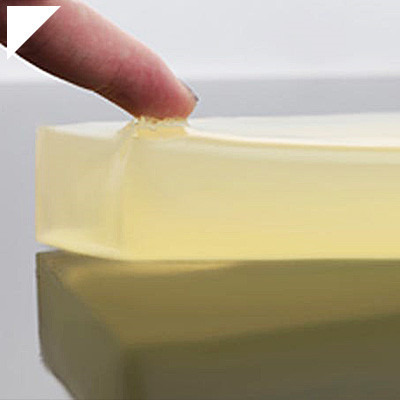
Time stands as a defining factor in adhesive bonding, and at its core lies the marvel of fast curing adhesives. These remarkable solutions are the vanguards of efficiency, swiftly forming formidable bonds that save crucial time and elevate productivity to new heights. Fast curing adhesives are the pioneers of rapid bond formation, boasting characteristics that set them apart from traditional adhesives in the speed with which they solidify, creating robust connections in mere moments. Their chemical compositions are a careful blend, often leveraging cutting-edge components that expedite the curing process without compromising strength.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat defines fast curing adhesives and their primary characteristics?
In today’s industrial landscape, fast curing adhesives are essential solutions, transforming assembly operations with rapid bonding capabilities. These adhesives redefine efficiency and reliability, playing a pivotal role across diverse sectors due to their unique characteristics.
Key points on fast curing adhesives and their primary characteristics:
- Rapid Curing Time:The hallmark feature of fast curing adhesives lies in their ability to set and cure swiftly, significantly reducing assembly time and boosting productivity.
- Chemical Composition:These adhesives, which comprise reactive compounds such as cyanoacrylates, acrylics, or UV-curable materials, exhibit strong bonding properties.
- Versatility Across Substrates:Their adaptability extends to bonding various substrates, including plastics, metals, glass, and composites, enhancing their utility in different applications.
- Strength and Durability:Despite their quick setting, these adhesives offer robust bond strength and durability, ensuring enduring connections that withstand operational stress.
- Temperature and Environmental Resilience:Tailored variants endure extreme temperatures or harsh environments, maintaining stability and integrity under adverse conditions.
- Precision Application and Control:Fast curing adhesives provide precise application, crucial for intricate assemblies or delicate components, allowing for meticulous bonding control.
- Low Emission and Eco-Friendly Solutions:Many variants are solvent-free, reducing environmental impact and health risks and aligning with eco-friendly standards without compromising efficiency.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency:Their rapid curing properties streamline production lines, minimizing downtime and accelerating manufacturing processes, optimizing overall operational efficiency.
Fast curing adhesives have emerged as indispensable elements across industries, integrating speed, reliability, and adaptability to elevate productivity and ensure superior quality in assembly and manufacturing processes.
How do fast curing adhesives differ from traditional adhesives in terms of curing time?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized bonding processes across industries with their rapid setting times and enhanced efficiency. Their distinctive properties starkly contrast with traditional adhesives, impacting the speed and effectiveness of bonding in numerous applications.
- Curing Time:Fast curing adhesives, as the name suggests, set remarkably quicker than traditional adhesives. While conventional adhesives might take hours or even days to cure fully, fast curing counterparts accomplish the same task in a fraction of that time, often within seconds to minutes.
- Chemical Composition: The formulation of fast curing adhesives incorporates advanced chemical compounds and additives, optimizing the reaction rate for swift bonding. Traditional adhesives, on the other hand, rely on slower-reacting components, necessitating longer curing periods.
- Temperature and Environmental Factors:Fast curing adhesives are more sensitive to temperature variations, as they often require specific temperature conditions for optimal curing. Although also impacted by temperature, traditional adhesives might exhibit less sensitivity and can cure under a broader range of environmental requirements.
- Bond Strength Development:While both types of adhesives eventually achieve bond strength, fast curing adhesives tend to reach initial bond strength rapidly, allowing for quicker handling and further processing of the bonded materials. However, traditional adhesives offer superior long-term strength after a curing period.
- Application Flexibility:Fast curing adhesives are preferred when the rapid assembly or immediate functionality is critical, such as in production lines or emergency repairs. Traditional adhesives are more suitable for applications where a slower, more gradual bonding process is acceptable, allowing for adjustments or repositioning of materials before curing.
- Specific Use Cases:Each type finds its niche in various industries and applications. Fast curing adhesives excel in scenarios where time is of the essence, like in the automotive, electronics, and medical device manufacturing sectors. Meanwhile, traditional adhesives find extensive use in woodworking, construction, and other applications where longer curing times are acceptable.
What are the key components or chemical compositions of these adhesives?
The composition of fast curing adhesives is pivotal in their effectiveness and rapid bonding capabilities. Understanding the key components and chemical compositions offers insight into their unique properties and applications in various industries.
- Resin Systems:Fast curing adhesives comprise resin systems forming the primary binding agent. Epoxy, cyanoacrylate, polyurethane, and acrylic resins offer distinct properties such as flexibility, strength, or temperature resistance.
- Initiators and Catalysts:These components kickstart the curing process by triggering the chemical reactions that lead to bonding. Initiators activate the reaction, while catalysts accelerate it, allowing for rapid setting times. For instance, peroxides and amines are often used as initiators in various fast curing adhesive formulations.
- Accelerators and Modifiers:Accelerators, also known as promoters, expedite curing by enhancing the effectiveness of initiators and catalysts. Conversely, modifiers adjust the adhesive’s properties, such as viscosity or flexibility, to suit specific application requirements.
- Fillers and Additives:These substances are incorporated to modify specific adhesive characteristics, such as improving strength, heat resistance, or viscosity. Fillers like silica, glass beads, or carbon nanotubes may be added to enhance mechanical properties or alter the adhesive’s texture.
- Solvents or Solvent Carriers:In certain formulations, solvents control viscosity and aid in application by temporarily reducing the adhesive’s thickness. However, with technological advancements, solvent-free formulations are increasingly preferred due to environmental and health considerations.
- Crosslinking Agents:These agents facilitate the formation of crosslinks between polymer chains, contributing to the adhesive’s overall strength and durability. Isocyanates, for instance, are commonly used as crosslinking agents in some fast curing adhesive types.
The composition of fast curing adhesives is a complex interplay of these key components and chemical compositions. Variations in the proportions and types of these constituents allow for a wide range of adhesive formulations, catering to diverse bonding needs across industries. Understanding these components enables tailoring adhesives for specific applications, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency in various bonding processes.
How does the rapid curing process work?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized various industries by offering swift bonding solutions. Their accelerated curing process enables quick adhesion, enhancing efficiency and productivity across manufacturing sectors. Understanding the mechanism behind this rapid curing unveils the intricate chemistry powering these adhesives.
Chemical Reaction Dynamics:
fast curing adhesives predominantly rely on reactive chemistry for their rapid bonding. Typically, these adhesives contain components that initiate a chemical reaction upon exposure to specific conditions, such as light, heat, or moisture. This initiation triggers polymerization, where monomers or oligomers combine to form long-chain polymers, transforming the adhesive into a solid state.
Initiators and Catalysts:
The curing process often involves initiators or catalysts that expedite the chemical reaction. These agents kickstart or accelerate the bonding process by reacting with the adhesive components. For instance, photoinitiators absorb light energy in light-cured adhesives, prompting a chain reaction that leads to rapid curing within seconds.
Controlled Formulation:
Formulating fast curing adhesives plays a pivotal role in their rapid bonding capabilities. Manufacturers carefully design these adhesives, balancing the composition to ensure quick reactivity without compromising strength and durability. Optimizing the formulation involves selecting the right combination of reactive elements and fine-tuning their concentrations to achieve the desired curing speed.
Environmental Factors:
External factors, such as temperature and humidity, can significantly influence the curing process of these adhesives. Some formulations require specific environmental conditions to achieve optimal curing speed and strength. Variations in these conditions can impact the adhesive’s performance, emphasizing the need for controlled environments in particular applications.
Application Versatility:
The rapid curing process of these adhesives facilitates versatile applications across industries. From bonding in electronics manufacturing to automotive assembly lines, their quick adhesion properties enable efficient workflows, reducing production time and costs.
How are fast curing adhesives utilized in the automotive manufacturing sector?
Fast curing adhesives have become indispensable in the automotive manufacturing sector, revolutionizing assembly processes with their swift bonding capabilities. Their application in this industry has streamlined production lines and enhanced vehicle durability while reducing assembly time.
Utilization of Fast Curing Adhesives in Automotive Manufacturing:
Structural Bonding:
fast curing adhesives are structural bonding agents in automotive construction, replacing or supplementing traditional welding methods. They securely join diverse materials like metals, composites, and plastics, contributing to the vehicle’s structural integrity and crash performance.
Sealing and Gasketing:
These adhesives are used for sealing components to prevent water ingress, noise reduction, and vibration damping. They ensure airtight seals around doors, windows, and other critical areas, enhancing the vehicle’s overall quality and weather resistance.
Lightweight and Fuel Efficiency:
fast curing adhesives allow lightweight material usage, promoting fuel efficiency without compromising vehicle strength. Bonding lightweight materials like aluminum or carbon fiber with these adhesives reduces overall vehicle weight while maintaining structural resilience.
Vibration Dampening and Noise Reduction:
These adhesives’ flexible yet robust properties enable them to absorb vibrations and reduce noise within the vehicle. They dampen vibrations from the engine, road, and other sources, improving the driving experience and overall comfort.
Streamlining Assembly Processes:
Their rapid curing nature significantly accelerates assembly line operations, decreasing production time. Unlike traditional methods, these adhesives require minimal curing time, allowing for immediate handling and advancing the pace of manufacturing.
Enhanced Durability and Longevity:
fast curing adhesives contribute to the longevity and durability of vehicles by forming solid bonds resistant to environmental elements, corrosion, and temperature variations. Implementing these measures ensures that the assembled parts have a longer lifespan, resulting in vehicles that last longer for consumers.
The integration of fast curing adhesives in the automotive manufacturing sector exemplifies a paradigm shift in assembly techniques, enabling more robust, lighter, and more efficient vehicles. Their multifaceted applications in structural bonding, sealing, lightweight, and noise reduction have redefined automotive production processes, emphasizing efficiency, durability, and performance.
What role do they play in rapid assembly lines in electronics and technology sectors?
Fast curing adhesives are pivotal components in the seamless functioning of rapid assembly lines within the electronics and technology sectors. These adhesives, renowned for their swift setting times and strong bonding properties, play an indispensable role in expediting production processes, enhancing efficiency, and ensuring the durability and reliability of electronic devices.
- Swift Assembly:Fast curing adhesives facilitate quick bonding, reducing assembly time significantly in electronic component placement and device assembly.
- Increased Throughput:Their rapid curing times enable faster throughput, optimizing production cycles and meeting high-demand requirements.
- Precision in Bonding:These adhesives offer precise application, ensuring accuracy in bonding delicate components without compromising quality.
- Diverse Material Compatibility:They exhibit compatibility with various substrates, including plastics, metals, and ceramics, fostering versatility in electronic device assembly.
- Enhanced Reliability:Despite their rapid curing, these adhesives provide robust and durable bonds, contributing to the long-term reliability of electronic products.
- Cost Efficiency:Their efficiency in reducing assembly time translates to cost savings in manufacturing, enhancing overall operational economics.
- Streamlined Processes:By eliminating the need for extended curing periods, fast adhesives streamline the production line, making it more agile and responsive to market demands.
- Innovation Enabler:They enable the development of compact, sophisticated electronic designs by allowing for intricate and rapid bonding in smaller spaces.
- Environmental Considerations:Advancements in formulations aim for eco-friendly options, aligning with sustainability goals in manufacturing processes.
These adhesives serve as the adhesive backbone in the fast-paced world of electronics and technology, creating innovative, durable, and reliable products while significantly enhancing production efficiency in modern assembly lines.
Are there notable applications in construction and infrastructure?
In the domain of construction and infrastructure, the deployment of fast curing adhesives has emerged as a transformative force, revolutionizing the efficiency and durability of various building processes. Their rapid setting times and exceptional bonding capabilities have become integral to expediting construction timelines while ensuring robust structural integrity across diverse projects.

- Rapid Repairs:Fast curing adhesives facilitate swift repairs for structural components, enabling quick fixes in concrete structures, bridges, and roadways, minimizing disruption and downtime in construction projects.
- Structural Reinforcement:They create resilient bonds between materials like concrete, metal, and composites, reinforcing the strength and stability of structures, from buildings to infrastructure like bridges and tunnels.
- Efficient Installations:These adhesives expedite the installation of components such as tiles, panels, and insulation, accelerating construction schedules and streamlining the building process.
- Resilience to Environmental Factors:Many formulations exhibit increased resistance to moisture, weathering, and temperature fluctuations, ensuring durability against harsh environmental conditions.
- Time and Cost Savings:Their rapid curing properties significantly reduce construction time, leading to cost savings and quicker project completions, especially in large-scale infrastructure developments.
- Versatile Applications:Fast curing adhesives cater to a wide range of construction materials, allowing for their application in various infrastructure projects, from masonry to glass installations.
- Precision in Bonding:They offer precise bonding, aiding in creating seamless joints and enhancing the structural and aesthetic quality of finished buildings and infrastructure.
- Underwater Utilization:Certain specialized formulations are engineered for underwater use, enabling repairs and installations in aquatic environments or areas prone to high moisture.
- Green Building Initiatives:Formulations designed with environmentally friendly components align with sustainability goals in construction, contributing to eco-conscious building practices.
Fast curing adhesives are indispensable assets in the construction and infrastructure landscape, offering expedited processes, heightened durability, and structural reinforcement. Their multifaceted applications have redefined industry standards, paving the way for more efficient, resilient, and sustainable building practices across diverse projects.
How are Fast curing adhesives employed in healthcare and medical device manufacturing?
Within healthcare and medical device manufacturing, fast curing adhesives have become instrumental in revolutionizing the fabrication and assembly of crucial medical equipment and devices. Their rapid bonding properties and biocompatibility play a pivotal role in ensuring medical products’ efficiency, reliability, and safety standards.
- Medical Device Fabrication:Fast curing adhesives are extensively employed in the assembly of medical devices, ensuring swift and secure bonding of components such as sensors, electrodes, and housings, enhancing the overall reliability and functionality of the devices.
- Sterile Bonding:These adhesives are formulated to maintain sterility during bonding, which is crucial for medical devices requiring a sterile environment, preventing contamination and ensuring patient safety.
- Biocompatibility and Safety:The formulations are designed to be biocompatible, posing no harm to patients upon usage, making them suitable for applications such as wound closures, wearable medical devices, and implants.
- Precision in Surgical Applications:In surgical settings, fast curing adhesives aid in precision bonding during procedures like wound closure, eliminating the need for traditional sutures and reducing operation time and patient discomfort.
- Medical Equipment Repairs:These adhesives facilitate rapid repairs for medical equipment, ensuring minimal downtime and swift restoration of functionality in critical medical machinery.
- Compliance with Regulatory Standards:Fast curing adhesive formulations adhere to stringent regulatory requirements, ensuring that medical devices and equipment meet safety and quality standards stipulated by health authorities.
- Innovations in Implant Technology:They contribute to advancements in implant technology by enabling secure bonding in the assembly of various implants, fostering durability and reliability in long-term medical applications.
- Enhanced Research and Development:Their versatility supports R&D efforts in developing innovative medical devices and equipment by providing efficient bonding solutions for prototypes and experimental models.
Fast curing adhesives have become indispensable in healthcare and medical device manufacturing, offering rapid, secure, and biocompatible bonding solutions critical for ensuring the efficacy, safety, and reliability of medical equipment and devices used in patient care and treatment. Their diverse applications span from device assembly to surgical procedures, continually shaping advancements in medical technology and patient care.
What are the distinct advantages of using fast curing adhesives?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized various industries due to their rapid bonding capabilities and efficient curing processes. These adhesives, known for their quick setting times and strong bonding properties, offer distinct advantages across multiple applications, making them indispensable in modern manufacturing and construction.
Quick Bonding and Assembly:
Fast curing adhesives excel in providing swift bonding solutions, significantly reducing assembly times in manufacturing processes. With their ability to bond materials in seconds or minutes, these adhesives expedite production lines, enhancing overall efficiency. Industries such as automotive, electronics, and aerospace benefit immensely from this accelerated bonding, enabling quicker turnaround times and increased productivity.
Enhanced Productivity and Cost Savings:
The rapid curing nature of these adhesives directly contributes to heightened productivity, allowing for faster throughput without compromising bond strength. This efficiency reduces labor costs associated with assembly and optimizes resources by enabling smaller production spaces and requiring fewer clamping fixtures or specialized equipment.
Flexibility and Adaptability:
Fast curing adhesives offer versatility in bonding many substrates, including metals, plastics, composites, and even dissimilar materials. Their adaptability to various surfaces and substrates makes them a preferred choice in applications where flexibility and compatibility are essential. Moreover, these adhesives often resist harsh environmental conditions, contributing to the durability and longevity of bonded assemblies.
Improved Quality and Precision:
The precise application and rapid curing of these adhesives result in uniform bond lines and minimal mess, ensuring higher-quality end products. Manufacturers benefit from the consistency and accuracy provided by fast curing adhesives, leading to better control over the bonding process and, consequently, superior product quality.
Reduced Downtime and Faster Time-to-Market:
Fast curing adhesives minimize downtime in production cycles by drastically reducing curing and setting times. This swift bonding capability accelerates the manufacturing process, enabling companies to bring their products to market faster. The shortened lead times offer a competitive edge by meeting consumer demands promptly and swiftly adapting to market changes.
Are there any limitations or challenges associated with their rapid curing nature?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized various industries with quick bonding properties, offering efficiency and time-saving advantages. However, their rapid curing nature also brings forth certain limitations and challenges that need consideration.
Fast curing adhesives possess remarkable characteristics, including:
- Rapid bonding:These adhesives set and cure much faster than traditional counterparts, reducing production time significantly.
- Increased productivity:Their quick curing time enhances production efficiency, allowing for faster assembly and manufacturing processes.
- Versatile applications:They find extensive use across multiple industries, from electronics to automotive, due to their adaptability and strong bonding capabilities.
Despite these advantages, limitations arise due to their rapid curing nature:
- Pot life constraints:Fast curing adhesives often have a shorter pot life, requiring swift application and precise handling before they harden.
- Bond strength development:While they offer rapid initial bonding, achieving maximum strength may take longer, impacting the assembly process.
- Compatibility issues: Some substrates may need to be compatible with these adhesives, necessitating thorough surface preparation for optimal adhesion.
Challenges associated with the rapid curing nature of these adhesives demand careful consideration and management:
- Process optimization:Manufacturers must fine-tune processes to match the adhesive’s rapid curing rate, ensuring consistent and reliable bonding.
- Storage and handling:Proper and precise storage conditions are crucial to maintain the adhesive’s efficacy and prevent premature curing.
- Compatibility testing:Understanding the compatibility of fast curing adhesives with various substrates is vital to avoid bonding failures and ensure product reliability.
While fast curing adhesives offer unparalleled speed and efficiency in bonding, their rapid curing nature presents challenges that necessitate meticulous handling, process optimization, and substrate compatibility testing to harness their full potential across diverse industries.
How does environmental factors impact the performance of these adhesives during rapid curing?
fast curing adhesives are pivotal in various industries due to their quick setting time and strong bonding capabilities. However, environmental factors can significantly influence their performance, prompting a closer examination of how these elements impact their effectiveness during rapid curing.
Understanding fast curing Adhesives:
fast curing adhesives encompass many bonding agents designed to set and achieve high-strength bonds in minimal time. These adhesives rely on chemical reactions or physical changes to rapidly solidify, making them invaluable in manufacturing processes where speed is crucial.
Environmental Factors at Play:
- Temperature:The ambient temperature directly affects the curing process of fast adhesives. Extreme temperatures, whether excessively high or low, can alter the chemical reactions, either accelerating or slowing down the curing process, potentially compromising bond strength.
- Humidity:Moisture in the environment can influence the curing mechanism of certain adhesives. High humidity levels might interfere with the adhesive’s ability to cure correctly, leading to weaker bonds or longer curing times.
- UV Exposure:Some fast curing adhesives are sensitive to ultraviolet (UV) light. Exposure to UV rays can trigger premature curing or degradation of the adhesive, impacting its bonding strength and durability.
Impact on Performance:
The influence of environmental factors on fast curing adhesives can be profound. Deviations from optimal conditions can result in:
- Reduced Bond Strength: Variations in temperature, humidity, or exposure to UV light may compromise the adhesive’s ability to form strong bonds, affecting the overall performance and reliability of the joint.
- Altered Curing Time: Environmental conditions can lead to inconsistencies in curing times, affecting production schedules and potentially causing delays if the adhesive takes longer than expected to cure or sets too quickly.
- Productivity and Quality Issues:Adverse environmental conditions can lead to inconsistencies in adhesive performance, impacting product quality and increasing the risk of defects or product failures.
Mitigating Environmental Impact:
To optimize the performance of fast curing adhesives, mitigating strategies can be employed:
- Controlled Environments: Creating controlled environments with regulated temperature and humidity levels can help maintain optimal conditions for curing.
- Formulation Adjustments:Adhesive formulations can be modified to be less sensitive to environmental factors, enhancing their resilience and reliability.
- Testing and Validation:Rigorous testing under various environmental conditions identifies vulnerabilities and helps design adhesives resilient to ecological variations.
How does substrate material influence the rapid curing process?
fast curing adhesives have revolutionized numerous industries, offering swift bonding solutions for diverse materials. However, the rapid curing process isn’t solely reliant on the adhesive’s properties; substrate materials play a pivotal role in determining the speed and efficiency of this process.
Factors Influencing Rapid Curing
Surface Porosity and Texture
- Porous surfaces tend to absorb adhesive, potentially prolonging the curing time.
- Smooth surfaces facilitate better contact between the adhesive and substrate, expediting curing.
Chemical Composition
- Compatibility between the adhesive and substrate material is crucial.
- Some materials, like plastics or metals, require specific adhesives tailored to their chemical properties for optimal curing speed.
Thermal Conductivity
- Substrates with high thermal conductivity aid in dissipating heat generated during curing, accelerating the process.
- Conversely, low thermal conductivity substrates might hinder heat dissipation, prolonging the curing time.
Flexibility and Structural Integrity
- Flexible substrates allow better adhesion and conformability, potentially enhancing the curing speed.
- Structural integrity impacts the ability of the adhesive to form a strong bond, influencing the curing time.
Surface Contaminants
- The presence of oils, dirt, or other contaminants can interfere with the adhesive-substrate interaction, slowing down the curing process.
- Preparing the substrate by cleaning or treating it can optimize the adhesive’s effectiveness.
Thickness and Area of Bond
- Thicker adhesive layers or larger bonding areas might require more time to cure uniformly.
- Optimal application techniques considering thickness and area can expedite curing.
Moisture Content
- Substrates with high moisture content can significantly impact the curing of certain adhesives.
- Understanding adhesive and substrate moisture sensitivity is crucial for rapid curing.
Understanding these factors allows for better selection and application of fast curing adhesives based on the substrate material, ensuring efficient and rapid bonding. For instance:
- Wood and Porous Materials:These substrates might absorb adhesive, necessitating formulations with quick penetration and curing properties.
- Metals: Specific adhesive formulations for metals might contain accelerators to speed up curing, considering their thermal conductivity and structural integrity.
- Plastics and Composites:Adhesives tailored to match these substrates’ chemical composition and flexibility promote faster curing and stronger bonds.
What role does the ambient temperature play in achieving optimal curing time?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized various industries by offering swift bonding solutions. However, achieving optimal curing times hinges significantly on the ambient temperature. Let’s delve into the pivotal role temperature plays in maximizing the efficiency of these adhesives.
Ambient Temperature: The Catalyst for Optimal Curing
Acceleration or Deceleration of Cure Time
- The rate of cure in fast curing adhesives is highly contingent on temperature. Higher temperatures generally expedite the curing process, leading to faster bonding.
- Conversely, lower temperatures can impede the curing reaction, prolonging the time required for adhesion.
Impact on Chemical Reaction
- Ambient temperature influences the chemical reactions that facilitate adhesive curing. Ideal temperatures ensure these reactions occur at optimal rates, promoting quicker bonding.
- Deviating from the recommended temperature range might hinder curing agent activation, affecting the adhesive’s performance.
Consistency and Strength
- Temperature directly affects the consistency of fast curing adhesives. Higher temperatures tend to lower viscosity, aiding in easier application.
- Optimal curing temperatures are crucial for achieving the desired strength and durability of the bond. Deviations may compromise the adhesive’s structural integrity.
Factors Governing Temperature’s Influence
Recommended Range
- Manufacturers specify an ideal temperature range for optimal curing. Adhering to these guidelines ensures the adhesive performs as intended.
- Variations from the recommended range could either slow down the curing process or, in extreme cases, cause irreparable damage to the bond.
Climate Variability
- Ambient temperature fluctuations due to seasonal changes or geographic location can pose challenges. Extreme temperatures, either too hot or too cold, can adversely affect curing times.
- Climate-controlled environments are often recommended for consistent curing, especially in industries where precision and reliability are paramount.
Strategies for Temperature Management
Pre-Application Conditions
- Preparing the bonding surfaces to match the recommended temperature range before adhesive application is critical.
- Heat sources or temperature-controlled chambers ensure the substrate and adhesive align in temperature, optimizing bonding conditions.
Adhesive Selection
- Some fast curing adhesives are designed to perform better in a broader temperature range. Choosing adhesives with versatile temperature tolerances can mitigate the impact of temperature fluctuations.
Are there specific techniques to optimize rapid curing in different applications?
In bonding materials, fast curing adhesives have revolutionized industries by offering quick solutions for various applications. The demand for rapid-curing adhesives continues to soar, whether in automotive, electronics, construction, or healthcare. But are there specific techniques to optimize their fast curing in different applications? Let’s delve into the intricacies of these techniques:
Understanding the Chemistry
- Fast curing adhesives encompass chemical compositions, such as cyanoacrylates, epoxies, and UV-curable adhesives.
- Each adhesive type requires a distinct understanding of its chemical properties and curing mechanisms to optimize its rapid application.
Surface Preparation
- Adequate surface preparation is crucial for promoting rapid curing. Cleaning and degreasing surfaces eliminate contaminants that may hinder adhesion.
- Techniques like plasma treatment or using primers enhance surface energy, ensuring better adhesion and faster curing.
Temperature and Humidity Control
- Temperature plays a pivotal role in accelerating or decelerating the curing process. For instance, heat can expedite the curing of certain adhesives, while cold temperatures may slow it down.
- Monitoring and controlling humidity levels prevent moisture interference, which can impede curing.
Proper Application Techniques
- Precise application techniques, such as dispensing and application tools, significantly impact curing time. Automated dispensing systems ensure consistent and efficient adhesive application.
- Employing the right amount of adhesive is crucial. Excessive adhesive can prolong curing, while insufficient amounts may compromise bond strength.
Light Exposure for UV-Curable Adhesives
- UV-curable adhesives rely on ultraviolet light for rapid curing. Optimizing exposure time and intensity is key to achieving quick and robust bonds.
- Implementing proper curing equipment, like UV lamps or LED systems, ensures uniform and efficient curing across various surfaces.
Catalysts and Accelerators
- Some adhesives incorporate catalysts or accelerators to expedite the curing process. These additives enhance reactivity, reducing curing time without compromising bond strength.
- Understanding the compatibility of catalysts and accelerators with specific adhesives is crucial for achieving desired results.
Tailored Formulations for Specific Applications
- Manufacturers often tailor adhesive formulations for specific applications. Customizing formulations based on substrate materials and environmental conditions can optimize curing time and bond strength.
How does proper application technique impact the final bond quality in fast curing?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized industries by offering swift bonding solutions for diverse materials. However, the final bond quality heavily relies on the application technique employed. Understanding the impact of application methods on fast curing adhesives is key to achieving optimal bond strength and durability.
Here’s a breakdown of how proper application techniques significantly influence the final bond quality in fast curing adhesives:
Surface Preparation
- Properly cleaning and preparing the surfaces to be bonded is paramount. Any contaminants or residues can compromise the adhesive’s effectiveness.
- Surface roughening or treatment might be necessary to enhance the adhesive’s grip, ensuring a stronger bond.
Adhesive Dispensing
- Accurate dispensing of the adhesive is crucial. Use precise tools and follow manufacturer guidelines for application.
- The uniform application prevents air entrapment or voids, contributing to a more robust bond.
Substrate Alignment
- Ensuring the correct alignment of substrates before the adhesive sets is essential. Misalignment can lead to stress concentrations and weaken the bond.
- Proper fixturing or clamping helps maintain alignment until the adhesive cures fully, optimizing bond strength.
Curing Conditions
- Monitoring and controlling curing conditions such as temperature, humidity, and curing time.
- Deviations from recommended conditions can affect the curing rate and ultimately impact the bond’s final strength.
Adhesive Compatibility
- Selecting the suitable adhesive for specific materials is vital. Not all fast curing adhesives are ideal for all substrates.
- Ensure compatibility between the adhesive and substrates to maximize adhesion and bond performance.
Post-Curing Inspection
- After the adhesive has cured, conduct thorough inspections to verify the bond quality.
- Look for any defects, inconsistencies, or areas of concern that may have arisen during the application process.
What are the standard methods for testing the strength of fast curing adhesives?
Fast curing adhesives are indispensable in various industries, offering swift bonding solutions. However, ensuring their strength is paramount to guarantee their reliability in diverse applications. Determining their strength involves rigorous testing methodologies that provide insights into their performance under different conditions. Here are the standard methods for assessing the strength of these adhesives:
Lap Shear Test
- Method:This test involves bonding two substrates and subjecting them to a shearing force perpendicular to the bonded surfaces.
- Purpose:It measures the adhesive’s ability to withstand stresses caused by forces applied parallel to the bond line.
- Benefits:Offers a realistic assessment of adhesive performance in applications with predominant shear forces.
Tensile Testing
- Method:Adhered materials are pulled apart to evaluate the adhesive’s resistance to tension.
- Purpose:Assess how well the adhesive maintains integrity when subjected to stretching forces.
- Benefits: Provides insights into the adhesive’s ability to resist external forces without breaking.
Peel Test
- Method:Evaluate the force required to peel apart bonded materials at a specified angle.
- Purpose:Measures the adhesive’s resistance to forces applied in a direction parallel to the bond interface.
- Benefits:This process mimics real-life scenarios in which materials undergo peeling forces, replicating realistic conditions for testing.
Cleavage Test
- Method: Determines the force needed to propagate a crack through the adhesive.
- Purpose:Evaluate the adhesive’s resistance to crack propagation and cohesive strength.
- Benefits: Helps in understanding the adhesive’s durability under stress, indicating its ability to maintain bond integrity.
Impact Testing
- Method:Applies sudden force or impact to the bonded materials to assess the adhesive’s resilience.
- Purpose: Measures the ability of the adhesive to withstand sudden shocks or impacts without bond failure.
- Benefits: Provides insights into the adhesive’s performance in dynamic or high-impact applications.
Environmental Testing
- Method:Subjects bonded samples to varying environmental conditions (e.g., temperature, humidity) to evaluate adhesive performance.
- Purpose:Assesses the adhesive’s stability and durability under different environmental factors.
- Benefits:Offers insights into how the adhesive performs in real-world conditions, ensuring reliability in diverse settings.
How is the reliability and durability of these adhesives evaluated considering their quick curing?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized numerous industries by offering quick bonding solutions. However, assessing their reliability and durability is crucial to ensure their effectiveness and long-term stability. The evaluation process involves key factors determining the adhesive’s performance beyond its rapid curing properties.

Adhesive Composition Analysis
- The chemical composition examination determines the adhesive’s fundamental constituents and reactivity, impacting its bonding strength and resistance to environmental factors.
- Understanding the interaction between different components aids in predicting the adhesive’s behavior under stress and varied conditions.
Curing Time and Adhesion Strength
- Rapid curing is a hallmark of these adhesives, but evaluating the correlation between curing time and adhesion strength is critical. Testing the bond strength post-curing at different intervals helps gauge initial strength and long-term durability.
- Assessments involve peel, shear, and tensile tests to measure the adhesive’s ability to withstand various forces and stresses.
Environmental and Chemical Resistance Testing
- Simulating real-world conditions is essential. Evaluations under different temperatures, humidity levels, and chemical exposures mimic the adhesive’s performance in diverse environments.
- Resistance to corrosion, moisture, UV radiation, and chemicals determines its reliability in specific applications.
Thermal Conductivity and Shock Resistance
- Some applications require adhesives to withstand extreme temperatures or sudden temperature changes without compromising bond integrity. Testing their thermal conductivity and shock resistance ensures reliability in such conditions.
Aging and Longevity Studies
- Long-term assessments involve accelerated aging tests to predict how the adhesive will perform over an extended period. Exposure to extreme conditions for extended durations is conducted to simulate aging in this context.
- Monitoring changes in adhesive properties, such as flexibility, viscosity, and bond strength, provides insights into its durability over time.
Quality Control and Certification
- Adhering to industry standards and certifications ensures the adhesive meets specific reliability benchmarks. Certifications from regulatory bodies validate the adhesive’s quality and performance standards.
Are there specific tests for assessing long-term performance or aging effects post-rapid curing?
fast curing adhesives have revolutionized various industries, providing quick bonding solutions. However, it is crucial to ensure their long-term performance and assess potential aging effects post-rapid curing. Are there specific tests to evaluate these aspects? Let’s delve into this critical inquiry.
Challenges of Rapid-Curing Adhesives
- Rapid curing often raises concerns about long-term durability and stability.
- Exposure to environmental factors can affect the adhesive’s performance over time.
Testing Methods for Long-Term Performance
- Accelerated Aging Tests: Simulating years of environmental exposure in a shorter timeframe to predict aging effects.
- Thermal Cycling Tests:Subjecting the adhesive to rapid temperature changes to mimic real-world conditions and assess its resilience.
- Humidity and Moisture Resistance Tests: Evaluating the adhesive’s endurance against moisture ingress, vital for applications in humid environments or exposure to liquids.
- UV Exposure Tests:Assessing the adhesive’s resistance to UV radiation is crucial for outdoor applications susceptible to sunlight exposure.
Standards and Protocols
- Various industry-specific standards, such as ASTM or ISO, outline specific testing protocols for assessing the long-term performance of adhesives.
- These standards provide guidelines for conducting tests under controlled conditions, ensuring evaluation consistency and reliability.
Considerations for Real-World Applications
- Substrate Compatibility:Assessing how the adhesive interacts with different substrates over an extended period, ensuring compatibility and preventing degradation.
- Service Life Predictions:Utilizing data from accelerated aging tests to predict the adhesive’s service life under real-world conditions.
Benefits of Thorough Testing
- Reliability:Ensures the adhesive meets performance expectations over its intended lifespan.
- Cost-Efficiency:Identifying potential issues early on can prevent costly failures and replacements in the future.
- Quality Assurance: Establishes confidence in the adhesive’s reliability, enhancing product quality and customer satisfaction.
What advancements are anticipated in fast curing adhesive technology?
Fast curing adhesives have revolutionized numerous industries by providing quick and efficient bonding solutions. As technology evolves, the anticipation for advancements in fast curing adhesive technology is at an all-time high. These innovations enhance efficiency, versatility, and environmental sustainability across various applications. Here are the anticipated advancements in fast curing adhesive technology:
Rapid Cure Time Reduction
- Nanotechnology Integration:Anticipate advancements leveraging nanotechnology for even faster curing times, reducing the bonding process to mere seconds.
- Enhanced Chemical Formulas:The development of advanced chemical compositions has accelerated curing, enabling instant bonding in some cases.
Improved Strength and Durability
- Nano-Reinforcements:Integration of nanomaterials to bolster adhesive strength, ensuring superior bonding even in extreme conditions.
- Hybrid Composites: Advancements in combining various materials to create hybrid adhesives with unparalleled durability and resilience.
Eco-Friendly Formulations
- Bio-Based Ingredients:Anticipate formulations integrating renewable and eco-friendly components, reducing environmental impact without compromising performance.
- Biodegradable Adhesives:Development of adhesives that degrade naturally over time, addressing waste and environmental pollution concerns.
Application-Specific Varieties
- Temperature-Sensitive Adhesives:Innovations in adhesives specifically designed for various temperature ranges have expanded their applications, particularly in industries operating under extreme conditions.
- Medical-Grade Adhesives:Advancements have been made to cater to the medical field, ensuring the development of adhesives that meet stringent safety and biocompatibility standards.
Smart Adhesive Technologies
- Self-Healing Adhesives:Expect progress in adhesives capable of self-repair, enhancing longevity and usability in critical applications.
- Responsive Adhesives:Developments have enabled adhesives to adapt to environmental changes or stress conditions, ensuring bonding integrity.
User-Friendly Application Methods
- Improved Dispensing Systems:Anticipate user-friendly dispensing mechanisms for precise application, reducing wastage and enhancing convenience.
- Enhanced Compatibility:Innovations have ensured compatibility with various materials, simplifying the bonding process across diverse substrates.
Real-Time Monitoring and Control
- Sensor-Embedded Adhesives: Integration of sensors within adhesives for real-time bonding integrity and strength monitoring.
- Automated Application Control: Advancements in mechanical systems have improved control over adhesive application parameters, ensuring optimal bonding in various applications.
How might these innovations impact various industries and revolutionize manufacturing processes in the future?
Innovation in fast curing adhesives has sparked a revolution across multiple industries, reshaping manufacturing processes and fostering efficiency like never before. Introducing these adhesives, designed to cure rapidly and securely bond diverse materials, has unveiled many possibilities across sectors.
Here’s a glimpse of how these innovations are poised to revolutionize industries:
Automotive Industry
- Streamlined Production:Fast curing adhesives are poised to replace traditional welding methods, significantly reducing production time and costs.
- Weight Reduction:These adhesives enable the bonding of lightweight materials, enhancing fuel efficiency and vehicle performance.
- Enhanced Safety:Superior bonding strength ensures heightened safety by reinforcing structural integrity.
Electronics and Technology
- Miniaturization and Precision:Fast curing adhesives facilitate the assembly of smaller components with precision, creating sleeker, more advanced devices.
- Heat Dissipation:Improved adhesives aid in better heat dissipation, which is crucial for maintaining optimal performance in electronic devices.
- Increased Durability:Enhanced bonding capabilities result in more durable electronic products, reducing the chances of component detachment or malfunction.
Aerospace and Aviation
- Weight Reduction in Aircraft:By allowing the bonding of lightweight composite materials, these adhesives contribute to the construction of lighter aircraft, leading to fuel savings.
- Maintenance and Repair:Rapid-curing adhesives simplify repair processes, minimizing downtime for aircraft maintenance.
- Enhanced Design Flexibility:The ability to bond dissimilar materials expands design possibilities, fostering innovation in aircraft construction.
Construction and Infrastructure
- Accelerated Construction:Fast curing adhesives expedite construction processes by swiftly bonding building materials, reducing project timelines.
- Improved Sustainability:Enhanced bonding capabilities enable the use of eco-friendly materials, contributing to more sustainable construction practices.
- Strengthened Structures:These adhesives reinforce structural integrity, ensuring resilience against natural calamities and wear over time.
Medical and Healthcare
- Advancements in Medical Devices:Rapid-curing adhesives play a crucial role in assembling intricate medical devices, enhancing precision and reliability throughout manufacturing.
- Faster Production of Equipment:Quick-curing adhesives facilitate the faster production of medical equipment, which is crucial during healthcare crises.
- Enhanced Biocompatibility:These adhesives offer improved compatibility with biological systems, making them suitable for medical applications.
CONCLUSION
Fast curing adhesives are the vanguards of efficiency, heralding a new era in adhesive technology. Their swift bonding capabilities redefine the landscape of time-sensitive bonding needs, offering rapid solidification and elevating productivity across industries. These adhesives promise continual evolution as we envision the future, with anticipated advancements poised to reshape manufacturing processes. In their swift bond formation, we find the key to unlocking new possibilities, not just saving time but revolutionizing assembly lines, enhancing precision in medical devices, and fortifying structures with unmatched reliability.
DeepMaterial
Based on the core technology of adhesives, DeepMaterial has developed adhesives for chip packaging and testing, circuit board level adhesives, and adhesives for electronic products. Based on adhesives, it has developed protective films, semiconductor fillers, and packaging materials for semiconductor wafer processing and chip packaging and testing. More…
UV Curing Adhesives
UV light cure have a number of benefits making them a popular choice among many product assembly and manufacturing applications. Many UV light cure adhesives can provide a nearly instantaneous bond to difficult substrates like glass and plastic. UV cure adhesives often require an accelerator or UV light for a bond to form.
Adhesive Blogs & News
The latest adhesive industry science and technology, Deepmaterial news, and market trends and forecasts.

In – depth Analysis of the Main Characteristics of UV Adhesives for Touch Screens
In – depth Analysis of the Main Characteristics of UV Adhesives for Touch Screens In the manufacturing of modern electronic devices, the touch screen serves as a crucial component for human – machine interaction, and its performance and quality are of utmost importance. As a key material for effectively bonding various components of the touch

The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy
The Quantitative Influence of Crosslinking Density on the Flexibility and Hardness of Adhesives and the Formulation Optimization Strategy This article systematically expounds the quantitative relationship between the crosslinking density and the flexibility and hardness of adhesives. Combining the theories of polymer physics with experimental analysis methods, it reveals the mechanism of the action of the

Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives
Technical Strategies for Balancing the Rapid Curing Property and Long Operating Time of UV Adhesives UV adhesives have been widely used in many fields such as electronics, optics, and medicine due to their advantages of rapid curing, high bonding strength, and environmental protection. However, their rapid curing property also brings challenges in some application scenarios.

Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields
Biocompatibility of LED UV Glue Adhesive and Its Application Potential in Medical and Food Packaging Fields LED UV glue adhesive has been widely applied in numerous fields due to its advantages such as rapid curing and easy operation. However, in fields with stringent safety requirements like medical and food packaging, its biocompatibility after curing

Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content
Exploring the Environmental Performance of UV Glue and Strategies for Optimizing Odor and VOC Content UV glue, as an adhesive that achieves rapid curing through ultraviolet (UV) light irradiation, has been widely applied in numerous fields such as electronics, optics, healthcare, and automobiles, thanks to its advantages of fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and

Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment
Compatibility Analysis and Countermeasures of LED UV Glue with Automated Production Equipment LED UV glue has been widely used in modern manufacturing due to its advantages such as fast curing speed, high bonding strength, and environmental friendliness. However, in the automated production process, if there are problems with the adaptability between the glue and equipment