isocyanates:React with polyols in polyurethane adhesives, initiating the curing process and providing high-strength bonds.
Chemical Initiators
- Peroxides or Amine Compounds:Trigger the polymerization process in some adhesives, initiating the bond formation.
Polymer Chains
- Polyethylene Glycol (PEG) or Polyvinyl Acetate (PVA):Comprise the polymer chains in various adhesive formulations, determining their properties and performance.
The chemical compositions of low-viscosity adhesives are carefully formulated to balance flowability and bonding strength. These components interact synergistically to achieve specific characteristics such as:
- Viscosity Control:Chemical constituents are adjusted to maintain low viscosity, allowing easy application and penetration into substrates.
- Adhesion Properties:Balanced compositions ensure firm adhesion to diverse materials like metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- Curing Speed: The right combination of curing agents and initiators determines the adhesive’s setting time, impacting productivity and application feasibility.
- Environmental Impact:With the rising focus on eco-friendliness, formulations with low VOCs or water-based carriers are being developed to reduce the ecological footprint.
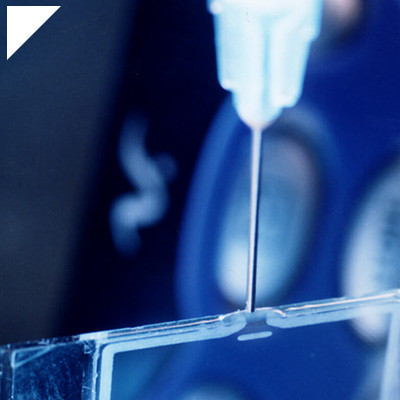
How does low viscosity facilitate application and penetration into substrates?
In adhesives, the viscosity factor is pivotal in determining the application ease and penetration capability into substrates. Low-viscosity adhesives, characterized by their fluidity and smooth flow, offer many advantages, particularly in enhancing the application process and ensuring deep penetration into various materials. Here’s an insightful exploration into how the low viscosity of adhesives facilitates seamless application and robust substrate penetration:
Improved Flow Properties
- Low-viscosity adhesives boast exceptional fluidity and smoothness, allowing them to spread effortlessly across surfaces.
- The reduced internal friction within these adhesives enables easy movement, ensuring consistent coverage without clumping or uneven distribution.
Enhanced Application Precision
- Their low viscosity enables precise application in intricate or hard-to-reach areas, ensuring thorough bonding without excess buildup.
- These adhesives are ideal for delicate assemblies with paramount application and controlled bonding.
Deeper Penetration into Substrates
- The fluid nature of low-viscosity adhesives facilitates their infiltration into porous materials, such as wood, fabric, or uneven surfaces.
- Capable of seeping into microscopic gaps and fissures, these adhesives establish stronger and more comprehensive bonds by maximizing surface contact.
Reduced Curing Time
- Their ability to penetrate substrates swiftly expedites bonding, leading to quicker curing times.
- The efficient penetration reduces the time required for the adhesive to set, accelerating the overall assembly or manufacturing process.
Optimized Strength and Durability
- By penetrating deeply into substrates, low-viscosity adhesives create stronger bonds, enhancing the overall strength and durability of the assembly.
- The comprehensive coverage ensures a robust connection that withstands various environmental factors and stressors.
Versatile Application Across Industries
- Low-viscosity adhesives find widespread use in industries like automotive, electronics, construction, and aerospace due to their versatility in bonding various materials.
- They cater to diverse needs, from bonding intricate electronic components to laminating materials in construction, showcasing their adaptability.
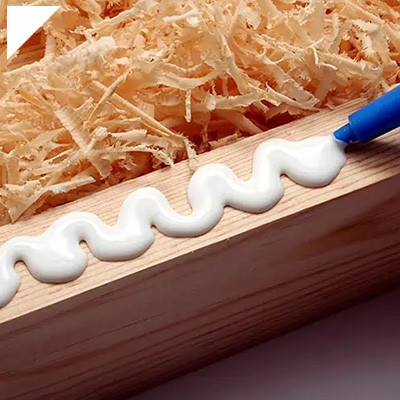
How are low-viscosity adhesives utilized in woodworking and furniture making?
Low-viscosity adhesives are a cornerstone in the woodworking and furniture-making industries, offering a transformative approach to bonding materials. Their unique fluidity and penetration capabilities make them indispensable in crafting and assembling wooden structures. Here’s an exploration of how low-viscosity adhesives are leveraged in woodworking and furniture making:
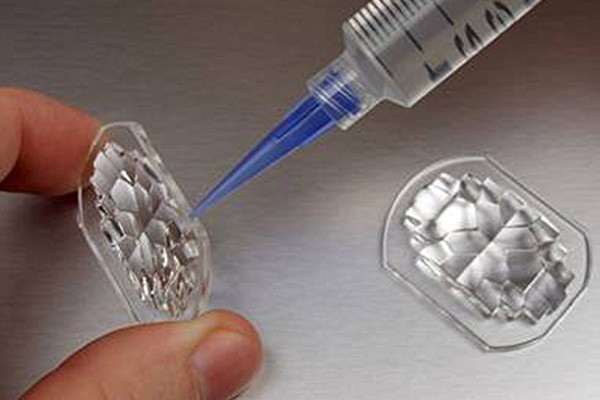
Optimal Penetration into Wood Fibers
- The low viscosity of these adhesives allows them to seep effectively into the intricate wood fibers, enhancing the bond strength between joints.
- This deep penetration ensures a more comprehensive and durable connection between wooden components, contributing to the longevity of furniture pieces.
Precision in Joint Bonding
- In intricate joinery, such as dovetails or mortise-and-tenon joints, low-viscosity adhesives offer precise application, filling gaps and ensuring a snug fit without excess adhesive buildup.
- Their ability to flow smoothly ensures seamless bonding without compromising the aesthetics or functionality of the jointed surfaces.
Efficiency in Laminating Wood Surfaces
- Low-viscosity adhesives facilitate lamination by evenly spreading across wood surfaces, creating solid and consistent bonds between layers.
- Whether laminating thin veneers or gluing larger panels, their fluidity ensures uniform adhesion, resulting in visually appealing and structurally sound finished products.
Moisture Resistance and Durability
- These adhesives often exhibit excellent moisture resistance, essential for wooden structures exposed to varying environmental conditions.
- The strong bonds formed by low-viscosity adhesives contribute to the durability of furniture, ensuring stability and structural integrity over time.
Streamlining Manufacturing Processes
- Their quick curing times expedite production schedules, reducing assembly times in woodworking and furniture manufacturing.
- The efficiency in bonding allows for faster processing and assembly, ultimately increasing productivity without compromising quality.
Versatility and Compatibility
- Low-viscosity adhesives cater to a wide array of wood types and finishes, showcasing compatibility with different species and surface treatments commonly used in woodworking.
- Their versatility extends to furniture-making techniques, from intricate joinery to edge gluing and veneer applications.
What role do they play in glass and plastic bonding for manufacturing?
In manufacturing, the cohesion of glass and plastic components plays a pivotal role in crafting durable and reliable products. Among the essential elements contributing to this synergy is the utilization of low-viscosity adhesive, a crucial agent that facilitates the seamless bonding of these materials. Here’s a closer look at the role these adhesives play in the glass and plastic bonding process:
Facilitating Strong Bonds
- Low-viscosity adhesives are engineered to penetrate the micro-level irregularities present on glass and plastic surfaces, ensuring a robust bond.
- Their low thickness enables these adhesives to spread evenly across surfaces, maximizing contact points and enhancing adhesive strength.
Adaptable to Different Materials
- These adhesives are formulated to work effectively with various types of glass and plastic, providing versatility in manufacturing processes.
- They can bond different grades and compositions of materials, allowing for diverse applications across industries.
Enhancing Efficiency and Precision
- Their low viscosity promotes quicker and more precise application, reducing production time and enhancing manufacturing efficiency.
- The fluid nature of these adhesives allows them to fill gaps and voids effectively, ensuring a seamless and aesthetically pleasing finish.
Durability and Longevity
- Despite their low viscosity, these adhesives offer exceptional durability, maintaining the integrity of bonds even under stress or varying environmental conditions.
- They exhibit resistance to factors like moisture, heat, and chemicals, contributing to the longevity of bonded glass and plastic components.
Improving Aesthetic Appeal
- Low-viscosity adhesives leave minimal residue or marks, contributing to the visual appeal of the final product.
- Their ability to create nearly invisible bonds enhances the aesthetics of glass and plastic assemblies.
Meeting Industry Standards
- These adhesives comply with stringent industry standards, ensuring the quality and reliability of bonded components.
- They undergo rigorous testing to meet performance benchmarks, guaranteeing their suitability for diverse manufacturing applications.
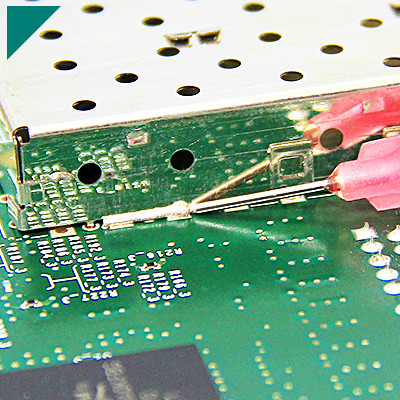
Are there notable applications in electronics and circuitry?
In the dynamic realm of electronics and circuitry, the quest for optimal performance and durability has led to exploring innovative materials. One such material making waves in the industry is the low-viscosity adhesive. This versatile substance offers a range of benefits, making it a noteworthy player in various applications within the electronics and circuitry landscape.
Features of Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Fluid Consistency:Unlike traditional adhesives, low-viscosity adhesives exhibit a liquid consistency, allowing them to flow easily into tight spaces and intricate circuitry components.
- Quick Curing:These adhesives often boast rapid curing times, contributing to increased efficiency in production processes.
- High Bond Strength:Despite their low viscosity, these adhesives offer robust bonding capabilities, ensuring the reliability and longevity of electronic components.
Applications in Electronics and Circuitry
Microelectronics Assembly
- Low-viscosity adhesives are ideal for bonding microelectronic components, facilitating the precise placement of small parts with minimal risk of damage.
- Their ability to flow into tiny crevices ensures complete coverage, enhancing the structural integrity of the assembled devices.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing
- In the production of PCBs, low-viscosity adhesives play a crucial role in securing components to the board, creating a durable and reliable connection.
- The fluid nature of these adhesives allows for uniform coating, minimizing the risk of air pockets or incomplete coverage.
Flexible Electronics
- With the rising demand for flexible and bendable electronics, low-viscosity adhesives offer a solution for bonding components on flexible substrates.
- Their adaptability and ability to conform to irregular surfaces make them well-suited for applications like flexible displays and wearable technology.
Semiconductor Packaging
- Semiconductor devices often require precise bonding to ensure optimal electrical performance. Low-viscosity adhesives provide the necessary precision in the packaging process.
- The quick curing time is particularly beneficial in semiconductor manufacturing, where efficiency is paramount.
Advantages for Electronic Manufacturers
- Improved Production Speed:Quick curing times and efficient flow characteristics contribute to faster production cycles.
- Enhanced Product Reliability:High bond strength and uniform coverage contribute to the durability and reliability of electronic devices.
- Cost-Effective Solutions:The versatility and efficiency of low-viscosity adhesives can lead to cost savings in manufacturing processes.
How are these adhesives employed in medical device assembly and healthcare applications?
In healthcare, using low-viscosity adhesives has become a game-changer in medical device assembly. These adhesives, characterized by their fluidity and low thickness, have opened new vistas in medical technology, transforming the landscape of healthcare applications.
Versatility in Medical Device Assembly
- Precision Bonding:Low-viscosity adhesives offer exceptional precision in bonding delicate medical components, ensuring a secure and reliable connection.
- Reduced Risk of Damage:Their low viscosity minimizes the risk of damage to sensitive components during assembly, maintaining the integrity of the devices.
- Enhanced Product Performance:These adhesives facilitate seamless assembly, improving medical devices’ overall performance and functionality.
Applications in Healthcare
- Wound Care Products:Low-viscosity adhesives are instrumental in creating advanced wound care products. They enable the production of efficient, comfortable, and non-invasive bandages and dressings.
- Medical Device Encapsulation:They play a pivotal role in encapsulating electronic components in medical devices, ensuring insulation and protection against external elements.
- Diagnostic Equipment:The use of these adhesives aids in assembling precise and compact diagnostic equipment, thereby enhancing accuracy in medical diagnoses.
- Implantable Devices:In creating implantable devices like pacemakers and orthopedic implants, low-viscosity adhesives provide the necessary adhesion strength without compromising the device’s biocompatibility.
Advantages in Healthcare Settings
- Biocompatibility:These adhesives are formulated to be biocompatible, minimizing adverse reactions when in contact with the human body.
- Sterilization Compatibility:They withstand various sterilization methods, crucial for medical devices requiring frequent sterilization to maintain hygienic conditions.
- Durability and Longevity:These adhesives contribute to the longevity and reliability of medical devices by ensuring a strong and durable bond.
- Cost-Efficiency:Their precise application and minimal waste reduce manufacturing costs, benefiting healthcare institutions and patients.
Future Prospects
The evolution of low-viscosity adhesives continues to shape the healthcare industry, promising further innovations. Researchers are exploring new formulations that address specific medical challenges, striving to enhance biocompatibility, adhesion strength, and versatility for diverse applications.
What are the distinct advantages of using low-viscosity adhesives?
Low-viscosity adhesives, often overlooked in bonding solutions, hold many advantages that significantly elevate their efficacy in various applications. With their fluid-like consistency, these adhesives offer distinct benefits that make them indispensable in multiple industries. Let’s delve into the advantages that make low-viscosity adhesives a preferred choice:
Enhanced Penetration and Coverage
- These adhesives’ fluid nature allows them to seep into intricate surfaces and cavities easily.
- They ensure comprehensive coverage, even in hard-to-reach areas, promoting a stronger bond.
Faster Curing Time
- Their low viscosity accelerates the curing process, expediting the assembly or manufacturing process.
- Rapid curing minimizes production downtime, leading to increased productivity and efficiency.
Improved Bond Strength
- Despite their low viscosity, these adhesives maintain excellent bond strength, ensuring reliable and durable connections.
- The adhesive’s ability to penetrate substrates contributes to stronger adhesion, even in challenging environments.
Reduced Waste and Mess
- Their fluid consistency facilitates precise application, minimizing waste and excess material usage.
- Cleanup becomes hassle-free due to their minimal mess during application.
Versatility in Applications
- Low-viscosity adhesives are adaptable across various materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites.
- They find utility in industries ranging from automotive and electronics to medical devices and construction.
Enhanced Product Performance
- These adhesives often offer improved thermal and chemical resistance, augmenting the durability and performance of the bonded products.
- They contribute to better product lifespan and reliability.
Cost-Effective Solution
- Their efficient application, reduced waste, and faster curing times lead to cost savings in production and manufacturing processes.
- The minimized need for rework or repair further adds to cost-effectiveness.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with their fluid nature?
Low-viscosity adhesives, renowned for their fluid-like consistency, offer unparalleled advantages in various industries. However, their fluid nature has limitations and challenges, impacting their application and efficiency.
Quick Dispersion, Quick Absorption
- Low-viscosity adhesives disperse rapidly, making them prone to quick absorption by porous materials. This attribute limits their ability to form a strong bond, especially on surfaces with high absorbency.
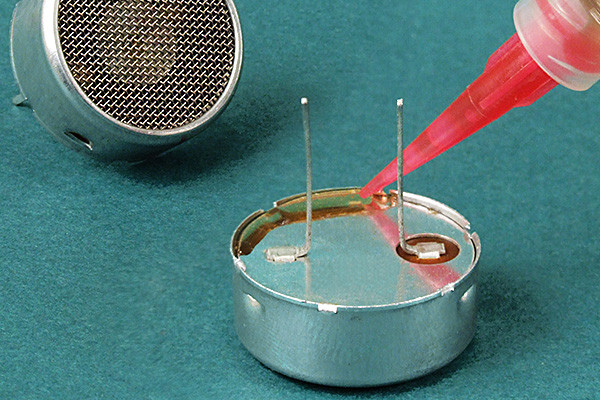
Thinning Under Pressure
- These adhesives might thin out further when subjected to pressure during application, reducing their bonding strength. This thinning effect can compromise their ability to hold components together firmly.
Run-off and Spillage
- Their fluidity increases the risk of run-off and spillage. Containing and applying these adhesives precisely becomes challenging, particularly on vertical surfaces or intricate structures, leading to wastage and inefficiency.
Difficulty in Gap Filling
- While their fluid nature aids in reaching tight spaces, low-viscosity adhesives struggle with gap-filling. Their tendency to flow easily may result in insufficient material buildup, compromising the structural integrity of the bond.
Limited Load-Bearing Capacity
- The fluid consistency of these adhesives often translates to a compromise in load-bearing capacity. They might not withstand heavy loads or stresses, reducing their suitability for robust bonding applications.
Potential Migration
- Due to their fluidity, these adhesives might migrate from the intended application area, affecting adjoining components or surfaces. This migration can lead to unintended bonding and affect the overall performance.
Environmental Sensitivity
- Low-viscosity adhesives can be sensitive to environmental factors like temperature and humidity. Extreme conditions might alter their viscosity, affecting application consistency and bond strength.
Addressing these limitations requires strategic approaches:
Formulation Enhancement
- Researchers continually strive to develop formulations that balance viscosity with bonding strength, aiming to mitigate the challenges associated with fluid adhesives.
Application Techniques
- Innovations in application methods, such as controlled dispensing systems or additives to control flow, help manage the challenges of run-off, absorption, and precise application.
Surface Preparation
- Proper surface preparation can significantly enhance the effectiveness of low-viscosity adhesives. Techniques like priming or surface modification improve bonding on absorbent materials.
While low-viscosity adhesives offer versatility and ease of application, acknowledging and addressing their limitations is crucial for optimizing their performance across diverse industrial and commercial applications. These challenges can be navigated through ongoing advancements and tailored application techniques, unlocking the full potential of fluid adhesives in various sectors.
How do temperature and environmental factors affect their performance?
Low-viscosity adhesives, renowned for their versatile bonding capabilities, are susceptible to external factors that can significantly impact their performance. Temperature and environmental conditions play pivotal roles in determining the efficacy of these adhesives, influencing their adhesive strength, curing time, and overall functionality.
Temperature Sensitivity
- Viscosity Alteration:Low-viscosity adhesives are sensitive to temperature fluctuations. High temperatures tend to decrease viscosity, making the adhesive thinner and potentially altering its bonding properties. Conversely, lower temperatures increase viscosity, potentially slowing the adhesive’s flow and impacting its ability to bond effectively.
- Curing Rate:Temperature directly affects the curing rate of these adhesives. Elevated temperatures often accelerate the curing process, enabling quicker bonding. However, excessively high temperatures may lead to rapid curing, limiting the time available for proper alignment or adjustment of parts.
- Thermal Expansion:Differential thermal expansion between bonded materials and the adhesive can occur at varying temperatures. Such conditions can cause stress at the bond line, compromising the adhesive’s long-term durability.
Environmental Influences
- Humidity Levels:Low-viscosity adhesives can be sensitive to moisture. High-humidity environments affect the adhesive’s properties, potentially leading to decreased bonding strength or prolonged curing times. Conversely, arid conditions might accelerate the curing process, impacting the adhesive’s workability.
- Chemical Exposure:Certain environmental chemicals can interfere with the adhesive’s composition, reducing bonding strength or altering adhesive properties. It’s crucial to consider the exposure of the adhesive to specific chemicals present in the environment where bonding occurs.
- UV Radiation:Exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation can degrade specific adhesive formulations. UV-sensitive adhesives may experience reduced performance or even degradation when exposed to direct sunlight or UV-rich environments, compromising their bonding capabilities.
Optimization Strategies
- Controlled Environments:Creating controlled environments with consistent temperatures and humidity levels can enhance the reliability and predictability of low-viscosity adhesive performance.
- Adhesive Selection:Choosing adhesives to withstand specific environmental conditions or temperature ranges can mitigate performance issues. Some formulations are tailored to resist extreme temperatures or exposure to certain chemicals.
- Application Techniques:Adhering to recommended application guidelines, including surface preparation and curing conditions, ensures optimal adhesive performance despite varying environmental factors.
How does the formulation of these adhesives impact their viscosity?
Low-viscosity adhesives have become a cornerstone in various industries due to their unique formulation and versatile applications. The viscosity of these adhesives plays a pivotal role in their effectiveness and functionality. Understanding how the formulation influences their viscosity is crucial for optimizing their performance. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors impacting the viscosity of low-viscosity adhesives:
Chemical Composition
- The primary constituents of low-viscosity adhesives include polymers, solvents, and additives.
- Polymers like acrylics, epoxies, or cyanoacrylates determine the adhesive’s base structure and viscosity.
- Solvents aid in controlling the adhesive’s flow and viscosity by adjusting the polymer’s molecular weight or concentration.
- Additives, such as thickeners or flow agents, can modify the viscosity by enhancing or reducing the adhesive’s flow properties.
Proportion and Ratios
- The precise ratio of polymers to solvents significantly affects viscosity. Higher polymer concentrations often result in higher viscosity.
- Balancing the ratio between the base polymer and solvents is crucial to achieve the desired viscosity without compromising performance.
Molecular Weight and Chain Length
- Longer polymer chains generally contribute to higher viscosity due to increased entanglement and resistance to flow.
- Molecular weight influences the adhesive’s ability to form strong bonds and impacts its flow behavior.
Temperature and Environmental Factors
- Viscosity can be temperature-dependent; some adhesives exhibit lower viscosity at higher temperatures due to decreased molecular interaction.
- Environmental conditions, such as humidity, can impact solvent evaporation rates, affecting the adhesive’s viscosity.
Curing Mechanism
- Certain low-viscosity adhesives cure upon exposure to specific conditions like UV light, moisture, or heat.
- The curing process can alter the adhesive’s viscosity, transitioning it from a low-viscosity state to a higher viscosity or solid state.
Application Method and Surface Characteristics
- The application method can influence the adhesive’s viscosity requirements, whether by spraying, brushing, or dipping.
- Surface roughness and porosity affect how the adhesive spreads and adheres, impacting its perceived viscosity during application.
What role does temperature control play in maintaining optimal viscosity for application?
Low-viscosity adhesives are indispensable in various industries, offering versatile bonding solutions. However, their effectiveness heavily relies on maintaining optimal viscosity during application. Temperature control is a critical factor influencing the adhesive’s viscosity and, consequently, its performance.
Key Points
- Viscosity and Temperature Relationship:The viscosity of a low-viscosity adhesive is inversely proportional to temperature. As temperature rises, viscosity decreases, making the adhesive more fluid. Conversely, lower temperatures increase viscosity, thickening the adhesive.
- Application Consistency:Controlling temperature ensures consistent viscosity for application. Maintaining the adhesive within the specified temperature range allows for uniform spreading and better penetration into substrates, enhancing bonding strength.
- Precision in Application:Temperature regulation aids in precise application. Optimal viscosity facilitates accurate dispensing and placement of the adhesive, which is crucial in intricate assemblies or automated processes, reducing waste and enhancing productivity.
- Environmental Factors:External temperatures can significantly impact adhesive viscosity. Extremes in climate or storage conditions can alter the adhesive’s viscosity, affecting its usability. Temperature control mitigates these effects, preserving the adhesive’s intended performance.
- Bonding Quality:Temperature-induced viscosity variations directly impact bonding quality. Deviating from the recommended temperature range might compromise adhesion strength and durability, leading to potential product failures or performance issues.
Optimizing Viscosity through Temperature Control
- Precision Heating/Cooling Systems:Industries employ sophisticated equipment to regulate adhesive temperature during storage, transportation, and application. These systems maintain consistency, ensuring the adhesive retains its desired viscosity.
- Thermal Management during Application:Adhesive applicators incorporate temperature control mechanisms to regulate viscosity during dispensing. This control ensures uniform and efficient application across diverse substrates.
- Quality Assurance Protocols:Stringent quality checks and monitoring procedures verify temperature control adherence, guaranteeing that adhesives meet prescribed viscosity standards for optimal performance.
Are there specific application techniques to optimize bonding with low-viscosity adhesives?
In adhesive technology, low-viscosity adhesives have emerged as versatile solutions for various industrial applications. These adhesives, characterized by their fluid consistency, offer unique advantages such as quick penetration and efficient bonding. However, specific application techniques must be employed to unlock their full potential. This article explores the intricacies of using low-viscosity adhesives and unveils essential techniques to optimize the bonding process.
Understanding Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Low-viscosity adhesives have a thin and fluid consistency.
- They exhibit excellent flow properties, allowing them to fill gaps and create strong bonds.
Challenges in Bonding with Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Quick flow can lead to uneven distribution.
- Limited gap-filling capability compared to thicker adhesives.
Optimizing Application Techniques
Surface Preparation
- Ensure surfaces are clean, dry, and free from contaminants.
- Abrade surfaces gently to enhance adhesive bonding.
- Use suitable cleaning agents to remove oils and residues.
Precision Dispensing
- Employ precision dispensing equipment for accurate application.
- Choose dispensing nozzles that control the adhesive flow rate.
- Adjust dispensing pressure to match the viscosity of the adhesive.
Substrate Compatibility
- Consider the substrate material and its compatibility with the adhesive.
- Adjust the application technique based on the nature of the materials being bonded.
Temperature Control
- Low-viscosity adhesives may be sensitive to temperature changes.
- Optimize application conditions by adhering to recommended temperature ranges.
- Use heated dispensing systems for cold environments.
Curing Time Management
- Monitor the curing time of low-viscosity adhesives to prevent premature bonding.
- Employ curing accelerators or UV light for faster curing when necessary.
- Allow sufficient time for the adhesive to achieve maximum strength.
Gap Control
- Manage the gap between substrates carefully.
- Use fixtures, spacers, or jigs to maintain the desired bond line thickness.
- Adjust application techniques for varying gap sizes.
Testing and Quality Assurance
- Conduct adhesive compatibility and bond strength tests.
- Implement quality assurance measures to ensure consistent application results.
- Periodically evaluate and adjust application techniques based on test outcomes.
How does substrate material affect the effectiveness of these adhesives?
When it comes to bonding materials, the choice of adhesive is crucial. Low-viscosity adhesives, characterized by their fluidity and excellent penetration, offer versatility across various materials. However, their effectiveness is significantly influenced by the substrate material they’re applied to.
Factors to Consider
Surface Porosity
- Porous surfaces like wood or paper tend to absorb adhesives, affecting their bonding strength.
- Low-viscosity adhesives might seep into these surfaces, reducing their ability to create a strong bond due to decreased surface contact.

Chemical Composition
- Different materials have distinct chemical properties, affecting how adhesives interact with them.
- For instance, metals might require adhesives with corrosion resistance, while plastics demand adhesives capable of bonding to their specific polymers.
Surface Energy
- Surface energy impacts the wettability of an adhesive on a substrate.
- Low-viscosity adhesives might spread more evenly on high-energy surfaces like metals but struggle to adhere effectively to low-energy surfaces like plastics.
Temperature and Environmental Conditions
- Substrate materials expand or contract with temperature changes, potentially affecting the adhesive’s bond strength.
- Low-viscosity adhesives might perform differently under varying environmental conditions, necessitating specific formulations for optimal performance.
Effects on Adhesive Performance
Bond Strength Variation
- The nature of the substrate material can alter the adhesive’s ability to form a strong, durable bond.
- Low-viscosity adhesives might demonstrate varying bond strengths across different materials, impacting their effectiveness.
Adhesion Duration
- Substrate materials can influence how long the adhesive maintains its bond.
- Low-viscosity adhesives might initially excel on certain materials but degrade faster on others over time.
Adhesive Penetration
- Some materials may resist the penetration of low-viscosity adhesives due to their composition or surface characteristics.
- This limited penetration can hinder the adhesive’s ability to create a robust bond, affecting its effectiveness.
What are the standard methods for testing the strength of low-viscosity adhesives?
Low-viscosity adhesives play a crucial role in various industries, offering versatility and ease of application. However, assessing their strength is paramount to ensure their reliability in different applications. This article delves into the standard methods employed to test the strength of low-viscosity adhesives.
Methods for Testing Low-Viscosity Adhesives
Shear Testing
- Purpose:Measures the adhesive’s resistance to sliding forces.
- Procedure:Applied force perpendicular to the adhesive joint, simulating real-world stresses.
- Results:Reveals the adhesive’s ability to withstand shear forces.
Tensile Testing
- Purpose:Evaluate the adhesive’s resistance to pulling forces.
- Procedure:Applies force to pull the bonded materials apart.
- Results: Measures the tensile strength and elongation of the adhesive.
Peel Testing
- Purpose: Assesses the adhesive’s resistance to peeling or tearing forces.
- Procedure: Separates bonded materials at a 180-degree angle.
- Results:Measures the adhesive’s peel strength.
Cohesion Testing
- Purpose:Determines the internal strength of the adhesive.
- Procedure:Measures the adhesive’s ability to maintain integrity within itself.
- Results:Indicates the cohesive strength of the adhesive.
Impact Testing
- Purpose:Evaluate the adhesive’s ability to withstand sudden forces.
- Procedure: Applies a sudden impact to the bonded materials.
- Results:Measures the adhesive’s impact resistance.
Creep Testing
- Purpose: Examines the adhesive’s ability to withstand prolonged stress.
- Procedure:Applies a constant load over an extended period.
- Results: Reveals the adhesive’s resistance to deformation over time.
Environmental Testing
- Purpose: Assesses the adhesive’s performance under varying conditions.
- Procedure: Exposes the adhesive to different environmental factors (temperature, humidity, etc.).
- Results:Indicates the adhesive’s stability in diverse operating conditions.
How is the reliability and durability of these adhesives evaluated considering their fluid nature?
In adhesive technology, low-viscosity adhesives stand out for their fluidity and versatile bonding capabilities. However, assessing the reliability and durability of these adhesives poses unique challenges due to their fluid nature. Understanding how these qualities are evaluated ensures their effectiveness across various applications.
Characteristics of Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Fluidity:These adhesives possess a low resistance to flow, enabling them to spread quickly across surfaces.
- Penetration:They can infiltrate small gaps and spaces, enhancing contact between bonded surfaces.
- Fast curing:Despite their fluidity, they often exhibit rapid curing times, expediting the bonding process.
Evaluating Reliability
- Bond Strength Testing: Measures the force required to break the adhesive bond, indicating its reliability under stress.
- Shear and Tensile Testing:Assesses how well the adhesive withstands forces perpendicular or parallel to the bond line.
- Peel Testing: Determines the force needed to peel apart bonded materials, reflecting the adhesive’s durability under different loads.
- Environmental Resistance Testing:Evaluates performance under varying conditions like temperature, humidity, and chemicals, ensuring stability in real-world settings.
Addressing Challenges Due to Fluidity
- Viscosity Control:Maintaining consistent viscosity ensures uniformity in application and bond strength.
- Surface Preparation:Proper surface treatment is critical to enhance adhesion, compensating for the fluid’s tendency to flow away from the desired area.
- Curing Optimization:Balancing fast curing times with sufficient bonding strength requires precise control over curing conditions.
Specialized Evaluation Methods
- Rheological Analysis:Studies flow behavior to understand how the adhesive interacts with surfaces and how it fills gaps.
- Accelerated Aging Tests:Simulate long-term exposure to harsh conditions, predicting the adhesive’s durability over time.
- Microscopic Examination:Offers insights into the adhesive’s penetration and bonding at a microscopic level, aiding in understanding its performance.
Industry Applications and Advancements:
- Electronics:Low-viscosity adhesives are pivotal in bonding delicate electronic components due to their ability to reach small spaces.
- Automotive: Used in structural bonding for lightweight materials, ensuring reliable and durable joints.
- Medical Devices:Finding applications in medical devices due to their biocompatibility and ability to bond various materials without causing harm.
Are there specific tests for assessing long-term performance or resistance to environmental stress?
However, ensuring their reliability over the long haul, especially in challenging environmental conditions, necessitates comprehensive testing protocols. Are there specific tests designed to evaluate these adhesives’ enduring performance and resistance to environmental stress? Let’s delve into the crucial examination methods that validate their reliability.
Understanding Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Low-viscosity adhesives boast fluid-like properties, penetrating surfaces for solid bonding.
- They’re extensively utilized in automotive, electronics, and construction industries for their superior bonding strength.
Challenges and Importance of Testing
- Environmental Stress:Adhesives often face harsh ecological conditions, temperature variations, humidity, and UV exposure that can compromise their integrity.
- Long-Term Reliability:Assessing adhesives for extended durability is crucial to ensure their performance over time.
Specific Tests for Long-Term Performance and Environmental Resistance:
Accelerated Aging Test
- They are subjecting adhesives to elevated temperatures and humidity to simulate long-term exposure.
- They are assessing changes in viscosity, bond strength, and chemical composition over time.
Thermal Cycling Test
- Alternating adhesives between extreme temperatures to mimic real-world thermal stresses.
- Evaluating their ability to withstand expansion and contraction without compromising the bond.
UV Exposure Test
- Exposing adhesives to UV radiation to assess their resistance to degradation and yellowing.
- Monitoring changes in color, flexibility, and bond strength after prolonged UV exposure.
Chemical Resistance Test
- Immersing adhesives in various chemicals they might encounter in their application environment.
- Examining for any degradation, property changes, or bond strength loss.
Environmental Simulation Test
- Simulating real-world conditions such as rain, salt spray, or pollutants helps gauge adhesive resilience.
- Assessing any deterioration in bonding properties under these simulated conditions.
Evaluation Criteria
- Bond Strength Retention: Ensuring the adhesive maintains a strong bond even after prolonged exposure to stressors.
- Viscosity Stability:Monitoring viscosity changes to ascertain the adhesive’s fluidity over time.
- Chemical Integrity:Verifying the adhesive’s resistance to chemical exposure without compromising its properties.
What advancements are anticipated in low-viscosity adhesive technology?
These adhesives, characterized by their fluidity and ability to seep into small spaces, have revolutionized various industries. Anticipating the future of low-viscosity adhesives brings advancements poised to redefine their capabilities and applications.
Nanotechnology Integration
- Nano-sized particles:The integration of nanoparticles enhances adhesive properties.
- Improved bonding strength:Incorporating nanotechnology enhances adhesion on various surfaces.
- Precise application:Nanostructures enabling precise adhesive placement in micro-level applications.
Enhanced Durability and Performance
- Resistance to extreme conditions:Advancements to render adhesives resilient in harsh environments (temperature, moisture, chemicals).
- Extended lifespan:Formulations are aimed at increasing adhesive lifespan without compromising efficiency.
- Customizable properties:Tailoring adhesives for specific industries or use cases, ensuring optimal performance.
Eco-Friendly Formulations
- Biodegradable solutions:Environmentally friendly adhesives are being developed to reduce ecological impact.
- Recyclable materials: Utilizing recyclable components without sacrificing adhesive effectiveness.
- Reduced emissions:These formulations are designed to minimize volatile organic compound (VOC) emissions.
Innovative Adhesives with Functional Properties
- Self-healing capabilities: Adhesives capable of repairing themselves upon damage or wear.
- Thermally conductive adhesives: Integration into electronics for efficient heat dissipation.
- Responsive to external stimuli:Adhesives reacting to temperature, light, or other stimuli for specialized applications.
3D Printing Integration
- Printable adhesive materials:Tailored for additive manufacturing processes, allowing intricate designs.
- Support structures:Low-viscosity adhesives are used as temporary supports during 3D printing.
- Material diversity:Compatibility with various substrates in the 3D printing realm.
Application Diversity and Precision
- Medical advancements:Low-viscosity adhesives are used in surgical procedures and assembling medical devices.
- Microelectronics and wearables:Adhesive technology catering to miniaturized electronics and wearable devices.
- Automotive and aerospace:We offer enhanced bonding solutions for lightweight materials that ensure safety and durability.
Industry Standards and Regulations
- Standardization efforts: Collaborative initiatives to set benchmarks for quality and safety.
- Compliance with regulations:Formulations meeting stringent industry regulations and safety standards.
- Certifications and testing:Rigorous testing methodologies to ensure reliability and performance.
How might these innovations impact various industries and revolutionize bonding techniques in the future?
Innovation in adhesive technology has reached new heights with the emergence of low-viscosity adhesives, marking a pivotal moment in how industries approach bonding techniques. These groundbreaking solutions, characterized by their fluidity and remarkable bonding capabilities, are set to revolutionize various sectors, offering unparalleled efficiency, versatility, and performance advantages. Let’s explore how these innovations might impact diverse industries and reshape the future of bonding.
Advantages of Low-Viscosity Adhesives
- Exceptional Bonding Properties:These adhesives possess remarkable bonding strength and are capable of securely joining diverse materials, including metals, plastics, ceramics, and composites. Their ability to create strong, durable bonds surpasses conventional adhesive options.
- Enhanced Efficiency:With their low viscosity, these adhesives facilitate easy application, spreading evenly over surfaces, even in complex or hard-to-reach areas. This characteristic streamlines manufacturing processes, reducing application time and improving overall efficiency.
- Versatility in Applications:Their adaptability across industries is unparalleled. From automotive manufacturing, electronics, and aerospace to healthcare, these adhesives find applications in various sectors due to their ability to meet specific requirements without compromising performance.
Impact Across Industries
- Automotive Sector:Low-viscosity adhesives are poised to transform vehicle manufacturing. Their high bonding strength and ability to withstand varying temperatures make them ideal for joining lightweight materials, enhancing structural integrity while reducing weight. “This helps to enhance fuel efficiency and safety standards.”
- Electronics and Semiconductor Industry:These adhesives offer precision bonding for delicate components in electronics manufacturing. Low curing temperatures prevent damage to sensitive parts, ensuring higher quality and reliability in electronic devices.
- Aerospace and Aviation:The stringent demands for lightweight materials and high-performance bonding make low-viscosity adhesives indispensable in aerospace. Their ability to bond dissimilar materials with precision addresses the industry’s need for durability without adding unnecessary weight to aircraft structures.
- Healthcare and Medical Devices:These adhesives offer biocompatible bonding solutions for surgical instruments and assembly. Their low-impact curing process ensures safety for sensitive materials used in healthcare applications.
Future Implications
- Environmental Impact:Low-viscosity adhesives often boast eco-friendly formulations, reducing harmful emissions and volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Their adoption can contribute to a greener approach in manufacturing processes, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Innovations in Material Science:Continued research and development in adhesive technology will lead to further enhancements, such as self-healing properties, tailored adhesion for specific substrates, and improved resistance to extreme conditions.
- Collaborative Integration:The future may witness collaborative efforts between adhesive manufacturers and industries, tailoring formulations to meet specialized needs and fostering innovations that push the boundaries of traditional bonding techniques.
CONCLUSION
As these innovations continue to unfold, the impact on diverse industries is undeniable. The efficient bonding capabilities of low-viscosity adhesives are not just a technical marvel but a transformative force. They have the potential to revolutionize bonding techniques, offering a glimpse into a future where adaptable, reliable connections are the cornerstone of manufacturing, construction, healthcare, and beyond.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing becomes

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment

Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions
Influence of Viscosity and Thixotropy of Glue on the Quality of Glue Dots in the Dispensing Process and Solutions The dispensing process is an important part of the application of LED UV glue adhesive, and the quality of this process directly affects the final performance of the product. The physical properties of the glue,

Aging Mechanism and Modification Strategies of LED UV Glue under Long-term Ultraviolet Irradiation
Aging Mechanism and Modification Strategies of LED UV Glue under Long-term Ultraviolet Irradiation LED UV glue, with its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness, has been widely used in fields such as optical device packaging, electronic assembly, and medical devices. However, in scenarios where it is exposed to ultraviolet environments