- Home
- >
- UV Cure Adhesive
- >
- UV Cure Acrylic Adhesive
UV Cure Acrylic Adhesive

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on UV-cured acrylic adhesives! These innovative adhesives are famous for their rapid curing and exceptional bonding properties. UV-cure acrylic adhesives utilize ultraviolet light to initiate curing, offering quick and efficient bonding solutions across various applications.
UV cure acrylic adhesives find extensive use in industries such as electronics, automotive, medical devices, and more. Their ability to provide robust and durable bonds without needing heat or solvents makes them a preferred choice for many manufacturing processes.
Table of Contents
ToggleHow does UV-cure acrylic adhesive work?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives cure or harden when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. These adhesives typically consist of acrylic monomers, oligomers, photoinitiators, and other additives. Here’s how the UV-curing process generally works:
- Formulation:UV-cure acrylic adhesives are formulated with various components. The primary components include acrylic monomers and oligomers, which are the building blocks of the adhesive. Photoinitiators are also crucial; they initiate polymerization when exposed to UV light.
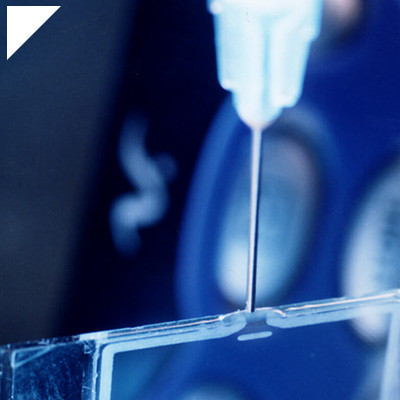
- Application:The adhesive is applied to the surfaces to be bonded. This could be through dispensing, coating, or another application method.
- Exposure to UV Light:The curing process begins when the adhesive is exposed to ultraviolet light. UV light is a form of electromagnetic radiation with shorter wavelengths than visible light. The energy from the UV light activates the photoinitiators in the adhesive.
- Initiation of Polymerization:The photoinitiators absorb the UV light and undergo a chemical reaction, generating free radicals. These free radicals then initiate the adhesive polymerization of the acrylic monomers and oligomers. Polymerization is forming larger molecules (polymers) from smaller ones.
- Crosslinking and Hardening:As the polymerization progresses, the acrylic molecules crosslink. Crosslinking involves the formation of chemical bonds between adjacent polymer chains. This process results in the adhesive’s hardening and forming a durable bond between the bonded surfaces.
- Cured Bond:Once the polymerization is complete, the adhesive is fully healed, and the bonded surfaces are securely joined. The curing time is generally very short, often a matter of seconds or minutes, depending on the adhesive formulation and the intensity of the UV light.
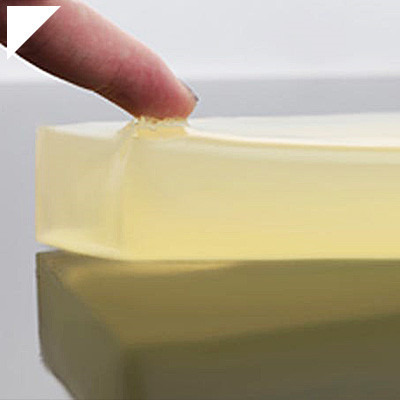
UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer several advantages, including rapid curing, high bond strength, and the ability to bond various substrates. They are commonly used in applications where fast processing times and solid and reliable bonds are essential, such as in electronics, optics, and medical device manufacturing.
What are the critical features of UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are a type of adhesive that cures rapidly when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. These adhesives offer several critical features that make them suitable for various applications. Here are some key characteristics of UV-cure acrylic adhesives:
Rapid Cure Time:
- One of the most significant advantages is the rapid curing capability. UV-cure acrylic adhesives can cure within seconds to minutes when exposed to UV light. This enables fast assembly processes and increased production efficiency.
Versatility:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives are versatile and can bond many substrates, including plastics, glass, metals, and ceramics. This versatility makes them suitable for various industries and applications.
Low Volatility:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives typically have low volatility, producing minimal or no volatile organic compounds (VOCs). This makes them environmentally friendly and suitable for applications with strict regulatory requirements.
High Strength:
- These adhesives often provide high bond strength, creating durable and reliable bonds. The strength of the bond can be tailored based on the specific formulation and application requirements.
Clear and Transparent:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives can be formulated transparently, allowing for optically clear bonds. This is particularly useful in applications where aesthetics or optical clarity is essential, such as electronics or optical industries.
Excellent Chemical Resistance:
- Many UV-cure acrylic adhesives resist chemicals, solvents, and environmental factors. This enhances the durability of bonded components and ensures the adhesive’s performance in challenging conditions.
Temperature Resistance:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives can exhibit good temperature resistance, making them suitable for applications where the bonded materials may be exposed to various temperatures.
Adaptability to Automated Processes:
- Due to their rapid curing time, UV-cure acrylic adhesives are well-suited for automated manufacturing processes. This can lead to increased productivity and cost-effectiveness in large-scale production settings.
Low Shrinkage:
- These adhesives often have low shrinkage during curing, minimizing stress on bonded components. Low shrinkage is crucial in applications with critical alignment and dimensional stability.
UV Cure Monitoring:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives allow for easy monitoring of the curing process. Manufacturers can use UV intensity monitors to ensure the adhesive receives sufficient UV light for complete and uniform curing.
It’s important to note that the specific features of UV-cure acrylic adhesives can vary based on the formulation and intended application, so choosing the suitable adhesive for a particular use case requires consideration of these factors.
Where are UV-cure acrylic adhesives commonly used?
Due to their unique properties and advantages, UV-cure acrylic adhesives are commonly used in various industries and applications. Some of the common uses include:
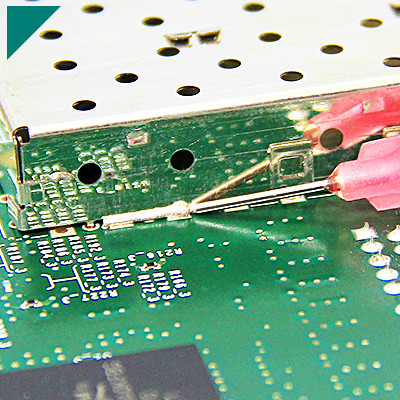
Electronics Assembly:
- Bonding and encapsulating electronic components.
- Attaching connectors and other components onto circuit boards.
Medical Devices:
- Bonding and assembling medical devices, such as catheters and sensors.
- Ensuring secure and biocompatible bonding in medical applications.
Optics and Optoelectronics:
- Bonding lenses and optical components.
- Assembly of optical sensors and devices.
Automotive Industry:
- Bonding components in automotive electronics.
- Use in headlamp assembly and other optical components.
Aerospace Industry:
- Bonding and assembling aerospace components.
- Use in the fabrication of lightweight structures.
Glass Bonding:
- Joining glass components in various applications.
- Bonding glass to metal or other substrates.
Jewelry and Watchmaking:
- Bonding and assembling delicate components in jewelry and watches.
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing:
- Attaching components to PCBs.
- Encapsulating sensitive electronic parts.
Displays and Touchscreens:
- Bonding layers in display and touchscreen manufacturing.
Medical Imaging:
- Bonding components in medical imaging devices.
- Assembly of sensors and detectors.
General Bonding Applications:
- Bonding plastics, metals, and other materials in various industries.
- Use in prototyping and rapid manufacturing processes.
UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer fast curing times, high bond strength, and the ability to bond dissimilar materials. The curing process is initiated by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, making them suitable for applications where precise control over the bonding process is essential.
Are there different formulations available for specific applications?
The term “formulations” can refer to various contexts, and there are different formulations for specific applications in various fields. Here are a few examples:
Chemical Formulations:
- In chemistry and pharmaceuticals, formulations refer to a mixture or solution’s particular composition and preparation. Different formulations may be designed for specific applications, such as drug delivery, industrial processes, or consumer products.
Cosmetic Formulations:
- Other formulations of cosmetics and skincare products are developed in the beauty and skincare industry to address specific skin types, concerns, or desired effects. For instance, moisturizer formulations for dry skin, anti-aging formulations, and sensitive skin.
Agricultural Formulations:
- In agriculture, formulations of pesticides, fertilizers, and herbicides are tailored for specific crops, soil types, and pest management strategies. These formulations aim to optimize efficacy while minimizing environmental impact.
Food Formulations:
- The food industry has formulations for various products to achieve specific taste, texture, and shelf-life characteristics. This includes formulations for baked goods, beverages, and processed foods.
Material Science Formulations:
- Different materials science and engineering formulations of materials are developed for specific applications. For example, in developing polymers, composites, and alloys, formulations are adjusted to meet the mechanical, thermal, or electrical properties required for a particular application.
Software Formulations:
- Different formulations (software configurations and architectures) are created in software development for specific applications or use cases. For instance, a database management system may have different formulations for transactional databases versus analytical databases.
Medical Formulations:
- In medicine, formulations of pharmaceuticals are often tailored for specific medical conditions, patient demographics, or modes of administration. This includes variations in dosage forms like tablets, capsules, and liquid formulations.
Industrial Formulations:
- Various industries develop specific formulations for their processes. For example, formulations for cleaning agents, lubricants, and coatings may be optimized for particular machinery and production requirements in manufacturing.
In each of these cases, the formulation process involves selecting and combining ingredients or components to achieve desired properties or outcomes for a given application.
How fast is the curing process of UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
The curing process of UV-cure acrylic adhesives is generally relatively fast compared to other adhesive curing methods. The exact curing time can vary depending on factors such as the specific formulation of the adhesive, the UV light source’s intensity, the adhesive layer’s thickness, and the substrate materials involved.
In many cases, UV-cure acrylic adhesives can achieve a complete cure in seconds to a few minutes. The curing is initiated when the adhesive is exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. The UV light activates photoinitiators in the adhesive, leading to a rapid polymerization or cross-linking reaction that results in a hardened and bonded adhesive joint.
The advantage of UV-curing adhesives lies in their quick cure time, which allows for faster production processes and reduces the need for lengthy drying or curing times associated with other types of adhesives. However, following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific adhesive product is crucial to ensure optimal curing conditions and performance.
Can UV cure acrylic adhesives bond dissimilar materials?
UV-curable acrylic adhesives are versatile and can bond with various materials, including dissimilar ones. These adhesives are often used in electronics, medical devices, and optics due to their fast curing times, high bond strength, and excellent adhesion properties.
The ability of a UV-curable acrylic adhesive to bond dissimilar materials depends on several factors, including the specific adhesive formulation, surface preparation of the materials, and the nature of the substrates. UV-curable acrylic adhesives can generally bond materials such as plastics, glass, metals, and composites. Some standard applications include bonding metal to plastic, glass to metal, or different types of plastics together.
It’s important to note that proper surface preparation is crucial for achieving solid bonds. Surfaces should be clean, dry, and free from contaminants that might interfere with the adhesive’s bondability. Additionally, the adhesive must be compatible with the specific materials being bonded.
UV curing offers the advantage of rapid curing, allowing for quick processing and high throughput in manufacturing. The exposure to UV light triggers the polymerization process in the adhesive, creating a solid and durable bond.
Before using a UV-curable acrylic adhesive for bonding dissimilar materials in a specific application, it is recommended to consult the adhesive manufacturer’s guidelines and perform testing to ensure compatibility and desired performance. Manufacturers often provide technical data sheets and guidelines for proper usage, including information on substrate compatibility and recommended curing conditions.
What are the advantages of using UV-cure acrylic adhesives over traditional adhesives?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer several advantages over traditional adhesives, making them increasingly popular in various industries. Some key benefits include:
Rapid Cure Time:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives instantly cure when exposed to ultraviolet (UV) light. This rapid curing allows for faster production processes and increased efficiency.
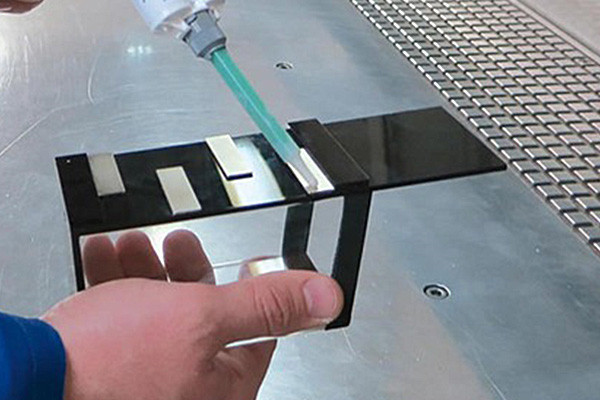
Precision and Control:
- UV curing is a highly controllable process, enabling precise adhesive application. This is particularly beneficial in industries where accuracy and fine details are crucial.
Low Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs):
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives typically have low or no VOCs, making them more environmentally friendly than traditional adhesives that may release harmful substances during curing.
Reduced Heat Generation:
- Conventional adhesives may generate heat during curing, which can be a concern when bonding heat-sensitive materials. UV-cure adhesives produce minimal heat, making them suitable for bonding temperature-sensitive substrates.
No Solvents or Mixing Required:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives are often solvent-free and do not require mixing before application. This simplifies the adhesive process, reduces waste, and eliminates the need for additional handling steps.
Versatility:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives can bond many substrates, including plastics, glass, metal, and composites. Their versatility makes them suitable for diverse applications in electronics, medical devices, and automotive industries.
Improved Strength and Durability:
- UV-cured adhesives can provide strong and durable bonds. The rapid curing process allows for quicker assembly of components, and the resulting bonds often exhibit excellent resistance to environmental factors, such as moisture and temperature fluctuations.
Enhanced Aesthetics:
- UV-cure adhesives are usually transparent and have a clean appearance. This can be advantageous in applications where aesthetics are essential, such as electronics or display assembly.
Reduced Wastage:
- Since UV-cure adhesives cure on demand and do not have a pot life, there is less risk of wastage due to premature curing. This can lead to cost savings in terms of material usage.
Ease of Inspection:
- The rapid curing of UV adhesives allows for quick inspection of bonds. Manufacturers can quickly assess the quality of the adhesive bond shortly after the UV curing process, ensuring product quality and consistency.
While UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer these advantages, it’s essential to consider specific application requirements and material compatibility before choosing an adhesive for a particular task.
Are there any limitations or considerations for using UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
Yes, UV-cure acrylic adhesives, also known as ultraviolet (UV) adhesives, have various advantages but also come with limitations and considerations. Here are some key points to keep in mind:
Substrate Compatibility:
- UV adhesives may not adhere well to specific substrates, especially those that are not transparent or do not transmit UV light effectively. Some materials may block UV light, preventing proper curing.
Thickness of Adhesive Bond:
- UV light may have difficulty penetrating through thick layers of adhesive. For optimal curing, ensuring that the adhesive layer is not too thick is essential. If more comprehensive bonds are required, multiple exposures or a UV adhesive formulated for deeper curing may be necessary.
UV Light Intensity and Exposure Time:
- The curing process depends on the UV light’s intensity and exposure duration. Following the manufacturer’s recommendations for the specific adhesive being used is crucial. Inadequate exposure may result in incomplete curing and reduced bond strength.
Moisture Sensitivity:
- Some UV adhesives are sensitive to moisture, and the presence of moisture can interfere with the curing process. It’s essential to keep the work environment dry and ensure that substrates are moisture-free before applying the adhesive.
UV Light Shielding:
- UV adhesives typically come in opaque containers to prevent premature curing. Exposure to ambient UV light can initiate the curing process before the adhesive is applied to the substrate. Therefore, storing and handling UV adhesives in a controlled environment is crucial.
Temperature Sensitivity:
- The curing rate of UV adhesives can be influenced by temperature. Some formulations may require elevated temperatures for faster curing, while others may be formulated for low-temperature curing. Understanding the temperature requirements is essential for achieving optimal bond strength.
Safety Considerations:
- UV light can be harmful to the eyes and skin. When working with UV adhesives, appropriate personal protective equipment, such as UV-blocking safety glasses and gloves, must be used. Follow safety guidelines provided by the adhesive manufacturer.
Surface Preparation:
- Proper surface preparation is critical for achieving solid bonds. Surfaces should be clean, contaminant-free, and adequately prepared according to the manufacturer’s recommendations.
UV Adhesive Formulations:
- Different UV adhesives are formulated for specific applications and substrates. Choosing the correct formulation for your needs ensures a successful bond.
Post-Cure Considerations:
- In some cases, a post-curing process may be recommended to enhance the performance of the adhesive. This involves additional exposure to UV light or other curing methods.
Always refer to the product datasheet and guidelines provided by the manufacturer for specific information regarding the UV adhesive you are using.
What safety measures should be taken when applying UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are commonly used in various industries for bonding and assembling applications. To ensure safety when working with UV-cure acrylic adhesives, consider the following measures:
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE):
- Wear appropriate PPE, including safety glasses or goggles, to protect your eyes from UV radiation.
- Use gloves to protect your skin from direct contact with the adhesive.
UV Radiation Protection:
- Avoid direct exposure to UV radiation from the curing lamp. Use UV-blocking safety shields or curtains to protect your skin and eyes.
- Use a UV lamp with an enclosure or safety interlocks to prevent accidental exposure.
Ventilation:
- Work in a well-ventilated area to avoid inhaling fumes or vapors emitted during the curing process.
- Use local exhaust ventilation or wear a suitable respirator if necessary.
Temperature and Humidity Control:
- Follow the recommended temperature and humidity conditions specified by the adhesive manufacturer for optimal curing.
- Avoid working in extreme environmental conditions that may affect the performance of the adhesive.
Material Compatibility:
- Ensure that the materials being bonded are compatible with the UV-cure adhesive. Some substrates may be sensitive to UV radiation or may inhibit curing.
Proper Application:
- Apply the adhesive well-controlled to avoid excessive use and minimize waste.
- Follow the recommended application thickness for the adhesive to ensure adequate curing.
Training and Education:
- Provide sufficient training to personnel working with UV-cure acrylic adhesives, including understanding the potential hazards and safety precautions.
Emergency Response:
- Be familiar with emergency procedures in case of accidental exposure or spills. Have appropriate first aid measures in place.
Storage and Handling:
- Store UV-cure adhesives according to the manufacturer’s recommendations, including temperature and light exposure requirements.
- Handle the adhesive with care to prevent spills or leaks.
Regular Maintenance of Equipment:
- Regularly inspect and maintain UV-curing equipment to ensure it functions properly and safely.
Dispose of Waste Properly:
- Dispose of adhesive waste by local regulations. Some UV-cure adhesives may require special handling for disposal.
Always refer to the specific safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer of the UV-cure acrylic adhesive, as different products may have unique considerations. Additionally, consult with safety professionals or industrial hygiene experts to ensure compliance with applicable regulations and standards.
Can UV-cure acrylic adhesives withstand harsh environmental conditions?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are known for their excellent performance in various applications. Still, their ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions can depend on multiple factors, including the adhesive’s specific formulation and the nature of the environmental conditions.
In general, UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer several advantages, such as fast curing times, high bond strength, and resistance to yellowing. However, their performance in harsh environments can be influenced by temperature extremes, exposure to chemicals, moisture, and UV radiation.
Here are some considerations:
Temperature Resistance:
- UV-cure acrylic adhesives can exhibit good temperature resistance, but their performance may vary depending on the formulation. Some formulations may be designed to withstand higher temperatures, while others may have limitations.
Chemical Resistance:
- Acrylic adhesives, in general, can have good chemical resistance. However, the resistance to specific chemicals will depend on the formulation of the adhesive. It’s essential to check the product datasheet or consult with the manufacturer to ensure compatibility with the chemicals present in the environment.
Moisture Resistance:
- Acrylic adhesives are typically resistant to moisture, but prolonged exposure to water or high humidity levels might affect their performance. Some formulations may have better moisture resistance than others.
UV Resistance:
- While UV-cure adhesives cure rapidly when exposed to UV light, the cured adhesive may or may not be highly resistant to prolonged UV exposure. Some formulations may include UV stabilizers to enhance resistance to UV radiation.
Manufacturer Guidelines:
- Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and technical data sheets for your specific UV-cure acrylic adhesive. These documents provide information on the adhesive’s performance characteristics, limitations, and recommended applications.
UV-cure acrylic adhesives can perform well in harsh environmental conditions, but their suitability will depend on the specific formulation and the nature of the ecological challenges. Choosing an adhesive that aligns with your application’s requirements and follows the manufacturer’s guidelines for proper usage and environmental compatibility is crucial. Consultation with the adhesive manufacturer or a materials engineer can provide valuable insights for your application.
Are there variations in viscosity for different application methods?
Yes, the viscosity of a substance can vary depending on the application method. Viscosity is a measure of a fluid’s resistance to flow, and it can be influenced by factors such as temperature, pressure, and shear rate. Different application methods may subject the substance to varying conditions, leading to changes in viscosity. Here are a few examples:

Spraying or Atomization:
- When a substance is sprayed or atomized, it is typically subjected to high shear rates and changes in pressure. This can result in a temporary reduction in viscosity as the substance is broken down into smaller droplets.
Pouring or Pumping:
- The viscosity of a substance can change when it is poured or pumped. For example, some fluids may exhibit a higher viscosity under static conditions but become less dense when subjected to shear forces during pumping.
Brushing or Rolling:
- Application methods like brushing or rolling may not induce high shear rates compared to spraying. The substance may maintain a relatively consistent viscosity in these cases, especially if the shear rate is low.
Temperature Changes:
- Viscosity is often sensitive to temperature. Some substances become less dense as temperature increases, while others become more viscous. The application method might involve temperature changes, affecting the overall viscosity of the substance during application.
Curing or Drying:
- In applications where a substance undergoes curing or drying, the viscosity may change as the material solidifies or evaporates. The viscosity during application might be different from the final cured or dried state.
Considering these factors is essential when choosing and applying substances in various processes. Manufacturers and users often test and optimize the viscosity of materials for specific application methods to ensure the desired performance and results.
How does temperature affect the curing of UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
The curing process of UV-cure acrylic adhesives involves using ultraviolet (UV) light to initiate a photochemical reaction that leads to the hardening or curing of the adhesive. Temperature can significantly impact the curing process of UV-cure acrylic adhesives, and the effects can vary based on the specific formulation of the adhesive.
- Reaction Rate:Generally, an increase in temperature accelerates chemical reactions, including the curing reactions in UV-cure adhesives. Higher temperatures can lead to faster curing, while lower temperatures may slow it down. However, there is an optimal temperature range for curing, and excessively high temperatures can sometimes lead to undesirable side effects.
- Viscosity:Temperature can affect the viscosity of the adhesive. As temperature increases, the viscosity of the adhesive typically decreases. Lower viscosity can improve the wetting and spreading of the adhesive on substrates, enhancing bond formation.
- Shelf Life:Elevated temperatures can reduce the shelf life of UV-cure adhesives. It is essential to store these adhesives in a relaxed environment to prevent premature curing before they are applied.
- Depth of Cure:The depth to which the adhesive cures may be influenced by temperature. Higher temperatures can lead to a more complete and deeper cure, while lower temperatures limit the depth of cure.
- Post-Cure Properties:The final properties of the cured adhesive, such as strength, flexibility, and thermal resistance, can be influenced by the curing temperature. The adhesive manufacturer usually specifies optimal curing conditions to achieve the desired performance characteristics.
Following the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines for curing temperature and exposure time is crucial to ensure the adhesive cures properly and attains the desired mechanical and chemical properties. Deviating from the recommended temperature range can result in incomplete curing, reduced bond strength, or other performance issues. Additionally, it’s essential to consider the temperature sensitivity of substrates and materials being bonded, as extreme temperatures may also affect their properties.
Are these adhesives suitable for automated manufacturing processes?
However, it provides general information that may help determine whether an adhesive suits automated manufacturing processes.
When selecting adhesives for automated manufacturing, consider the following factors:
- Curing Time:Adhesives with fast curing times are often preferred for automatic processes to ensure efficient production cycles.
- Consistency and Viscosity:The adhesive should have a consistent viscosity to provide accurate and repeatable dispensing. This is crucial for automated dispensing systems.
- Dispensing Method:Some adhesives are designed for specific dispensing methods, such as robotic or computerized applicators. Ensure the adhesive is compatible with the dispensing equipment used in manufacturing.
- Bond Strength:Assess whether the adhesive provides the required bond strength for your specific application. This is particularly important in industries where the strength and durability of bonds are critical.
- Temperature Resistance:Consider the operating temperatures in your manufacturing process. Ensure that the adhesive can withstand these temperatures without compromising its performance.
- Compatibility with Substrates:Verify that the adhesive is compatible with the materials you are bonding. Different adhesives work better with certain types of substrates.
- Environmental Considerations:Some manufacturing processes may involve exposure to harsh chemicals or other environmental factors. Ensure that the adhesive can withstand such conditions.
- Regulatory Compliance:Ensure that the adhesive meets any relevant industry standards or regulatory requirements for your application.
- Ease of Integration:The adhesive should be easily integrated into your automated manufacturing system without causing disruptions.
Before making a decision, it’s advisable to consult with the adhesive manufacturer or supplier for specific product recommendations based on your application and automation requirements. Testing the adhesive in a controlled setting that simulates your manufacturing conditions can also help verify its suitability for automated processes.
What is the shelf life of UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
The shelf life of UV-cure acrylic adhesives can vary depending on the specific formulation and brand of the adhesive. Generally, UV-cure acrylic adhesives have a relatively long shelf life when stored properly. Proper storage typically involves keeping the adhesive in its original container, tightly sealed, and away from direct sunlight, heat, and moisture.
As a general guideline, many UV-cure acrylic adhesives have a shelf life of around six months to 1 year. However, some formulations may have a longer or shorter shelf life. It’s essential to check the manufacturer’s guidelines and recommendations for the specific adhesive you use, as they will provide accurate information about the shelf life and storage conditions.
An adhesive beyond its recommended shelf life can reduce performance and may not achieve the desired bond strength. If you have a specific UV-cure acrylic adhesive in mind, refer to the manufacturer’s technical data sheet or contact the manufacturer directly for precise information on shelf life and storage recommendations.
Can UV-cure acrylic adhesives be used in medical applications?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are commonly used in various industrial applications due to their fast curing time, strong bonding capabilities, and versatility. However, when considering their use in medical applications, several factors must be considered, and the specific requirements of the medical field should be carefully considered.
In medical applications, adhesives are often used for bonding medical devices, assembling components, or adhering materials. The suitability of UV-cure acrylic adhesives for medical use depends on factors such as biocompatibility, cytotoxicity, sterilization compatibility, and the application’s specific requirements.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Biocompatibility:The adhesive should be tested for biocompatibility to ensure it does not cause adverse reactions when in contact with living tissues.
- Cytotoxicity:Cytotoxicity testing is essential to determine whether the adhesive releases harmful substances that could affect cell viability.
- Sterilization Compatibility:Medical devices often need to undergo sterilization processes. Ensure that the adhesive can withstand standard sterilization methods without compromising its performance.
- Chemical Resistance:Consider the resistance of the adhesive to body fluids and chemicals it may come into contact with during medical use.
- Regulatory Compliance:Adhesives used in medical applications must comply with regulatory standards, such as those set by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) or equivalent regulatory bodies in other countries.
Before using UV-cure acrylic adhesives in medical applications, it’s crucial to consult with adhesive manufacturers and, if necessary, conduct relevant tests to ensure that the chosen adhesive meets the specific requirements and standards for medical devices and applications.
Always follow the guidelines and regulations provided by relevant health authorities and industry standards when using adhesives in medical contexts to ensure the safety and efficacy of the final medical product. Additionally, consult with medical device manufacturing or materials science experts to ensure proper selection and application of adhesives in medical settings.
Are there color options available for UV-cure acrylic adhesives?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are versatile and can be formulated in various ways to meet specific application requirements, including color preferences. Manufacturers often offer a range of color options for UV-cure acrylic adhesives to accommodate different needs in industries such as electronics, optics, and medical devices.
Standard color options for UV-cure acrylic adhesives include:

- Clear/Transparent:Many UV-cure acrylic adhesives are formulated as transparent or clear. This is beneficial when the appearance of the bonded materials is critical and a visible bond line is undesirable.
- Black:Some applications may require UV-cure adhesives with black coloring. This can be useful when UV light exposure needs to be minimized or for aesthetic reasons.
- White:UV-cure acrylic adhesives with a white color may be preferred for bonding applications with a light or bright appearance. This can be important in applications where the color of the adhesive is visible.
- Other Colors:Depending on the manufacturer and application requirements, UV-cure acrylic adhesives may also be available in custom or standard colors. This flexibility allows for customization to match specific product design needs.
It’s important to note that the availability of color options can vary among different manufacturers and product lines. Suppose a specific color is required for your application. In that case, it’s recommended to check with adhesive suppliers or manufacturers to inquire about their color options for their UV-cure acrylic adhesives.
How does UV cure acrylic adhesives cost compared to other adhesive options?
The cost of UV-cure acrylic adhesives compared to other adhesive options can vary based on several factors. Here are some considerations:
Material Costs:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:The raw materials used in UV-cure acrylic adhesives can sometimes be more expensive than traditional adhesives. The photoinitiators and other specialized components needed for curing may contribute to higher material costs.
- Other Adhesive Options:The cost of materials for other adhesives, such as solvent-based or water-based adhesives, can vary depending on the specific formulation and required properties.
Equipment Costs:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:UV curing requires particular equipment such as UV lamps or LEDs. The initial investment in UV curing equipment can be higher, but the process is generally faster.
- Other Adhesive Options:Some adhesives may not require specialized curing equipment, but the process may take longer, leading to potential labor costs.
Energy Consumption:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:UV curing is often quicker than other curing methods, which may result in lower energy consumption during the manufacturing process.
- Other Adhesive Options:Traditional adhesives require longer curing times and higher energy consumption, potentially impacting production costs.
Labor Costs:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:The fast curing time of UV adhesives can contribute to increased efficiency, potentially reducing labor costs associated with longer curing processes.
- Other Adhesive Options:Slower curing adhesives may require more labor hours, impacting overall production costs.
Application Requirements:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:UV adhesives are suitable for applications where rapid curing is essential, and the assembly line can accommodate the necessary UV curing equipment.
- Other Adhesive Options:Depending on the application’s specific requirements, traditional adhesives may still be a cost-effective choice, especially if rapid curing is not a critical factor.
Performance Characteristics:
- UV-Cure Acrylic Adhesives:UV-cured adhesives often provide high bond strength, clarity, and resistance to yellowing. These properties may justify the higher cost in certain applications.
- Other Adhesive Options:Traditional adhesives offer comparable performance at a lower cost, depending on the application.
The cost comparison between UV-cure acrylic adhesives and other adhesive options depends on various factors, including material costs, equipment costs, energy consumption, labor costs, and application requirements. It’s essential to evaluate these factors based on the application’s specific needs to determine the most cost-effective adhesive solution.
Can UV-cure acrylic adhesives be removed or reworked after curing?
UV-cure acrylic adhesives are known for their fast curing process and strong bond formation upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light. Once these adhesives are cured, they become rugged and durable, making them challenging to remove or rework. However, there are some methods you can consider:
Mechanical Removal:
- If the adhesive is in a thick layer, you may be able to remove it by scraping or chiseling mechanically. This method is more feasible for larger areas.
- Be cautious not to damage the underlying surfaces, as excessive force can cause harm.
Chemical Solvents:
- Some chemical solvents might soften or break down UV-cure adhesives. However, it would help if you were careful about the compatibility of the solvent with the materials involved.
- Test the solvent on a small, inconspicuous area first to ensure it doesn’t damage the substrate.
Heat:
- Applying heat to the cured adhesive can soften it in some cases, making it easier to remove. This method is more suitable for heat-resistant substrates.
- Be cautious with this method, as excessive heat can damage your working materials.
UV Light:
- Exposure to intense UV light can sometimes weaken the bond of UV-cure adhesives. This method may not work as effectively as other methods, but it is worth considering.
- It’s important to note that prolonged exposure to UV light may only be suitable for some materials.
Specialized Adhesive Removers:
- Some companies offer specialized adhesive removers designed for specific types of adhesives. These products might be effective, but their success depends on the particular adhesive composition.
Always exercise caution and perform tests in inconspicuous areas before attempting to remove or rework UV-cured acrylic adhesives. The success of these methods can vary depending on factors such as the adhesive formulation, the substrate materials, and the curing conditions. If in doubt, consult the adhesive manufacturer or seek professional advice for the specific situation.
What role does wavelength play in the curing process?
The role of wavelength in the curing process depends on the specific context, as curing processes can vary across different industries and applications. However, I’ll provide a general overview of how wavelength is relevant in particular curing processes, particularly in polymer chemistry and material science.
Ultraviolet (UV) Curing:
- In UV curing processes, the wavelength of the UV light is a critical factor. UV light is commonly used to cure or polymerize certain materials, such as inks, adhesives, and coatings. The UV light activates photoinitiators in the material, initiating a chemical reaction that leads to the curing or hardening of the substance.
- The choice of UV wavelength is important because different materials and photoinitiators have specific absorption spectra. Matching the UV light’s wavelength to the photoinitiator’s absorption peak ensures efficient curing.
Infrared (IR) Curing:
- Infrared curing is another standard method, especially for curing coatings and paints. In this process, heat is generated using infrared radiation, and the material cures through a combination of elevated temperature and chemical reactions.
- The wavelength of the infrared radiation affects the depth of penetration into the material. Different wavelengths may penetrate the material to varying depths, influencing the curing process and the properties of the cured material.
Microwave Curing:
- In specific applications, microwaves are used for curing processes. The wavelength of microwaves is in the range of centimeters, and they can penetrate materials to some extent, causing the molecules to generate heat due to molecular friction.
- The choice of microwave wavelength and frequency can influence the uniformity and efficiency of the curing process.
Visible Light Curing:
- In some cases, visible light is used for curing processes. This is particularly relevant in dental applications with light-curable materials for bonding and filling. The wavelength of visible light affects the curing time and depth of penetration into the dental material.
The role of wavelength in the curing process is often tied to the type of energy used (e.g., UV, IR, microwaves) and the specific requirements of the cured material. Matching the wavelength to the material’s characteristics ensures optimal energy absorption and efficient and controlled curing.
Are there any emerging trends or advancements in UV cure acrylic adhesive technology?
There were several trends and advancements in UV cure acrylic adhesive technology, and new developments have likely occurred since then. Here are some trends that were notable at that time:
- Improved Cure Speed and Efficiency:Advances were being made to enhance the cure speed of UV-cure acrylic adhesives. Manufacturers worked on formulations that cured more quickly without compromising the adhesive’s performance.
- Low-VOC Formulations:There was a growing emphasis on developing UV-cure acrylic adhesives with lower levels of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) to meet environmental and regulatory standards.
- Customization and Tailored Solutions:Companies increasingly focus on providing customized solutions to meet specific industry needs. This involved tailoring formulations to address challenges in various applications, such as electronics, medical devices, and automotive.
- Improved Bond Strength and Durability:Research and development efforts were directed towards enhancing UV cure acrylic adhesives’ bond strength and overall durability. This was particularly important in industries where adhesives are subjected to challenging environmental conditions.
- Adoption in New Applications:UV cure acrylic adhesives were finding applications in new areas, expanding beyond traditional uses. For example, they were being explored in assembling medical devices, automotive components, and electronics.
- Innovative Adhesives:Some advancements involved incorporating intelligent features into UV cure acrylic adhesives. This could include properties such as self-healing capabilities or responsiveness to external stimuli.
- Biocompatible Formulations:In the medical field, there was an increasing focus on developing UV-cure biocompatible UV-cure acrylic adhesives, making them suitable for medical devices and applications within the human body.
- UV LED Technology:UV LED technology for curing was becoming more prevalent. UV LED systems offer benefits such as energy efficiency, longer life, and more precise control of the curing process.
It’s advisable to check more recent sources or directly consult with experts in the field to get the latest information on emerging trends and advancements in UV cure acrylic adhesive technology.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, UV-cure acrylic adhesives offer a versatile and efficient solution for bonding applications. With their rapid curing time, strong bonding capabilities, and suitability for various industries, these adhesives play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing processes. Stay informed with our guide to make informed decisions regarding using UV-cure acrylic adhesives in your specific applications.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

In – depth Analysis of the Main Characteristics of UV Adhesives for Touch Screens
In – depth Analysis of the Main Characteristics of UV Adhesives for Touch Screens In the manufacturing of modern electronic devices, the touch screen serves as a crucial component for human – machine interaction, and its performance and quality are of utmost importance. As a key material for effectively bonding various components of the touch

The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy
The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy This article systematically expounds the quantitative relationship between the crosslinking density and the flexibility and hardness of adhesives. Combining the theories of polymer physics with experimental analysis methods, it reveals the mechanism of the action of the

Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives
Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives UV adhesives have been widely used in many fields such as electronics, optics, and medicine due to their advantages of rapid curing, high bonding strength, and environmental protection. However, their rapid curing property also brings challenges in some application scenarios.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment